Hair thinning is a prevalent concern among women as they age, often causing distress and impacting self-esteem. While some degree of hair loss is normal with aging, excessive thinning can signal underlying health issues or genetic predispositions. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the various factors contributing to hair thinning in women as they age, from hormonal changes to lifestyle factors, and explore management and prevention strategies.
Overview of Hair Thinning in Women
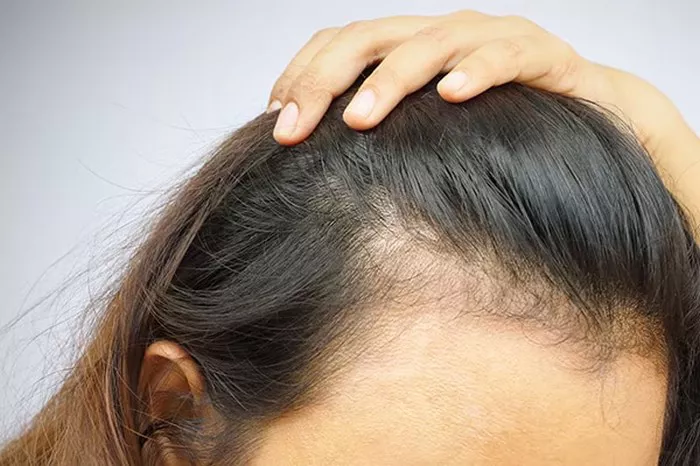
Hair thinning, medically known as alopecia, is a common condition characterized by the gradual loss of hair density and thickness. While it can affect individuals of any gender, women often experience unique patterns and causes of hair thinning compared to men. As women age, the density and diameter of individual hairs tend to decrease, resulting in overall thinning of the hair.
Hair Growth Cycle
To understand hair thinning, it’s essential to grasp the basics of the hair growth cycle. The hair follicle undergoes three main phases: anagen (growth phase), catagen (transitional phase), and telogen (resting phase). In a healthy individual, each hair follicle cycles independently through these phases. However, with age, the duration of the anagen phase may shorten, leading to shorter hair lengths and reduced hair density over time.
Common Causes
Several factors contribute to hair thinning in aging women. Hormonal changes, particularly during menopause, play a significant role. The decline in estrogen levels can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to increased shedding and reduced hair thickness. Additionally, genetic predispositions, such as female-pattern hair loss (androgenetic alopecia), can become more pronounced with age, causing progressive thinning primarily at the crown and temples.
Apart from hormonal and genetic factors, various underlying health conditions can contribute to hair thinning in women. These may include thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata, and nutritional deficiencies such as iron or vitamin D deficiency. Stress, both physical and emotional, can also exacerbate hair loss and thinning.
Impact of Lifestyle and Diet
While genetics and hormonal changes play significant roles, lifestyle factors and diet also influence hair health. Poor nutrition, particularly deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals like biotin, zinc, and iron, can impair hair growth and contribute to thinning. Additionally, excessive styling, heat exposure, and chemical treatments can damage the hair shaft, leading to breakage and thinning over time.
Treatment and Management Options
Fortunately, several treatment options are available to address hair thinning in women. Topical minoxidil, a medication approved by the FDA for female-pattern hair loss, can help stimulate hair growth and improve density. Prescription medications like finasteride may also be prescribed in certain cases, although its use in women is off-label and requires careful consideration of potential side effects.
In cases where hair loss is irreversible, cosmetic approaches such as hair transplantation or scalp micropigmentation can provide lasting solutions. These procedures involve transplanting healthy hair follicles from donor areas to thinning or balding regions, restoring natural-looking hair density.
Preventive Measures
While not all causes of hair thinning can be prevented, adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help maintain optimal hair health and minimize the risk of excessive thinning. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients for hair growth, such as proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Gentle hair care practices, such as avoiding tight hairstyles and minimizing heat and chemical damage, can also promote hair thickness and resilience.
Regular scalp massages can stimulate blood flow to the hair follicles, promoting growth and reducing shedding. Additionally, using products specifically formulated for thinning hair, such as volumizing shampoos and conditioners, can help improve the appearance of fine or thinning hair.
When to See a Doctor
While some degree of hair shedding is normal, certain signs warrant medical attention for further evaluation and management. These include sudden or excessive hair loss, hair thinning accompanied by scalp irritation or inflammation, or noticeable changes in hair texture or appearance. Consulting a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist or trichologist, can help identify underlying causes and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Emotional Support and Coping
Hair thinning can have a profound emotional impact on women, affecting self-confidence and body image. It’s essential to acknowledge and address these emotional aspects while managing the physical symptoms. Seeking support from loved ones or joining support groups for individuals experiencing hair loss can provide valuable emotional support and coping strategies.
Additionally, exploring hairstyles and accessories that enhance volume and conceal thinning areas can boost confidence and improve self-esteem. Remember that hair thinning is a common experience shared by many women, and seeking professional help and support can empower individuals to navigate this challenge with resilience and grace.
In conclusion, hair thinning is a multifaceted issue influenced by various factors, including hormonal changes, genetic predispositions, lifestyle choices, and underlying health conditions. By understanding the causes and adopting proactive measures, women can effectively manage hair thinning and maintain optimal hair health as they age. Remember, seeking professional guidance and emotional support are essential components of addressing hair thinning and embracing self-confidence and well-being.