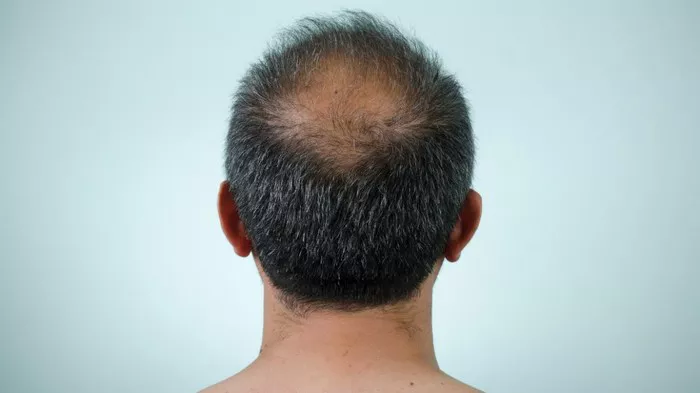
Hair loss is a common concern affecting millions of individuals worldwide, transcending age, gender, and ethnicity. While it’s often associated with aging, various factors can contribute to this condition, including genetics, hormonal changes, and lifestyle habits. While not always indicative of a serious health issue, hair loss can sometimes signal an underlying medical condition that requires attention and treatment. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of hair loss, explore its common causes, and shed light on serious illnesses that can lead to hair loss. Additionally, we will discuss symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, when to seek medical advice, and preventive measures.
Overview of Hair Loss
Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, refers to the gradual or sudden loss of hair from the scalp or other parts of the body where hair grows. It can manifest in various forms, ranging from mild thinning to complete baldness. While it’s natural to shed hair daily (an estimated 50 to 100 strands), excessive hair loss beyond this range may indicate an underlying issue. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, approximately 80 million men and women in the United States experience some degree of hair loss.
Hair plays a significant role in one’s appearance, self-esteem, and cultural identity, making hair loss a distressing experience for many individuals. It’s essential to recognize that hair loss can occur at any age and may affect both men and women differently. While men commonly experience pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia) characterized by a receding hairline and thinning crown, women may notice diffuse thinning across the scalp.
Common Causes
Hair loss can stem from various factors, including:
1. Genetics: Family history plays a crucial role in determining one’s susceptibility to hair loss. Androgenetic alopecia, commonly referred to as male-pattern or female-pattern baldness, is the most prevalent type of hair loss influenced by genetic predisposition.
2. Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or thyroid disorders can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to temporary hair loss.
3. Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions such as autoimmune diseases, thyroid disorders, and scalp infections can contribute to hair loss. Additionally, chronic illnesses like diabetes and lupus may also impact hair health.
4. Medications and Treatments: Some medications used to treat cancer, arthritis, depression, and high blood pressure can cause hair loss as a side effect. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and certain medical procedures such as gastric bypass surgery may also result in temporary or permanent hair loss.
5. Stress and Trauma: Physical or emotional stress, trauma, or significant life events can trigger a type of hair loss called telogen effluvium, where hair follicles prematurely enter the resting phase, leading to increased shedding.
6. Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of essential nutrients such as iron, protein, vitamins (particularly B vitamins), and minerals like zinc and biotin can impair hair growth and lead to hair loss.
While these causes account for a significant portion of hair loss cases, it’s essential to note that not all instances of hair loss are indicative of a serious underlying health issue.
Serious Illnesses Linked to Hair Loss
While many cases of hair loss are benign or temporary, several serious illnesses can lead to persistent or severe hair loss. Understanding these conditions is crucial for prompt diagnosis and management:
1. Autoimmune Diseases: Autoimmune disorders such as alopecia areata, alopecia universalis, and lupus can cause hair loss by prompting the immune system to attack healthy hair follicles.
2. Thyroid Disorders: Imbalances in thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism) can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to thinning or loss of hair.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies: Severe deficiencies in essential nutrients such as iron, protein, vitamin D, and biotin can compromise hair health and contribute to hair loss.
4. Scalp Infections: Fungal infections of the scalp, such as ringworm (tinea capitis), can cause hair loss, scalp itching, and inflammation if left untreated.
5. Cancer: Certain types of cancer, especially those affecting the blood (e.g., leukemia) or lymphatic system (e.g., lymphoma), can lead to hair loss due to the effects of chemotherapy or radiation therapy on rapidly dividing cells, including hair follicles.
6. Chronic Illnesses: Chronic conditions like diabetes, lupus, and sarcoidosis can indirectly affect hair health through systemic inflammation or medication side effects.
Identifying the underlying cause of hair loss often requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and sometimes additional tests such as blood tests, scalp biopsies, or imaging studies.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms accompanying hair loss vary depending on the underlying cause but may include:
- Gradual thinning of hair on the scalp
- Patchy or circular bald spots (alopecia areata)
- Complete loss of scalp hair (alopecia totalis)
- Loss of body hair (alopecia universalis)
- Itching, redness, or scaling of the scalp (indicative of scalp infections)
- Changes in hair texture or quality
- Excessive shedding during washing or brushing
Diagnosing the specific cause of hair loss involves a systematic approach, which may include:
1. Medical History: A thorough discussion of symptoms, family history, medications, and recent life events can provide valuable insights into the potential cause of hair loss.
2. Physical Examination: A dermatologist or healthcare provider will examine the scalp, hair shafts, and overall hair density to assess the pattern and severity of hair loss.
3. Blood Tests: Blood tests may be ordered to evaluate levels of hormones (e.g., thyroid function tests), iron, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients that can impact hair health.
4. Scalp Biopsy: In cases where the cause of hair loss is unclear, a small sample of the scalp tissue may be collected and examined under a microscope to identify any underlying abnormalities.
5. Additional Tests: Depending on the suspected cause, additional tests such as fungal cultures, thyroid ultrasound, or autoimmune antibody tests may be recommended.
Treatment Options
Treatment for hair loss associated with serious illnesses focuses on addressing the underlying condition while managing symptoms and promoting hair regrowth. Treatment options may include:
1. Medications: Depending on the underlying cause, medications such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, thyroid hormones, or antifungal agents may be prescribed to manage the condition and promote hair regrowth.
2. Topical Treatments: Topical medications like minoxidil (Rogaine) may help stimulate hair follicles and promote hair regrowth in certain types of hair loss, including androgenetic alopecia and alopecia areata.
3. Nutritional Supplements: In cases of hair loss due to nutritional deficiencies, supplementation with vitamins, minerals, and protein may be recommended to support healthy hair growth.
4. Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, stress management techniques, regular exercise, and adequate sleep, can promote overall well-being and support hair health.
5. Hair Restoration Procedures: In some cases, hair restoration procedures such as hair transplantation or scalp micropigmentation may be considered to restore hair density and improve cosmetic appearance.
It’s important to note that treatment outcomes may vary depending on the underlying cause, severity of hair loss, and individual response to therapy. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider are essential to track progress and adjust treatment as needed.
When to See a Doctor
While occasional hair shedding is normal, persistent or excessive hair loss warrants evaluation by a healthcare professional, particularly if accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as scalp irritation, hair thinning, or changes in hair texture. It’s advisable to consult a dermatologist or primary care physician if:
- Hair loss is sudden or severe
- Hair loss is accompanied by itching, redness, or scaling of the scalp
- Hair loss occurs in conjunction with other symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, or changes in menstrual cycles
- There is a family history of early-onset baldness or autoimmune diseases
Early diagnosis and intervention can improve treatment outcomes and prevent further hair loss.
Prevention Tips
While some causes of hair loss are beyond one’s control, adopting healthy habits can help promote optimal hair health and reduce the risk of hair loss. Consider the following preventive measures:
1. Maintain a Balanced Diet: Consume a nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients vital for hair growth.
2. Manage Stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies and activities that promote relaxation.
3. Protect Hair: Minimize exposure to heat styling tools, harsh chemicals, and tight hairstyles that can damage hair follicles and contribute to hair breakage or thinning.
4. Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can impair circulation, hinder nutrient absorption, and contribute to hair loss.
5. Follow a Gentle Hair Care Routine: Use mild shampoos and conditioners suited to your hair type, avoid over-washing or vigorous rubbing of the scalp, and use a wide-tooth comb to minimize hair breakage.
6. Stay Hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water daily to maintain hydration and support overall hair and scalp health.
7. Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to promote circulation, reduce stress, and support overall well-being, which can indirectly benefit hair health.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can help safeguard against hair loss and promote optimal hair growth and vitality.
In conclusion, while hair loss can be a distressing experience, it’s essential to approach it with a comprehensive understanding of its potential causes, including serious illnesses. By recognizing the signs and symptoms, seeking timely medical evaluation, and adopting preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps to address hair loss and maintain optimal hair health and quality of life. Remember, hair loss is not just a cosmetic concern; it can also serve as a valuable indicator of underlying health issues that require attention and treatment.