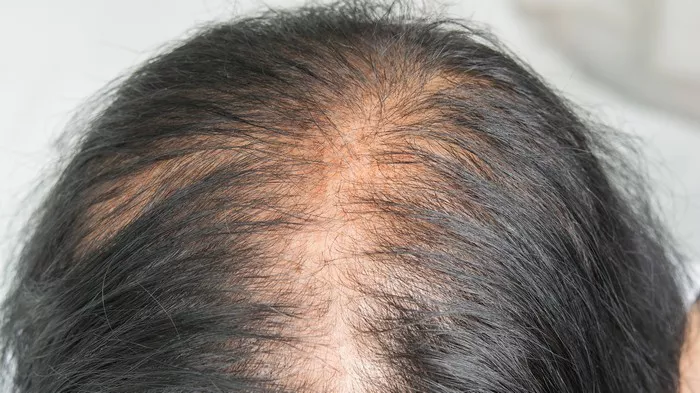
Hair loss, a common concern for many individuals, can be distressing, especially when it occurs suddenly and unexpectedly. Acute telogen effluvium is a temporary form of hair loss characterized by excessive shedding of hair from the scalp. While it can be alarming, understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis can help individuals manage the condition effectively.
Definition of Acute Telogen Effluvium
Acute telogen effluvium is a type of hair loss characterized by a sudden and temporary increase in the shedding of hair from the scalp. Unlike chronic telogen effluvium, which is a long-term condition, acute telogen effluvium typically lasts for a short duration, ranging from a few weeks to several months. It is often triggered by a sudden physiological or psychological stressor, leading to disruption of the hair growth cycle.
Symptoms of Acute Telogen Effluvium
The primary symptom of acute telogen effluvium is increased hair shedding. Individuals may notice more hair falling out than usual during activities such as washing, brushing, or styling their hair. The shedding is typically diffuse, meaning hair loss occurs evenly across the scalp rather than in specific patches. While hair thinning is most noticeable on the top of the head, it can affect the entire scalp.
In addition to increased shedding, individuals with acute telogen effluvium may experience other symptoms such as a decrease in hair density, a noticeable decrease in hair volume, and a change in the texture of the remaining hair.
Causes of Acute Telogen Effluvium
Acute telogen effluvium can be triggered by various factors, including:
1. Severe Stress: Physical or emotional stressors such as surgery, illness, trauma, or major life events can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to acute telogen effluvium.
2. Dietary Changes: Sudden changes in diet, especially those resulting in nutritional deficiencies or rapid weight loss, can contribute to hair loss.
3. Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes associated with pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or thyroid disorders can disrupt the hair growth cycle and trigger hair shedding.
4. Illnesses: Acute illnesses such as febrile illnesses, infections, or chronic diseases can cause temporary hair loss.
5. Medications: Certain medications, including chemotherapy drugs, anticoagulants, retinoids, and beta-blockers, may induce hair shedding as a side effect.
It is important to note that while these factors can trigger acute telogen effluvium, the condition may not develop in every individual exposed to them. Genetic predisposition, underlying health conditions, and individual response to stressors also play significant roles in determining susceptibility to hair loss.
Diagnosis of Acute Telogen Effluvium
Diagnosing acute telogen effluvium typically involves a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and sometimes additional tests to identify potential underlying causes. The healthcare provider may inquire about recent stressors, dietary habits, medication use, and any other relevant factors contributing to hair loss.
During the physical examination, the healthcare provider may assess the pattern and extent of hair loss, examine the scalp for signs of inflammation or infection, and evaluate the overall health of the hair and scalp.
In some cases, additional tests such as blood tests to assess hormone levels, thyroid function, and nutritional status may be recommended to rule out underlying medical conditions contributing to hair loss.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for acute telogen effluvium focuses on addressing the underlying cause and promoting hair regrowth. Depending on the trigger and individual circumstances, treatment and management strategies may include:
1. Stress Management: Implementing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or counseling may help alleviate stress and promote hair regrowth.
2. Dietary Modifications: Ensuring a well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and proteins can support healthy hair growth. Supplements may be recommended if nutritional deficiencies are identified.
3. Medication Adjustment: If medication use is identified as a contributing factor, adjusting the dosage, switching to alternative medications, or discontinuing the medication under medical supervision may be necessary.
4. Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter topical minoxidil (Rogaine) solution or foam may help promote hair regrowth by prolonging the growth phase of the hair cycle and increasing hair follicle size.
5. Scalp Treatments: Certain scalp treatments containing ingredients such as ketoconazole, zinc pyrithione, or salicylic acid may help reduce inflammation, itching, and scaling associated with acute telogen effluvium.
It is important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any treatment regimen to ensure safety and effectiveness, especially if underlying medical conditions are present.
Prognosis
The prognosis for acute telogen effluvium is generally favorable, with most individuals experiencing spontaneous hair regrowth within three to six months after the resolution of the triggering event. However, the timeline for regrowth may vary depending on individual factors such as overall health, genetic predisposition, and the severity of hair loss.
While the condition typically resolves on its own without medical intervention, some individuals may experience recurrent episodes of acute telogen effluvium or progress to chronic telogen effluvium, requiring ongoing management and monitoring.
In conclusion, acute telogen effluvium is a temporary form of hair loss characterized by sudden and excessive shedding of hair from the scalp. Understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis can help individuals effectively manage the condition and promote hair regrowth. Consulting a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance is essential for addressing underlying factors contributing to hair loss and determining the most appropriate treatment approach.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between acute and chronic telogen effluvium?
Acute telogen effluvium refers to a sudden onset of excessive hair shedding, usually triggered by a significant stressor such as surgery, childbirth, or severe illness. This condition typically resolves on its own within a few months once the underlying cause is addressed. In contrast, chronic telogen effluvium involves persistent or recurrent hair shedding over an extended period, often without an identifiable trigger. It can be more challenging to manage and may require ongoing treatment to control.
2. How do you prevent acute telogen effluvium?
Preventing acute telogen effluvium primarily involves minimizing stressors known to trigger the condition. This may include practicing stress-reduction techniques, maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding extreme weight loss or crash diets, and managing underlying medical conditions effectively. Additionally, ensuring adequate rest and seeking prompt medical attention for any significant physical or emotional stressors can help reduce the risk of developing acute telogen effluvium.
3. Will hair grow back after telogen effluvium?
Yes, in most cases, hair will grow back after telogen effluvium. Once the underlying cause is addressed or the body adjusts to the stressors, the hair follicles typically return to their normal growth phase, leading to regrowth of lost hair. However, it may take several months for noticeable regrowth to occur, and in some cases, the regrowth may not fully restore the hair’s original density or texture.
4. What can be mistaken for telogen effluvium?
Several conditions can mimic the symptoms of telogen effluvium, including male and female pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia), alopecia areata (an autoimmune condition causing patchy hair loss), thyroid disorders, nutritional deficiencies, and certain medications. Proper diagnosis by a healthcare professional, often through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and sometimes additional tests such as blood work or scalp biopsy, is crucial for distinguishing telogen effluvium from other causes of hair loss and determining the most appropriate treatment.