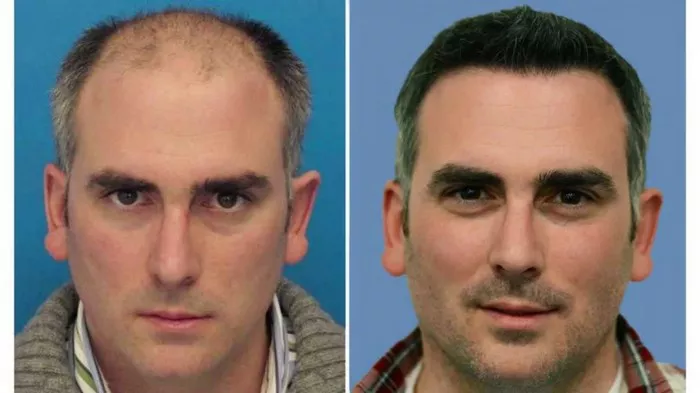
Hair transplantation has become an increasingly popular solution for individuals experiencing hair loss. This surgical procedure involves the removal of hair follicles from one part of the body, known as the donor site, and transplanting them to the balding or thinning area, referred to as the recipient site. The success of a hair transplant largely depends on the quality and suitability of the donor hair. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of what hair is used for hair transplants, covering the criteria for selecting donor hair, the techniques employed in the process, and the factors influencing the outcomes.
The Fundamentals of Hair Transplantation
Before exploring the specifics of donor hair, it is essential to understand the basic principles of hair transplantation. This procedure primarily targets individuals suffering from androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness. It can also address other forms of hair loss, including those resulting from trauma, surgery, or medical treatments.
There are two primary methods of hair transplantation:
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): Also known as strip harvesting, this technique involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, usually the back of the head, and dissecting it into individual follicular units for transplantation.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): This method involves extracting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area using a specialized punch tool. FUE is less invasive than FUT and leaves minimal scarring.
Criteria for Selecting Donor Hair
The success of a hair transplant is significantly influenced by the quality of the donor hair. Several key factors are considered when selecting donor hair:
1. Donor Area Location
The most common donor area for hair transplants is the back and sides of the scalp. These regions are genetically resistant to hair loss, making them ideal for transplantation. The hair in these areas tends to remain robust and healthy, even in individuals experiencing extensive hair loss on the top of the head.
2. Hair Density
A high density of hair follicles in the donor area is crucial for achieving a natural-looking result. Hair density refers to the number of hair follicles per square centimeter of the scalp. Higher density allows for more follicles to be harvested without significantly impacting the appearance of the donor area.
3. Hair Characteristics
The characteristics of the donor hair, including its color, texture, and curliness, play a vital role in the overall aesthetics of the transplant. Matching these characteristics with the recipient area ensures a seamless blend and natural appearance.
4. Scalp Elasticity
The elasticity of the scalp in the donor area is an important consideration, particularly for FUT procedures. Higher scalp elasticity allows for the removal of a larger strip of tissue without causing excessive tension or scarring.
5. Patient’s Age and Health
The patient’s age and overall health can impact the suitability of donor hair. Younger patients with stable hair loss patterns are ideal candidates, as their donor hair is likely to remain healthy and viable for a longer period. Additionally, individuals in good health typically experience better healing and recovery post-transplant.
Donor Hair Harvesting Techniques
The method used to harvest donor hair is a critical factor in the success and outcome of a hair transplant. The two primary techniques, FUT and FUE, have distinct approaches and advantages.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
In FUT, a strip of scalp is removed from the donor area, typically from the back of the head. The strip is then divided into individual follicular units under a microscope. Each unit contains one to four hair follicles. The donor area is sutured, leaving a linear scar that is usually concealed by surrounding hair.
Advantages of FUT:
1. Higher Yield: FUT allows for the harvesting of a larger number of follicles in a single session, making it suitable for patients requiring extensive hair restoration.
2. Better Follicle Protection: The microscopic dissection of follicular units reduces the risk of damage to the follicles, ensuring higher graft survival rates.
3. Cost-Effective: FUT is generally less expensive than FUE, as it requires less time and fewer resources.
Disadvantages of FUT:
1. Linear Scar: The primary drawback of FUT is the linear scar left in the donor area, which may be visible if the patient chooses to wear their hair very short.
2. Longer Recovery: The recovery time for FUT is typically longer compared to FUE, with more postoperative discomfort.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE involves the extraction of individual hair follicles directly from the donor area using a specialized punch tool. The follicles are then transplanted to the recipient area. FUE is a more recent and less invasive technique compared to FUT.
Advantages of FUE:
1. Minimal Scarring: FUE leaves tiny, dot-like scars that are virtually undetectable, even with short hairstyles.
2. Faster Recovery: Patients generally experience quicker recovery times and less postoperative discomfort.
3. Flexibility: FUE allows for the extraction of follicles from various parts of the body, including the beard and chest, providing additional donor hair options.
Disadvantages of FUE:
1. Time-Consuming: FUE is a more time-consuming process than FUT, as each follicle is individually extracted.
2. Higher Cost: The precision and time required for FUE often make it more expensive than FUT.
3. Limited Yield: The number of follicles that can be harvested in a single session is usually lower than with FUT.
Alternative Donor Sites
While the scalp is the most common donor area, alternative donor sites can be considered in certain cases. These include:
1. Beard
The beard area, particularly the underside of the chin, can provide robust and thick hair follicles suitable for transplantation. Beard hair is often used to enhance density in areas where scalp hair is sparse.
2. Chest
Chest hair can serve as an additional donor source, especially for body hair transplants or in cases where scalp donor hair is insufficient. Chest hair is typically coarser and may be used to create a natural appearance in specific areas.
3. Body Hair
Other parts of the body, such as the legs and arms, can also provide donor hair. However, body hair is generally used as a last resort due to differences in texture and growth cycles compared to scalp hair.
Factors Influencing Donor Hair Quality
Several factors influence the quality and suitability of donor hair for transplantation. Understanding these factors helps in planning and executing a successful hair transplant.
1. Genetic Factors
Genetics play a crucial role in determining the quality and longevity of donor hair. Hair follicles in the donor area are typically resistant to the effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the hormone responsible for androgenetic alopecia. This genetic resistance ensures that transplanted hair continues to grow and thrive in the recipient area.
2. Hormonal Balance
Hormonal imbalances can affect hair growth and quality. Conditions such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, as well as hormonal therapies, can influence the health of donor hair. It is important to address any underlying hormonal issues before undergoing a hair transplant.
3. Nutritional Status
Adequate nutrition is essential for healthy hair growth. Deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, such as iron, zinc, and biotin, can compromise the quality of donor hair. Maintaining a balanced diet and addressing nutritional deficiencies can enhance the success of a hair transplant.
4. Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices, including smoking, alcohol consumption, and stress levels, can impact hair health. Smoking reduces blood flow to the scalp, affecting hair follicle viability. Reducing stress through relaxation techniques and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can promote better outcomes.
5. Medical History
A comprehensive medical history is essential to identify any conditions that may affect hair growth or healing. Conditions such as diabetes, autoimmune diseases, and scalp infections need to be managed to ensure optimal results.
Preparing for a Hair Transplant
Preparing for a hair transplant involves several steps to ensure the best possible outcome. These steps include:
1. Consultation and Evaluation
A thorough consultation with a qualified hair transplant surgeon is the first step. The surgeon will evaluate the patient’s hair loss pattern, donor hair availability, and overall health. This evaluation helps in creating a personalized treatment plan.
2. Preoperative Instructions
Patients are provided with specific preoperative instructions to follow in the weeks leading up to the surgery. These may include avoiding certain medications, refraining from smoking, and maintaining a healthy diet.
3. Scalp Conditioning
Conditioning the scalp through regular massages and the use of prescribed topical treatments can improve blood circulation and scalp health, enhancing the success of the transplant.
4. Mental Preparation
Understanding the realistic outcomes and recovery process is crucial for mental preparation. Patients should have realistic expectations and be aware of the time required for the transplanted hair to grow and blend with existing hair.
Post-Transplant Care
Proper post-transplant care is essential for the survival and growth of transplanted hair. Patients are provided with detailed instructions on how to care for their scalp and hair in the days and weeks following the procedure.
1. Scalp Care
Keeping the scalp clean and avoiding harsh chemicals or shampoos is important. Patients are usually advised to use a mild shampoo and avoid direct sunlight or strenuous activities that can cause sweating.
2. Medication
Prescribed medications, including antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, help prevent infection and reduce swelling. Minoxidil or finasteride may be recommended to promote hair growth and prevent further hair loss.
3. Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon allow for monitoring the progress of hair growth and addressing any concerns. The surgeon can evaluate the success of the transplant and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
4. Patience and Realistic Expectations
Hair growth after a transplant occurs in phases. Initially, transplanted hair may shed, which is a normal part of the process. New hair growth typically begins within three to four months, with significant improvement visible after six to nine months. Full results can take up to a year or more.
Conclusion
Understanding the source and selection of donor hair is crucial for the success of a hair transplant. The choice of donor hair, influenced by factors such as location, density, characteristics, and scalp elasticity, plays a significant role in achieving natural and lasting results. Both FUT and FUE techniques offer distinct advantages and considerations, with the selection depending on individual patient needs and preferences.
Alternative donor sites, such as the beard and chest, provide additional options for patients with limited scalp donor hair. The quality of donor hair is influenced by genetic, hormonal, nutritional, lifestyle, and medical factors, all of which need to be carefully considered and managed.
Proper preparation and post-transplant care are essential components of the hair transplant journey. By following preoperative and postoperative instructions, patients can maximize the success and longevity of their transplanted hair.
In conclusion, a well-planned and executed hair transplant can significantly improve the appearance and confidence of individuals experiencing hair loss. By understanding the complexities of donor hair selection and the factors influencing hair transplant outcomes, patients can make informed decisions and achieve the best possible results.
FAQs
How do genetics affect the success of a hair transplant?
Genetics play a crucial role in the quality and longevity of donor hair. Hair in the donor area is typically resistant to the effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the hormone responsible for pattern baldness, ensuring that transplanted hair continues to grow and thrive.
How long does it take to see results from a hair transplant?
Hair growth after a transplant occurs in phases. Initial shedding of transplanted hair is normal, with new growth typically beginning within three to four months. Significant improvement is usually visible after six to nine months, with full results taking up to a year or more.
Are there any risks associated with hair transplants?
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks associated with hair transplants, including infection, scarring, and unnatural-looking results. However, these risks can be minimized by choosing an experienced surgeon and following pre- and postoperative care instructions.
Is a hair transplant suitable for everyone experiencing hair loss?
A hair transplant may not be suitable for everyone. It is most effective for individuals with stable hair loss patterns and sufficient donor hair. A thorough evaluation by a hair transplant surgeon is necessary to determine suitability and the best approach for each individual.