Hair restoration has become a popular solution for individuals dealing with hair loss, thinning hair, and baldness. Whether due to genetic factors, hormonal imbalances, medical conditions, or lifestyle choices, hair loss can significantly impact self-esteem and quality of life. Hair restoration techniques, ranging from surgical procedures to non-invasive treatments, offer hope to many. But do these methods really work? This article will explore the effectiveness of various hair restoration options, the science behind them, and what you can expect from each treatment.
Understanding Hair Loss
Before delving into hair restoration methods, it’s essential to understand the causes of hair loss. Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, can occur due to several factors:
- Genetics: Androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, is the most common form of hair loss. It is hereditary and affects millions of people worldwide.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal imbalances, such as those caused by thyroid disorders or menopause, can lead to hair loss.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like alopecia areata, lupus, and scalp infections can cause hair loss.
- Medications: Certain medications, including those used for cancer, arthritis, and depression, can cause hair loss as a side effect.
- Lifestyle Factors: Stress, poor nutrition, and excessive use of heat styling tools can contribute to hair loss.
- Age: As we age, hair naturally thins and becomes more prone to falling out.
Surgical Hair Restoration Methods
Surgical hair restoration techniques involve transplanting hair follicles from one part of the scalp to another. These procedures are generally more invasive but can provide long-lasting results.
- Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT):
- Process: In FUT, a strip of skin is removed from the back of the scalp, and individual hair follicles are extracted from this strip. These follicles are then transplanted to the balding areas.
- Effectiveness: FUT is highly effective for restoring hair density and natural-looking results. It is suitable for individuals with significant hair loss.
- Recovery: Recovery time is longer compared to other methods, and there may be visible scarring at the donor site.
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE):
- Process: In FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted from the donor area and transplanted to the recipient area. This method does not require a strip of skin to be removed.
- Effectiveness: FUE provides natural-looking results and is less invasive than FUT. It is ideal for individuals with minor to moderate hair loss.
- Recovery: Recovery time is shorter, and there is minimal scarring. However, it can be more time-consuming and expensive.
- Scalp Reduction:
- Process: Scalp reduction involves surgically removing the balding area and pulling the surrounding skin together to cover the area.
- Effectiveness: Scalp reduction can be effective for individuals with localized bald spots. It is often combined with hair transplantation for better results.
- Recovery: Recovery time is longer, and there may be visible scarring and a risk of complications.
- Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP):
- Process: SMP involves tattooing the scalp with pigments that mimic the appearance of hair follicles. This creates the illusion of a full head of hair.
- Effectiveness: SMP is non-invasive and can provide immediate results. It is suitable for individuals with thinning hair or those who want to camouflage scars from previous hair restoration procedures.
- Maintenance: Results are semi-permanent and may require touch-ups over time.
Non-Surgical Hair Restoration Methods
Non-surgical hair restoration methods are less invasive and can be effective for various degrees of hair loss. These treatments can be used alone or in combination with surgical methods.
Topical Treatments:
Minoxidil (Rogaine): Minoxidil is an over-the-counter topical solution that promotes hair growth by increasing blood flow to the hair follicles. It is available in 2% and 5% strengths.
Effectiveness: Minoxidil is effective for mild to moderate hair loss and can help regrow hair and prevent further loss.
Side Effects: Common side effects include scalp irritation and dryness. It must be used consistently to maintain results.
Finasteride (Propecia): Finasteride is a prescription medication that blocks the hormone DHT, which is responsible for hair loss. It is taken orally.
Effectiveness: Finasteride is highly effective for male pattern baldness and can prevent further hair loss and promote regrowth.
Side Effects: Potential side effects include sexual dysfunction and mood changes. It is not recommended for women or children.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT):
Process: LLLT involves using a laser device, such as a helmet or cap, to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. The low-level laser energy increases blood flow and cell metabolism.
Effectiveness: LLLT is effective for mild to moderate hair loss and can be used in conjunction with other treatments. It is generally well-tolerated with minimal side effects.
Maintenance: Regular sessions are required to maintain results, typically several times per week.
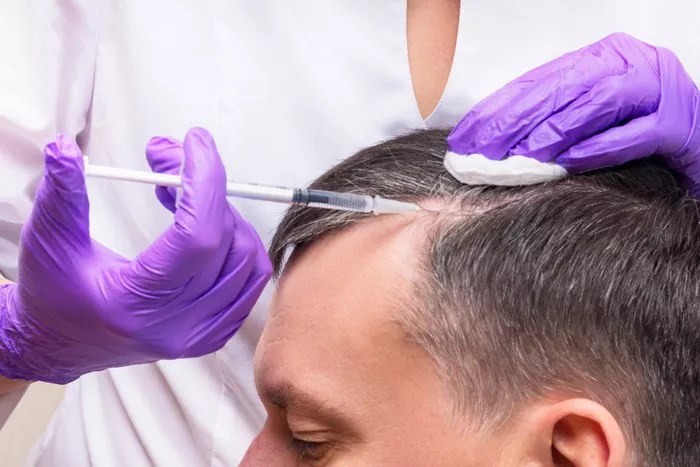
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
Process: PRP therapy involves extracting blood from the patient, processing it to isolate platelet-rich plasma, and injecting it into the scalp. PRP contains growth factors that can stimulate hair growth and improve scalp health.
Effectiveness: PRP therapy is effective for various types of hair loss, including androgenetic alopecia and alopecia areata. It can promote hair regrowth and thicken existing hair.
Maintenance: Multiple sessions are typically required, spaced several weeks apart, to achieve optimal results.
Hair Fibers and Toppings:
Hair Fibers: Hair fibers are small, colored fibers that adhere to the scalp and existing hair, creating the appearance of a fuller head of hair.
Effectiveness: Hair fibers are a quick and easy solution for camouflaging thinning hair. They are available in various colors and can be washed out.
Maintenance: Hair fibers need to be reapplied after washing and can be affected by rain and sweat.
Hair Toppings: Hair toppings are pre-made hair pieces that can be attached to the scalp using clips, adhesives, or tape. They are designed to blend with existing hair.
Effectiveness: Hair toppings provide immediate results and can be customized to match the color and texture of your hair.
Maintenance: Hair toppings require regular maintenance, including cleaning and reapplication.
Herbal and Natural Remedies:
Essential Oils: Essential oils like rosemary, lavender, and peppermint can be applied topically to the scalp to stimulate hair growth and improve scalp health.
Effectiveness: Essential oils can be effective for mild hair loss and can be used in conjunction with other treatments. They are generally safe but should be diluted before use.
Aloe Vera: Aloe vera has natural anti-inflammatory and soothing properties that can help reduce scalp irritation and promote hair growth.
Effectiveness: Aloe vera can be applied topically to the scalp and left on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing off. It is gentle and suitable for daily use.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
In addition to medical and procedural treatments, making lifestyle and dietary changes can support hair restoration efforts and improve overall hair health.
Healthy Diet:
Nutrient-Rich Foods: Consume a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support hair growth, such as protein, iron, zinc, biotin, and omega-3 fatty acids. Foods like lean meats, eggs, nuts, seeds, and leafy greens can provide these essential nutrients.
Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your body and scalp hydrated. Dehydration can exacerbate hair loss and dryness.
Stress Management:
Relaxation Techniques: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, and regular exercise. High stress levels can exacerbate hair loss and other health issues.
Adequate Sleep: Get enough sleep to support overall health and reduce stress levels.
Avoid Harsh Chemicals and Heat:
Hair Care Products: Avoid using hair care products that contain harsh chemicals, such as sulfates, parabens, and artificial fragrances. Opt for gentle, sulfate-free products.
Heat Styling: Minimize the use of heat styling tools, such as blow dryers, straighteners, and curling irons. High heat can damage hair and exacerbate hair loss.
Regular Exercise:
Improved Circulation: Regular exercise can improve blood circulation, which can promote hair growth and overall scalp health.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can help balance hormones and reduce the risk of hair loss.
Expectations and Realistic Outcomes
While hair restoration methods can be effective, it’s important to set realistic expectations and understand the limitations of each treatment.
Results May Vary:
Individual Differences: The effectiveness of hair restoration treatments can vary based on individual factors such as age, genetics, and the severity of hair loss.
Consultation: Consult with a hair restoration specialist to determine the best treatment plan for your specific needs and goals.
Maintenance and Follow-Up:
Consistency: Many hair restoration treatments require consistent use or multiple sessions to achieve and maintain results.
Follow-Up Appointments: Attend regular follow-up appointments with your hair restoration specialist to monitor progress and address any issues.
Combination Therapy:
Complementary Treatments: Combining multiple hair restoration methods can often yield better results. For example, using minoxidil and finasteride together can be more effective than using either alone.
Holistic Approach: Adopting a holistic approach that includes medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and proper hair care can maximize the effectiveness of hair restoration efforts.
Conclusion
Hair restoration methods can be highly effective for individuals dealing with hair loss, but the right approach depends on various factors, including the cause and severity of hair loss, individual preferences, and lifestyle considerations. Surgical methods like FUT and FUE can provide long-lasting, natural-looking results, while non-surgical methods such as topical treatments, LLLT, and PRP therapy offer less invasive alternatives. Lifestyle and dietary changes can also support hair restoration efforts and improve overall hair health.
Related topic:
- How Safe Is a Hair Transplant? The Risks and Benefits
- Understanding Grafts in Hair Transplant: A Complete Guide
- How Effective is Hair Transplant? Success and Longevity