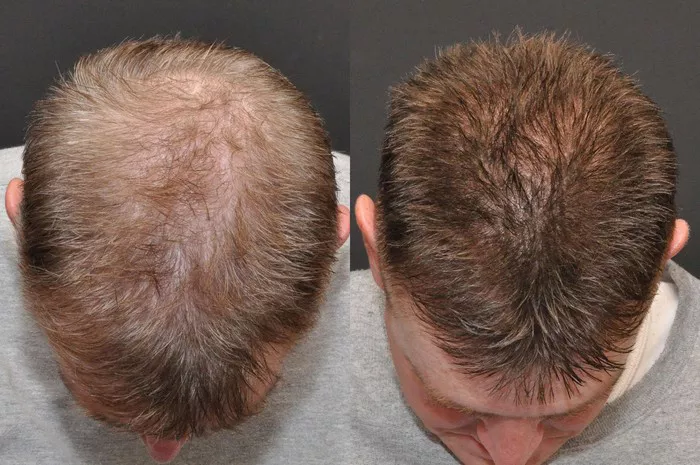
Hair loss can be a challenging experience for many individuals, leading to a growing interest in hair transplant procedures. One of the most frequently asked questions regarding this treatment is, “Where do they get the hair for hair transplants?” Understanding the sources of donor hair, the techniques used in transplantation, and the overall process is crucial for anyone considering this procedure. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of where hair is sourced for transplants, how it is harvested, and the various methods used in hair restoration.
Understanding Hair Transplants
1. What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves relocating hair follicles from a donor site to an area experiencing hair loss. The goal is to achieve a natural-looking head of hair that blends seamlessly with existing hair. There are two primary techniques: Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT).
2. The Importance of Donor Hair
Donor hair is essential for a successful hair transplant. The quality, texture, and growth characteristics of the donor hair significantly impact the overall results. Understanding where this hair comes from can help patients make informed decisions about their hair restoration options.
Sources of Donor Hair
1. Scalp
The Most Common Source
The most common source of hair for transplants is the scalp, specifically the areas at the back and sides. This region is typically more resistant to the effects of androgens, which cause hair loss in other areas.
Characteristics of Scalp Hair
Scalp hair is often thicker and has a stronger growth cycle compared to body hair. This makes it the ideal choice for transplantation, as it tends to integrate better with existing hair and provides a more natural appearance.
2. Body Hair
An Alternative Source
In cases where scalp hair is insufficient due to extensive hair loss or previous surgeries, body hair can be used as an alternative. This includes hair from areas such as the chest, back, or legs.
Techniques for Body Hair Extraction
The extraction of body hair involves similar methods as those used for scalp hair, primarily FUE. However, the texture and growth patterns of body hair can differ from scalp hair, which may impact the final results.
3. Facial Hair
Beard and Mustache Hair
Facial hair, including beard and mustache hair, can also serve as a donor source. This is particularly useful for individuals with thinning hairlines or patchy areas on the scalp.
Considerations for Facial Hair
Facial hair is usually coarser and thicker than scalp hair. While it can be effective for transplantation, it may not blend seamlessly with existing scalp hair, making it a consideration for specific cases.
4. Donor Hair from Relatives
Genetic Matching
In rare instances, hair follicles can be obtained from a close relative, such as a sibling or parent. This may be considered if a person has insufficient donor hair on their scalp.
Limitations
While genetic matching may enhance compatibility, the procedure still poses risks associated with surgical interventions.
Hair Harvesting Techniques
1. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
The Extraction Process
FUE involves harvesting individual hair follicles from the donor area using a small punch tool. This minimally invasive technique leaves tiny scars that are less noticeable than those from FUT.
Advantages of FUE
Minimal scarring
Shorter recovery time
Flexibility in donor hair selection
2. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
The Strip Method
FUT involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, which is then dissected into individual follicular units for transplantation. This method can yield a larger number of grafts in one session.
Considerations for FUT
While it provides a higher graft yield, FUT leaves a linear scar that may be more visible, particularly with short hairstyles.
Preparing for a Hair Transplant
1. Initial Consultation
Before any procedure, patients should have a thorough consultation with a qualified hair transplant surgeon. During this visit, the surgeon will assess the patient’s hair loss, discuss potential donor sites, and outline the best approach for the individual.
2. Evaluating Donor Area
The surgeon will examine the donor area for hair quality, density, and potential yield. This evaluation helps determine the feasibility of the transplant and the number of grafts required.
3. Planning the Procedure
Once the donor area is assessed, the surgeon will create a detailed plan that includes the extraction technique, placement of the transplanted hair, and anticipated outcomes.
The Hair Transplant Procedure
1. Anesthesia
To ensure patient comfort during the procedure, local anesthesia is administered to the donor and recipient areas. This allows patients to remain awake without feeling pain.
2. Hair Follicle Extraction
Depending on the chosen method (FUE or FUT), hair follicles are extracted from the donor area. For FUE, individual follicles are harvested, while FUT involves removing a strip of scalp.
3. Preparation of Donor Hair
In FUT, the strip is dissected into individual grafts under a microscope. For FUE, the follicles are prepared for immediate implantation.
4. Transplantation
The prepared follicles are then transplanted into the recipient area. The surgeon carefully places them to ensure a natural look, considering factors like angle and density.
5. Post-Procedure Care
After the procedure, patients receive specific aftercare instructions to promote healing and hair growth. This may include avoiding strenuous activities and protecting the scalp from direct sunlight.
Recovery and Results
1. Initial Healing
Patients may experience redness and swelling at the donor and recipient sites for several days post-procedure. Following the surgeon’s aftercare instructions is crucial for optimal healing.
2. Hair Growth Timeline
New hair growth typically begins around three to four months after the procedure. Full results can take up to a year, as hair grows gradually.
3. Long-Term Maintenance
Maintaining healthy hair post-transplant involves a good hair care routine, regular check-ups with the surgeon, and, if necessary, ongoing treatments for hair loss.
Conclusion
Understanding where hair for transplants is sourced and the techniques involved is essential for anyone considering this procedure. From scalp hair to alternative sources like body and facial hair, various options are available to achieve a natural-looking result. With advancements in techniques like FUE and the benefits of meticulous planning and skilled surgeons, individuals can regain their confidence and enjoy a fuller head of hair. By making informed decisions and consulting with experienced professionals, patients can navigate their hair restoration journey effectively.
Related topics:
- Sapphire FUE Hair Transplant: The Ultimate Guide
- When Is It Too Late for a Hair Transplant? A Full Guide
- Non-Surgical Hair Replacement: A Comprehensive Guide