Hairlines are often one of the first visible signs of aging, and for many individuals, the thought of a receding hairline can be concerning. Understanding when and why hairlines start to recede is crucial for early intervention and management. This article delves into the age-related patterns of hairline recession, the underlying causes, and what individuals can do to address this issue effectively.
Understanding Hairline Recession
What is a Receding Hairline?
A receding hairline refers to the gradual loss of hair along the forehead’s hairline, often resulting in a more prominent forehead. This condition can vary in severity and may lead to baldness if left unchecked.
Common Patterns of Hairline Recession
Hairline recession typically follows distinct patterns:
M-Shaped Hairline: This is characterized by a more pronounced recession at the temples, creating an “M” shape.
Straight Recession: The hairline recedes uniformly along the forehead without forming an “M” shape.
Widow’s Peak: A prominent V-shape at the center of the forehead, where the hairline dips.
When Does Hairline Recession Begin?
Age Factors
Late Teens to Early Twenties: Some individuals may start to notice subtle changes in their hairline during their late teens or early twenties. This is often the onset of male or female pattern baldness.
Mid-Twenties to Early Thirties: For many men, noticeable hairline recession typically begins in their mid-to-late twenties. Women may also experience hair thinning or recession during this period but often to a lesser degree.
Late Thirties and Beyond: By this age, hairline recession may become more pronounced for both genders. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the extent of hair loss during this stage.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics significantly influence when and how hairlines recede. If individuals have a family history of hair loss, they are more likely to experience similar changes at a younger age. Research suggests that up to 80% of hair loss cases can be attributed to genetic factors.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in androgens, can contribute to hairline recession. For men, dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a potent form of testosterone linked to hair loss. Women may experience hormonal changes due to pregnancy, menopause, or other factors that can lead to thinning hair.
Recognizing the Signs of Recession
Early Indicators
Thinning at the Temples: One of the first signs of a receding hairline is thinning at the temples. Individuals may notice that their hairline begins to form an “M” shape.
Increased Shedding: A noticeable increase in hair shedding during washing or styling can indicate underlying issues with hair health.
Visible Scalp: As the hairline recedes, the scalp may become more visible, particularly under bright lights or when hair is pulled back.
Progression of Recession
Uneven Growth: The hairline may start to appear uneven, with patches of thinner hair compared to denser areas.
Wider Forehead: As the hairline recedes, the forehead may seem larger, leading to concerns about aesthetics.
Widow’s Peak Development: In some individuals, a widow’s peak may become more pronounced as the hairline recedes.
Factors Influencing Hairline Recession
Lifestyle Factors
Stress: High stress levels can lead to a condition called telogen effluvium, which causes temporary hair shedding. Chronic stress may exacerbate genetic predispositions to hair loss.
Diet: Poor nutrition can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals necessary for hair health. A diet lacking in protein, iron, and vitamins A, C, D, and E can weaken hair.
Smoking: Research indicates that smoking may contribute to hair loss by affecting blood circulation and damaging hair follicles.
Health Conditions
Certain medical conditions can accelerate hairline recession, including:
Thyroid Disorders: Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can lead to hair loss and changes in hair texture.
Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like alopecia areata cause the immune system to attack hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women can result in hormonal imbalances that affect hair growth.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Early Intervention
Recognizing the early signs of hairline recession allows individuals to take proactive measures to manage their hair health.
Regular Scalp Checks: Regularly monitor your hairline and overall scalp health. Early detection can lead to more effective treatment options.
Consultation with Professionals: If you notice significant changes, consider consulting a dermatologist or trichologist for a thorough assessment and personalized advice.
Lifestyle Modifications
Healthy Diet: Incorporate a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals essential for hair health. Foods high in antioxidants, healthy fats, and proteins can promote hair growth.
Stress Management Techniques: Practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises to manage stress levels effectively.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can improve blood circulation and promote overall health, including hair health.
Hair Care Practices
Gentle Hair Care: Use mild shampoos and avoid harsh treatments that can damage hair. Limit the use of heat-styling tools and opt for protective hairstyles.
Scalp Health: Keep the scalp clean and free from excess oil or product buildup. Regularly exfoliate the scalp to promote healthy hair growth.
Hair Supplements: Consider supplements containing biotin, collagen, and other hair-supporting nutrients. Consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.
Medical Treatments
Minoxidil: An FDA-approved topical solution that promotes hair regrowth in both men and women. It works by increasing blood flow to hair follicles and prolonging the hair growth phase.
Finasteride: A prescription medication for men that reduces the conversion of testosterone to DHT, which can slow hair loss and promote regrowth.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: A treatment that involves injecting the patient’s own platelets into the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
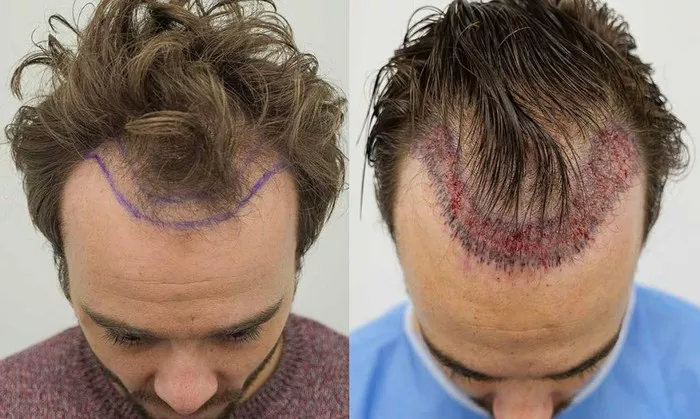
Hair Transplant Surgery: For more advanced cases, surgical options like hair transplants can provide a permanent solution for receding hairlines.
Conclusion
Understanding when hairlines start receding and the factors that contribute to this change is essential for early intervention and effective management. While genetic predisposition plays a significant role, lifestyle choices, health conditions, and care practices can also influence hair health. By recognizing the signs early and implementing preventive strategies, individuals can take charge of their hair health and address concerns related to hairline recession. Remember, if you notice significant changes in your hairline, consulting with a professional can provide tailored advice and effective solutions.
Related topics:
- Does an M-Shaped Hairline Mean Balding? Knowing the Signs
- How to Regrow Your Hairline Naturally: Effective Strategies
- Can You Get a New Hairline? Exploring Options and Techniques