Hair transplant surgery can significantly improve a person’s appearance by restoring hair to thinning or balding areas. While the procedure can yield excellent results, one concern many patients have is the healing process of the hair transplant scar. The length of time it takes for a hair transplant scar to heal depends on various factors, including the surgical technique used, the individual’s healing rate, and how well the post-operative care is followed.
In this article, we will provide an in-depth exploration of hair transplant scars, how long they take to heal, the factors affecting healing, and how you can care for your scars to ensure optimal recovery and results.
Understanding Hair Transplant Scars
Types of Hair Transplant Techniques
The type of hair transplant technique you undergo will determine the nature of the scar you will have after surgery. There are primarily two methods of hair transplant surgery, each leaving a different type of scar.
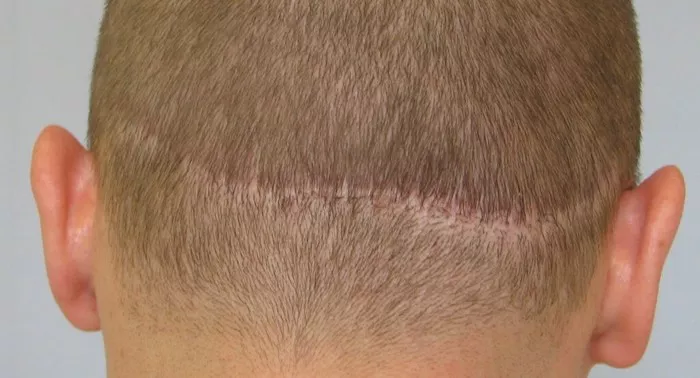
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): FUT, also known as the strip method, involves removing a thin strip of tissue from the donor area, typically from the back of the scalp. This strip is then dissected into individual hair follicles, which are transplanted into the recipient areas.
Scar Characteristics: This method leaves a linear scar at the donor site, which can be visible if you wear your hair short. The scar can be relatively narrow, but it can also be more prominent in some individuals, depending on how the tissue is sutured and healed.
Healing Time: The linear scar from FUT may take longer to heal than the scars from FUE, due to the more invasive nature of the technique.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): FUE involves extracting individual hair follicles from the donor area using a small, circular punch tool. This technique does not require the removal of a strip of skin, meaning the donor area heals with tiny circular scars instead of a single linear scar.
Scar Characteristics: FUE leaves small, round scars spread across the donor area. These scars are less visible than the linear scar from FUT, especially when the hair is short. However, they can still be noticeable if the scalp is shaved too closely.
Healing Time: The healing process for FUE scars is generally quicker than that of FUT, as it is a less invasive procedure.
Factors Affecting the Healing of Hair Transplant Scars
The Surgical Technique
The technique used during your hair transplant plays a significant role in the nature and healing time of your scars. As mentioned, FUT leaves a linear scar, while FUE leaves multiple dot-like scars. However, the overall healing time will depend on the technique, and FUE usually results in faster healing and less visible scarring.
Individual Healing Rate
Everyone heals at different rates, and factors such as age, overall health, and genetics can all play a role in how quickly your scar heals. Younger patients tend to heal faster, while older individuals may experience a longer healing period.
Genetics: Some people are more prone to keloid scarring, which can result in more noticeable and raised scars. It is important to discuss your potential for keloid formation with your surgeon beforehand.
General Health: A healthy lifestyle with proper nutrition, hydration, and exercise can promote faster healing. Smoking, poor nutrition, and underlying medical conditions like diabetes can slow down the healing process.
The Size and Location of the Donor Area
The size of the donor area and its location on the scalp can also influence the healing process. Larger donor areas or areas with thinner skin may take longer to heal. The location of the incision, whether it is closer to the crown or lower down at the back of the head, can impact both the visibility and healing time of the scar.
Post-Operative Care and Lifestyle Factors
Your post-operative care is vital in determining how quickly your scars heal. Failing to follow your surgeon’s aftercare instructions can increase the risk of infection, slow the healing process, and lead to unsightly scars.
Avoiding Sun Exposure: Direct exposure to the sun can lead to pigmentation issues or scarring. It is essential to protect your scalp from sunlight, especially in the first few weeks after the procedure.
Avoiding Stress: High-stress levels can negatively impact your body’s ability to heal. Stress can also cause inflammation, which may exacerbate scarring.
Diet: Eating a well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamins A, C, and E, can support healthy skin healing.
The Healing Process of Hair Transplant Scars
Immediately After Surgery (First Few Days)
In the immediate aftermath of your hair transplant, your donor area will be tender and may be covered with bandages or gauze. The first few days are crucial for the initial recovery, during which the following may occur:
Swelling and redness: The donor area may appear swollen and red, especially if you had FUT, which involves a larger incision. This is normal and should subside within a few days.
Crusting: Scabs and crusts will form around the newly transplanted follicles and the donor area. These should be left alone and not scratched, as this could cause the transplanted grafts to become dislodged.
Early Healing Stage (1 to 2 Weeks)
During the first one to two weeks, your scalp will begin the healing process:
Sutures: If you had FUT, sutures (stitches) may still be in place, but these are usually removed after about 7 to 10 days. The donor area may still show visible redness or scabbing at this stage.
Discomfort: You may feel some discomfort or itching around the donor area, but it should begin to lessen over time. Pain medication prescribed by your doctor can help manage this.
Scar Formation: The initial stages of scar formation occur, with both FUT and FUE patients developing scars in the donor area. The FUE scars will be small and circular, while the FUT scar will be linear.
Mid-Term Healing (3 to 6 Weeks)
By the third to sixth week after the hair transplant, significant healing should be evident:
Hair Shedding: At this point, most of the transplanted hair will begin to shed. This is completely normal, as the transplanted follicles enter a dormant phase before new hair begins to grow.
Scar Softening: The donor area should feel less tender, and the scars should start to soften. However, some redness or discoloration may persist.
Tissue Regeneration: The tissue around the donor site is regenerating, and the hair follicles are settling into their new location.
Long-Term Healing (6 to 12 Months)
The final stages of healing typically occur between 6 to 12 months after the transplant:
Hair Growth: The transplanted hair follicles will begin to sprout new hair, although the growth may be sparse at first. Full growth takes about 12 months to become apparent.
Scar Maturation: Scars continue to mature, becoming less noticeable. The redness and discoloration around the donor area should subside significantly, though the scars will still be visible upon close inspection.
Permanent Scar Formation: By 12 months, the scars have fully formed and have reached their final appearance. The scars from FUE will be small and dotted, while the FUT scar will be a thin, linear mark. Both scars may be covered by hair once the growth is thick enough.
How to Minimize and Care for Hair Transplant Scars
Follow Post-Operative Instructions
To promote proper healing and minimize scarring, following your surgeon’s post-operative care instructions is crucial. This includes instructions on:
- Shampooing: Avoid washing your hair too soon after surgery. Use gentle, mild shampoos and avoid any harsh chemicals for several weeks.
- Sun Protection: Keep your scalp covered or use sunscreen to protect it from UV rays.
Scalp Massage and Treatments
Once the initial healing has occurred, gentle scalp massages can improve circulation and promote healing. You can also use certain treatments recommended by your surgeon, such as silicone sheets or topical scar creams, to reduce scarring.
Avoid Smoking and Alcohol
Smoking and alcohol can delay the healing process and increase scarring. Refrain from smoking and limit alcohol consumption during the recovery phase to promote faster and more efficient healing.
Use of Hair Concealers or Scar Camouflage
For individuals who are concerned about the visibility of the scar, hair concealers and scar camouflage products can be used temporarily to cover the area until the scar matures. These products are often used until the hair has grown enough to naturally hide the scar.
Conclusion
Hair transplant scars take time to heal, and their healing process depends on several factors, including the technique used, individual healing rates, and the quality of post-operative care. While scarring is inevitable, it can be minimized with proper aftercare, and many patients find that the final result is a natural and smooth appearance, with the scars being barely noticeable after the hair has fully grown.
In general, FUT scars take longer to heal than FUE scars, but both can heal well if you follow your surgeon’s recommendations. If you’re concerned about scarring or if you notice any unusual symptoms, be sure to contact your surgeon for advice and guidance. With patience and proper care, your hair transplant scars will heal, and you will soon be able to enjoy the benefits of a fuller, thicker head of hair.
Related topic:
- Do Hair Transplants Look Natural? Understanding the Truth
- Can You Use Hair Fibers After a Hair Transplant?
- What to Expect Two Months After a Hair Transplant?