Hair loss is a common issue affecting millions of individuals worldwide. Whether due to genetics, age, hormonal imbalances, or medical conditions, many people seek hair restoration solutions to regain their confidence. Among the various treatments available, hair transplantation stands out as one of the most effective, permanent solutions for hair loss. This article will provide a detailed look at how hair implantation is done, including the step-by-step process, methods, considerations, and aftercare.
What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a medical procedure where hair follicles from one part of the body (usually the back or sides of the head) are transplanted to areas experiencing hair thinning or baldness. The procedure uses your natural hair to restore a fuller, more natural-looking hairline. It is commonly used to treat male pattern baldness, female hair thinning, and other forms of hair loss.
Hair transplants are typically performed by dermatologists, plastic surgeons, or specialized hair transplant surgeons. While the procedure is often regarded as minimally invasive, it does require precision, technical skill, and a thorough understanding of the hair growth cycle.
Why Choose a Hair Transplant?
Hair transplants offer several advantages over other hair restoration treatments:
Permanent Solution: Hair transplants offer a permanent solution to hair loss. The transplanted hair follicles are resistant to the hormones that cause hair thinning in the first place.
Natural Results: Since the procedure uses your natural hair, it creates a more natural look than wigs or other non-surgical treatments.
Minimal Maintenance: Once the transplanted hair has grown, it behaves like your natural hair, requiring no special treatment.
Improved Confidence: Many people experience a boost in self-esteem and confidence after a successful hair transplant.
Types of Hair Transplant Methods
There are two main methods for hair transplantation: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). Both have their advantages, but the choice depends on various factors such as the extent of hair loss, donor hair availability, and patient preferences.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT, also known as the strip method, involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area (usually the back of the head) where hair is thick and healthy. This strip contains several hair follicles, which are then dissected under a microscope into individual follicular units. These follicular units are then implanted into the balding areas of the scalp.
Higher Yield: Because a larger number of follicles are harvested in one strip, FUT allows for more hair grafts to be transplanted.
Less Expensive: FUT is often more affordable compared to FUE due to the nature of the procedure.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a more advanced method that involves extracting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area using a small, circular punch. The follicles are then implanted into the recipient area. This method does not require removing a strip of skin, making it a less invasive option compared to FUT.
Minimal Scarring: Since the follicles are extracted individually, the procedure leaves tiny, dot-like scars that are less noticeable.
Quicker Recovery: FUE generally offers a faster recovery time than FUT.
The Step-by-Step Process of Hair Implantation
Understanding the hair transplant procedure in detail is essential for anyone considering it. Here is an overview of the typical steps involved in a hair transplant:
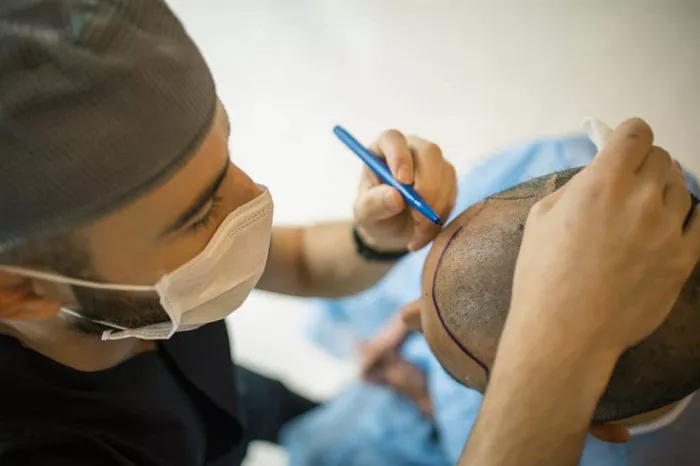
Step 1: Initial Consultation
Before undergoing a hair transplant, patients must first consult with a qualified surgeon to discuss their hair loss situation. During this consultation, the surgeon will:
Assess the patient’s hair type, the extent of hair loss, and the donor area.
Review the patient’s medical history to ensure they are suitable candidates for the procedure.
Discuss expectations, potential outcomes, and the available hair transplant methods (FUT vs. FUE).
Create a personalized treatment plan based on the patient’s needs.
Step 2: Pre-Operative Preparations
Prior to the transplant, the surgeon will provide the patient with guidelines to prepare for the surgery. These may include:
Avoiding certain medications: Patients may be instructed to stop taking blood-thinning medications, such as aspirin or ibuprofen, which can increase the risk of bleeding.
Shaving the donor area: In most cases, the hair in the donor area will need to be shaved to ensure better access to the follicles.
Washing and cleaning the scalp: A clean scalp is essential to reduce the risk of infection during the procedure.
Step 3: Local Anesthesia and Donor Area Harvesting
On the day of the procedure, the patient will be given a local anesthetic to numb the scalp. This will ensure the procedure is painless.
For FUT: The surgeon will remove a strip of skin from the donor area. The skin will be stitched back together, and the strip will be carefully dissected into individual follicular units.
For FUE: Individual follicles are harvested using a small, circular punch tool. This step is more time-consuming but less invasive.
Step 4: Recipient Area Preparation
Once the hair follicles have been harvested, the surgeon will prepare the recipient area (the balding part of the scalp) for implantation. This involves making small incisions where the hair follicles will be placed.
Step 5: Implantation of Hair Follicles
The harvested hair follicles are carefully implanted into the tiny incisions in the recipient area. The surgeon ensures that the follicles are placed at the correct depth and angle to mimic natural hair growth patterns. This step requires a great deal of precision to achieve the best aesthetic results.
Step 6: Post-Operative Care
After the implantation, the patient will receive instructions on how to care for the scalp during the recovery period. This may include:
Medication: Pain relief medications or antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce discomfort and prevent infection.
Avoiding physical activity: Patients should avoid strenuous physical activities for a few weeks to prevent unnecessary stress on the scalp.
Gentle washing: Patients should wash their hair gently to avoid dislodging the newly transplanted follicles.
Step 7: Follow-Up Appointments
The patient will have follow-up appointments to ensure that the scalp is healing correctly. These appointments will also help the surgeon assess how the hair follicles are taking root and growing.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
The recovery process following a hair transplant is crucial to achieving the best results. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Initial Healing: In the first few days, patients may experience some redness, swelling, or mild discomfort at the transplant sites. These symptoms usually subside within a few days.
Shedding Phase: It is common for transplanted hair to shed within the first 2 to 3 weeks. However, this is a normal part of the hair growth cycle, and new hair will start to grow in its place.
Full Results: It can take anywhere from 6 to 12 months for the transplanted hair to fully grow. Over time, the new hair will thicken and become indistinguishable from the natural hair.
Potential Risks and Complications
Although hair transplants are generally safe, there are some risks and complications associated with the procedure, including:
Infection: Any surgical procedure carries a risk of infection, though this can be minimized with proper aftercare and hygiene.
Scarring: Depending on the method used, scarring may occur, especially with FUT. However, FUE typically results in minimal scarring.
Poor Growth: In rare cases, the transplanted hair may not grow as expected, or the follicles may not take root. This is why it is crucial to choose an experienced surgeon.
Conclusion
Hair transplantation is a transformative procedure for individuals suffering from hair loss. With proper planning, an experienced surgeon, and appropriate aftercare, patients can achieve permanent, natural-looking hair restoration. Whether opting for FUT or FUE, understanding the procedure’s steps, recovery process, and potential risks will ensure that individuals are well-prepared for a successful hair transplant journey.
It’s important to consult with a professional who can help guide you through the entire process, from initial consultation to post-operative care. With the right approach, hair transplants can offer life-changing results that restore both hair and confidence.
Related topic:
- How Long Does It Take to Heal After Hair Transplant
- How to Regrow Edges for 4C Hair: A Comprehensive Guide
- How to Grow Your Edges Back Fast Naturally: A Comprehensive Guide