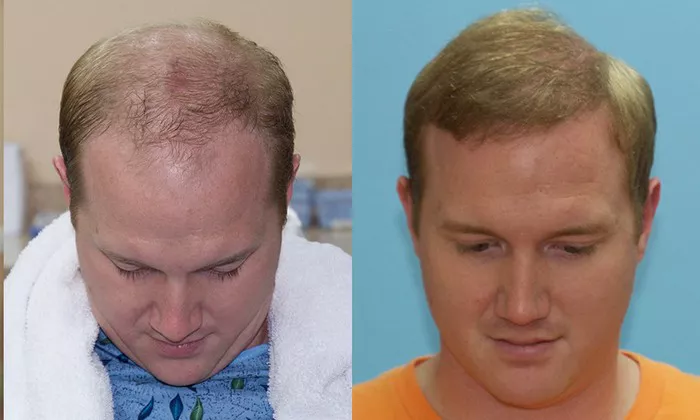
A mature hairline is a natural part of the aging process, and it can vary significantly from person to person. For many individuals, the development of a mature hairline is a gradual transition that occurs over several years. While some people may notice changes in their 20s, others might not experience significant changes until their 30s or even later. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore when a mature hairline typically develops, the factors that influence its timing, and what you can expect during this process. Whether you’re in your teens, 20s, or beyond, this article will provide valuable insights into the development of a mature hairline and how to manage any concerns you may have.
The term “mature hairline” refers to the natural recession of the hairline that occurs as a person ages. Unlike premature balding or androgenetic alopecia, which are often caused by genetic factors, a mature hairline is a normal part of the aging process and is not necessarily indicative of more severe hair loss. The development of a mature hairline is influenced by a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors, and it can vary widely between individuals.
What Is a Mature Hairline?
A mature hairline is characterized by a slight recession of the hairline, particularly at the temples, where the hairline begins to recede in an M-shaped pattern. This is different from a juvenile hairline, which is typically straight across the forehead and extends lower on the scalp. A mature hairline is a natural progression that most men experience as they age, but it can also occur in women, although less commonly.
When Does a Mature Hairline Typically Develop?
The timing of a mature hairline can vary depending on individual factors, but there are some general trends that can help you understand when to expect changes. Here’s a breakdown of the typical timeline for the development of a mature hairline:
1. Teens and Early 20s
For many individuals, the hairline remains relatively unchanged throughout adolescence and early adulthood. During this time, the hairline is often referred to as a “juvenile hairline” because it tends to be straight across the forehead and extends lower on the scalp. However, some people may begin to notice subtle changes in their late teens or early 20s, such as a slight recession at the temples or a more defined widow’s peak.
- What to Expect: In most cases, the hairline remains stable during this period, but some individuals may experience mild changes. If you notice any significant thinning or recession, it could be a sign of early androgenetic alopecia (male or female pattern baldness), rather than a normal maturation process.
- Factors to Consider: Genetics play a significant role in determining when a mature hairline will develop. If your parents or siblings experienced early hairline changes, you may be more likely to see similar patterns.
2. Mid to Late 20s
For many men, the mid to late 20s is when a mature hairline begins to take shape. During this time, the hairline may start to recede slightly at the temples, forming a more defined M-shape. This is a natural part of the aging process and is not necessarily a cause for concern. However, if the recession is more pronounced or accompanied by thinning in other areas, it could be a sign of androgenetic alopecia.
- What to Expect: By the mid to late 20s, most men will notice some degree of hairline recession. The temples may become more prominent, and the hairline may start to move back slightly. Women may also experience subtle changes, but these are usually less noticeable.
- Factors to Consider: Hormonal changes, particularly increases in dihydrotestosterone (DHT), can contribute to the development of a mature hairline. Lifestyle factors, such as stress, diet, and overall health, can also play a role in how quickly the hairline matures.
3. 30s and Beyond
By the 30s, most men will have a fully developed mature hairline. The hairline may continue to recede slightly, but the changes are generally slower and less dramatic than in earlier years. For some men, the hairline may stabilize around this time, while others may continue to experience gradual recession.
- What to Expect: In the 30s, the hairline is typically well-defined, with a more pronounced recession at the temples. Some men may also notice thinning on the crown or vertex of the scalp, especially if they are genetically predisposed to androgenetic alopecia. Women may experience more noticeable changes in their 30s, particularly after pregnancy or menopause.
- Factors to Consider: As you enter your 30s, hormonal fluctuations, particularly those related to aging, can influence the development of a mature hairline. Stress, poor nutrition, and certain medical conditions can also impact hair growth and recession.
Factors That Influence the Development of a Mature Hairline
Several factors can influence when and how a mature hairline develops. Understanding these factors can help you better anticipate changes and take steps to manage any concerns.
1. Genetics
Genetics is one of the most significant factors in determining when a mature hairline will develop. If your family members, particularly your father or brothers, experienced early hairline changes, you may be more likely to see similar patterns. Conversely, if your family has a history of thick, full hair, you may retain a more youthful hairline for longer.
- How It Works: Genes play a crucial role in regulating the sensitivity of hair follicles to hormones like DHT. Individuals with a genetic predisposition to androgenetic alopecia may experience more rapid hairline recession, while those without this predisposition may maintain a fuller hairline for longer.
2. Hormones
Hormones, particularly androgens like testosterone and DHT, play a key role in the development of a mature hairline. DHT is a derivative of testosterone that can shrink hair follicles over time, leading to hairline recession. While DHT levels naturally increase during puberty, they tend to stabilize in adulthood, which is why hairline changes often occur gradually.
- How It Works: In men, higher levels of DHT can accelerate hairline recession, especially at the temples. In women, hormonal changes related to pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders can also impact hair growth and recession. Managing hormone levels through lifestyle changes or medical interventions can help slow down the process.
3. Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle and environmental factors can also influence the development of a mature hairline. Poor nutrition, chronic stress, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can all negatively impact hair health and accelerate hairline changes. On the other hand, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help support hair growth and delay the onset of a mature hairline.
- How It Works: A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and proteins, is crucial for healthy hair growth. Stress management techniques, regular exercise, and proper sleep can also promote hormonal balance and support overall hair health. Avoiding harsh hair treatments and protecting your scalp from environmental damage can further protect your hairline.
4. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and autoimmune diseases, can affect hormone levels and contribute to hairline changes. If you suspect that a medical condition is impacting your hairline, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- How It Works: Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism, can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle, leading to thinning or recession. PCOS, which is characterized by hormonal imbalances, can also cause hair loss, particularly in women. Treating the underlying condition can help restore hormonal balance and improve hair health.
How to Manage a Maturing Hairline
While a mature hairline is a natural part of the aging process, there are several ways to manage changes and maintain a healthy hairline. Whether you’re in your 20s, 30s, or beyond, taking proactive steps can help you feel more confident about your appearance.
1. Monitor Changes
If you notice any significant changes in your hairline, such as rapid recession or thinning, it’s important to monitor the situation closely. Take photos of your hairline at regular intervals to track any changes over time. This can help you determine whether the changes are part of a normal maturation process or if they may be signs of more advanced hair loss.
- What to Look For: Pay attention to the shape of your hairline, particularly at the temples. If you notice a more pronounced M-shape or thinning in other areas, it could be a sign of androgenetic alopecia. In women, look for thinning along the part or on the crown of the scalp.
2. Consider Medical Treatments
If you’re concerned about hairline changes, there are several medical treatments available that can help slow down the process or promote hair regrowth. Common options include:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): A topical solution that stimulates blood flow to the scalp and promotes hair growth. It is effective for both men and women and can help prevent further hairline recession.
- Finasteride (Propecia): A prescription medication that blocks the conversion of testosterone to DHT, reducing the effects of androgenetic alopecia. It is primarily used for men but can also be prescribed for women in certain cases.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): A non-invasive treatment that uses red light to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. It can be used in combination with other treatments for optimal results.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: A procedure that involves injecting concentrated platelets from your own blood into the scalp to stimulate hair growth. It is particularly effective for individuals who have not responded to other treatments.
3. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle can support overall hair health and help delay the onset of a mature hairline. Focus on:
- Nutrition: Eat a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, including protein, vitamins, and minerals. Foods like eggs, lean meats, fish, leafy greens, and nuts can promote healthy hair growth.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. Chronic stress can disrupt hormone levels and accelerate hairline changes.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve circulation and support overall health, including hair growth. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Avoid Harsh Treatments: Be gentle with your hair and avoid harsh chemical treatments, heat styling tools, and tight hairstyles that can damage hair follicles. Use sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners to protect your scalp.
4. Consult a Professional
If you’re unsure about the changes in your hairline or if you’re experiencing more advanced hair loss, it’s important to consult with a qualified healthcare provider or dermatologist. They can help diagnose the underlying cause of your hairline changes and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
- What to Expect: During your consultation, your healthcare provider will assess your hairline, review your medical history, and possibly conduct tests to rule out any underlying conditions. Based on their findings, they can suggest personalized treatment options to help manage your hairline changes.
Conclusion
A mature hairline is a natural part of the aging process, and while the timing can vary from person to person, most individuals will experience some degree of hairline recession by their 30s. By understanding the factors that influence the development of a mature hairline and taking proactive steps to manage changes, you can maintain a healthy, confident appearance. Whether through medical treatments, lifestyle changes, or simply embracing the natural aging process, there are many ways to approach a maturing hairline with confidence. If you’re concerned about your hairline, don’t hesitate to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and support.
- Does Your Hair Grow Back After Hair Transplant
- Do You Need to Shave Your Head for Hair Transplant
- How Does Hair Transplant Work? A Comprehensive Guide