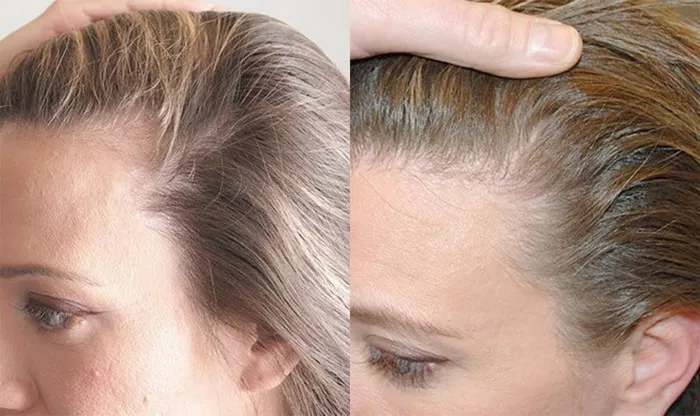
Hair loss is a common concern for many individuals, regardless of age or gender. It can manifest in various forms and for various reasons, leading to confusion about the underlying causes and appropriate treatments. One of the most well-known types of hair loss is male pattern baldness, which affects a significant portion of the male population. While these terms are often used interchangeably, it’s crucial to recognize that they refer to distinct conditions with different characteristics and underlying mechanisms. In this article, we delve into the nuances between hair loss and male pattern baldness, exploring their definitions, causes, and treatment options.
Understanding Hair Loss:
Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, is the partial or complete absence of hair from areas where it typically grows. This condition can affect the scalp, as well as other parts of the body. Hair loss can occur gradually or suddenly and may be temporary or permanent, depending on the underlying cause. There are several types of hair loss, each with its own set of characteristics and triggers:
1. Androgenetic Alopecia: Also referred to as male or female pattern baldness, androgenetic alopecia is the most common type of hair loss. It is hereditary and typically follows a predictable pattern. In men, it often starts with a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, eventually leading to baldness. Women with androgenetic alopecia may experience diffuse thinning across the scalp rather than distinct bald spots.
2. Alopecia Areata: This autoimmune condition causes patchy hair loss on the scalp and other areas of the body. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss. Alopecia areata can vary in severity, with some individuals experiencing small, coin-sized patches of hair loss, while others may lose hair more extensively.
3. Telogen Effluvium: This type of hair loss occurs when a significant number of hair follicles prematurely enter the telogen (resting) phase of the hair growth cycle. It can be triggered by factors such as physical or emotional stress, hormonal changes, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions. Telogen effluvium often manifests as diffuse hair shedding rather than specific bald patches.
4. Anagen Effluvium: Anagen effluvium is characterized by hair loss during the active growth phase (anagen) of the hair cycle. It is commonly associated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy for cancer treatment, as these treatments target rapidly dividing cells, including hair follicles.
5. Traction Alopecia: This type of hair loss occurs when excessive tension is applied to the hair follicles over time, often due to hairstyles such as tight ponytails, braids, or extensions. Traction alopecia typically affects the hairline or areas where hair is pulled tightly.
Understanding Male Pattern Baldness:
Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a specific form of hair loss that primarily affects men. It is characterized by a distinct pattern of hair thinning and loss, typically starting at the temples and crown of the scalp. Male pattern baldness is influenced by genetic and hormonal factors, specifically the presence of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone. DHT binds to hair follicles, causing them to shrink and produce thinner, shorter hairs in successive cycles. Over time, affected hair follicles may cease to produce hair altogether, leading to baldness in the affected areas.
Unlike other forms of hair loss, male pattern baldness follows a predictable progression known as the Norwood scale. This scale categorizes male pattern baldness into several stages based on the extent and pattern of hair loss. Stage I represents minimal hair loss, while stage VII denotes extensive baldness with only a horseshoe-shaped fringe of hair remaining at the sides and back of the scalp.
Differentiating Hair Loss from Male Pattern Baldness:
While hair loss and male pattern baldness share common features, there are key differences that distinguish them:
1. Pattern of Hair Loss: Male pattern baldness typically follows a specific pattern characterized by gradual thinning and recession of the hairline, often accompanied by thinning at the crown of the scalp. In contrast, other types of hair loss, such as alopecia areata or telogen effluvium, may result in patchy or diffuse hair loss without a distinct pattern.
2. Underlying Mechanisms: Male pattern baldness is primarily driven by genetic and hormonal factors, specifically the influence of DHT on hair follicles. On the other hand, other forms of hair loss may be triggered by autoimmune reactions, physiological stress, medical treatments, or lifestyle factors.
3. Age of Onset: Male pattern baldness typically begins to manifest in adulthood, with the risk increasing with age. It often becomes noticeable in the late teens or early twenties and progresses gradually over time. In contrast, other types of hair loss, such as alopecia areata or telogen effluvium, may occur at any age and can have sudden onset.
4. Response to Treatment: Male pattern baldness may respond to specific treatments aimed at blocking the effects of DHT or promoting hair growth, such as minoxidil or finasteride. However, these treatments may not be effective for other forms of hair loss that have different underlying causes. Treatment options for other types of hair loss vary depending on the specific condition and may include topical corticosteroids, immunotherapy, or hair transplant surgery.
Conclusion:
In summary, while hair loss and male pattern baldness are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct conditions with different characteristics and underlying mechanisms. Understanding the differences between these terms is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Whether you’re experiencing hair loss or male pattern baldness, consulting with a dermatologist or hair specialist can help determine the underlying cause and tailor a treatment plan to address your specific needs. Remember, early intervention is key to maximizing treatment efficacy and preserving hair health.