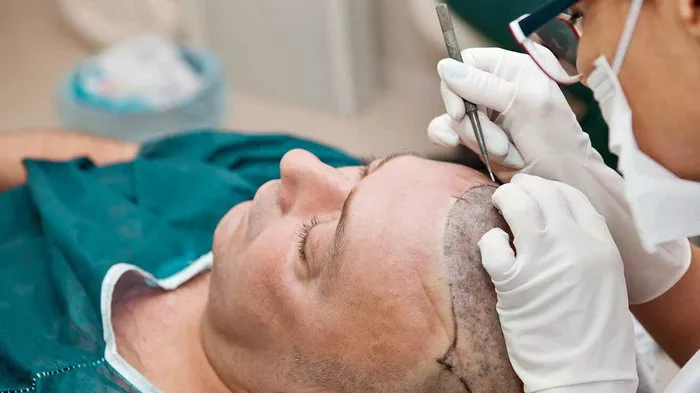
Hair loss can significantly impact one’s self-esteem and confidence, prompting many individuals to seek solutions to restore their hairline and regain a more youthful appearance. While there are various treatments available for hair loss, including medications and topical solutions, hair transplant surgery remains one of the most effective and long-lasting solutions. This article provides a detailed overview of how hair transplant surgery works, including the different techniques, eligibility criteria, preparation, aftercare, risks, benefits, success rates, recovery process, and cost considerations.
Overview of Hair Transplant Surgery
Hair transplant surgery is a cosmetic procedure designed to address hair loss by transplanting healthy hair follicles from donor areas, typically the back or sides of the scalp, to balding or thinning areas. The procedure is suitable for individuals experiencing male or female pattern baldness, as well as those with hair loss due to injury, burns, or previous surgical procedures.
Common reasons why individuals opt for hair transplant surgery include:
1. Desire for a fuller, thicker hairline.
2. Improved self-confidence and self-image.
3. Restoration of hair lost due to aging or genetics.
4. Correction of hair loss caused by trauma or medical conditions.
Hair transplant surgery offers a permanent solution to hair loss, as the transplanted hair follicles are resistant to the effects of Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the hormone responsible for male pattern baldness.
Types of Hair Transplant Techniques
There are two primary techniques used in hair transplant surgery: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
1. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): Also known as the strip method, FUT involves harvesting a strip of skin from the donor area, usually the back or sides of the scalp, under local anesthesia. The strip is then dissected into individual follicular units containing one to four hair follicles, which are subsequently transplanted into the recipient sites. FUT may leave a linear scar at the donor site, which can be concealed by surrounding hair.
2. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): FUE involves the extraction of individual follicular units directly from the donor area using a small, punch-like instrument. The harvested follicles are then implanted into the recipient sites, following a meticulous design to achieve a natural-looking hairline. FUE does not leave a linear scar and typically results in minimal scarring, making it a preferred option for individuals who prefer shorter hairstyles or have a history of extensive scarring.
Both FUT and FUE techniques require precision and expertise to ensure optimal results, and the choice between the two depends on various factors, including the patient’s hair type, scalp laxity, and personal preferences.
The Procedure
Hair transplant surgery typically involves the following steps:
1. Consultation: The process begins with a thorough consultation with a qualified hair transplant surgeon, during which the patient’s medical history, hair loss pattern, expectations, and goals are discussed. The surgeon evaluates the patient’s scalp and determines the most suitable technique and treatment plan.
2. Preparation: On the day of the surgery, the patient’s scalp is thoroughly cleaned, and the donor and recipient areas are marked for precise placement of the hair follicles.
3. Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to both the donor and recipient areas to ensure the patient’s comfort throughout the procedure.
4. Donor Harvesting: In FUT, a strip of skin is surgically removed from the donor area, while in FUE, individual follicular units are extracted using a specialized instrument. The donor site is then sutured or left to heal naturally, depending on the technique used.
5. Follicle Preparation: The harvested follicular units are carefully dissected under a microscope to separate them into individual grafts containing one to four hair follicles.
6. Recipient Site Creation: Tiny incisions are made in the recipient area, following the predetermined design and angle to mimic the natural hair growth pattern.
7. Graft Placement: The prepared follicular units are meticulously placed into the recipient sites, ensuring proper alignment and density for a natural-looking result.
8. Post-operative Care: Once the transplant is complete, the patient is provided with instructions for post-operative care, including how to clean the scalp, manage any discomfort, and avoid activities that may disrupt the healing process.
The duration of the procedure varies depending on the extent of hair loss and the number of grafts transplanted, ranging from a few hours to a full day.
Eligibility Criteria
While hair transplant surgery is a safe and effective treatment for most individuals experiencing hair loss, not everyone may be suitable candidates. Eligibility criteria for hair transplant surgery typically include:
1. Sufficient Donor Hair: Patients must have an adequate supply of healthy hair follicles in the donor area to achieve the desired coverage and density.
2. Stable Hair Loss: Candidates should have stabilized hair loss, as progressive hair loss may require additional transplant sessions to maintain optimal results.
3. Good General Health: Individuals should be in good overall health and free from any medical conditions that may impair healing or increase the risk of complications.
4. Realistic Expectations: Candidates should have realistic expectations about the outcome of the procedure, understanding that while hair transplant surgery can significantly improve the appearance of thinning or balding areas, it may not restore a full head of hair or prevent future hair loss.
Preparation and Aftercare
Preparing for hair transplant surgery involves several steps to ensure optimal results and minimize the risk of complications:
1. Consultation: A thorough consultation with the hair transplant surgeon to discuss the treatment plan, expectations, and any concerns.
2. Medical Evaluation: Evaluation of the patient’s medical history and current health status to determine eligibility for the procedure.
3. Medication Adjustment: Patients may be advised to temporarily discontinue certain medications, such as blood thinners or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), that can increase the risk of bleeding or interfere with healing.
4. Scalp Care: Keeping the scalp clean and avoiding any harsh treatments or styling products in the days leading up to the surgery.
After the surgery, patients are provided with detailed instructions for post-operative care, including:
1. Medication: Prescription medications to manage pain, swelling, and minimize the risk of infection.
2. Scalp Care: Gentle washing of the scalp with a mild shampoo to keep the area clean and prevent infection.
3. Avoiding Sun Exposure: Protecting the scalp from direct sunlight and wearing a hat or sunscreen when outdoors to prevent sunburn and minimize scarring.
4. Follow-up Appointments: Scheduled follow-up appointments with the surgeon to monitor healing progress and address any concerns.
Following these guidelines is essential for ensuring optimal healing and achieving the desired results.
Risks and Benefits
As with any surgical procedure, hair transplant surgery carries certain risks and potential complications, including:
1. Bleeding: Some bleeding at the donor or recipient sites is normal during and after the surgery but is usually minimal and resolves on its own.
2. Infection: While rare, there is a risk of infection at the donor or recipient sites, which can usually be treated with antibiotics.
3. Scarring: FUT may leave a linear scar at the donor site, while FUE may result in small, dot-like scars that are typically less noticeable. However, proper technique and post-operative care can minimize scarring.
4. Shock Loss: Temporary shedding of transplanted hair follicles, known as shock loss, may occur within the first few weeks following the surgery but is usually temporary, and new hair growth will gradually emerge.
5. Unnatural Results: Poorly executed hair transplant procedures can result in an unnatural appearance, such as an unnatural hairline or patchy growth. Choosing a skilled and experienced surgeon is essential for achieving natural-looking results.
Despite these potential risks, hair transplant surgery offers numerous benefits, including:
1. Permanent Results: Transplanted hair follicles are permanent and resistant to DHT, providing long-lasting results.
2. Natural Appearance: When performed by a skilled surgeon, hair transplant surgery can achieve a natural-looking hairline and seamless integration with existing hair.
3. Improved Self-confidence: Restoring a fuller, thicker hairline can significantly improve self-esteem and quality of life for individuals experiencing hair loss.
4. Minimal Downtime: While recovery times vary, most patients can resume normal activities within a few days to a week after the surgery, with minimal disruption to daily life.
Success Rates and Expectations
The success of hair transplant surgery depends on various factors, including the patient’s hair type, scalp characteristics, surgeon’s skill, and adherence to post-operative care instructions. While individual results may vary, hair transplant surgery generally has high success rates, with the vast majority of patients achieving significant improvement in hair density and appearance.
According to the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery (ISHRS), the average success rate for hair transplant surgery is over 90%, with many patients reporting a high level of satisfaction with the results. However, it’s important for patients to have realistic expectations about the outcome of the procedure, understanding that full results may take several months to a year to become apparent as the transplanted hair follicles grow and mature.
During the initial consultation, the surgeon will assess the patient’s hair loss pattern, donor hair supply, and expectations to provide a realistic prognosis and discuss what can be achieved through hair transplant surgery.
Recovery Process
The recovery process following hair transplant surgery typically follows a timeline as follows:
1. Immediate Post-operative Period (Days 1-7): Mild swelling, discomfort, and redness at the donor and recipient sites are common during the first week following surgery. Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and excessive sun exposure during this time.
2. First Month: Most of the transplanted hair follicles will shed within the first few weeks following surgery, a normal part of the healing process known as shock loss. New hair growth will gradually emerge over the coming months.
3. First Three Months: Initial signs of new hair growth may become visible within three to four months after the surgery, although the hair may appear thin and sparse at first.
4. Six Months: Significant improvement in hair density and coverage can be expected by the six-month mark, with continued growth and thickening over the following months.
5. One Year: Full results of the hair transplant surgery are typically visible by the one-year mark, with the transplanted hair follicles fully matured and integrated with existing hair.
Throughout the recovery process, patients are encouraged to follow the surgeon’s instructions for post-operative care and attend scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor progress and address any concerns.
Cost and Financing Options
The cost of hair transplant surgery varies depending on various factors, including the extent of hair loss, the number of grafts needed, the surgeon’s experience, and the geographic location of the clinic. On average, hair transplant surgery can range from $4,000 to $15,000 per session.
While hair transplant surgery is considered an elective cosmetic procedure and may not be covered by insurance, many clinics offer financing options to help make the procedure more affordable for patients. Financing options may include payment plans, credit card payments, or third-party financing through medical loan companies.
Before undergoing hair transplant surgery, patients are encouraged to consult with the surgeon and inquire about the cost of the procedure, as well as any available financing or payment options to ensure that it fits within their budget.
In conclusion, hair transplant surgery is a safe and effective treatment option for individuals experiencing hair loss, offering permanent results and a natural-looking appearance. By understanding the different techniques, eligibility criteria, preparation, aftercare, risks, benefits, success rates, recovery process, and cost considerations associated with hair transplant surgery, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment options and take the necessary steps to restore their hairline and regain their confidence.
FAQs
How long do hair transplants last?
Hair transplants are typically considered a permanent solution for hair loss. The transplanted hair is taken from areas of the scalp that are not prone to balding, such as the back or sides, and is genetically resistant to the hormone that causes hair loss. Once transplanted, the hair should continue to grow naturally for the rest of your life.
Is it painful to get a hair transplant?
During a hair transplant procedure, local anesthesia is used to numb the scalp, so you shouldn’t feel any pain during the surgery. However, some patients may experience mild discomfort or soreness in the days following the procedure, which can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain medication.
Do you still bald after a hair transplant?
Hair transplants can provide a long-term solution for baldness, but they don’t necessarily prevent further hair loss. While the transplanted hair is permanent, existing hair follicles that were not transplanted may continue to thin over time due to genetic factors or other causes of hair loss.
How is hair removed in a hair transplant?
In a hair transplant procedure, hair follicles are typically harvested from a donor area on the scalp, usually the back or sides, using either follicular unit extraction (FUE) or follicular unit transplantation (FUT) techniques. FUE involves individually extracting hair follicles using a small punch tool, while FUT involves removing a strip of scalp tissue containing hair follicles and then dissecting it into individual grafts. The method used depends on various factors including the patient’s preferences and the surgeon’s expertise.