Genetic baldness, medically known as androgenetic alopecia, is a prevalent condition affecting millions of people worldwide, predominantly men but also women. It’s characterized by a progressive thinning of the hair follicles, leading to hair loss primarily in a predictable pattern. This type of baldness differs from other forms of hair loss, such as alopecia areata or telogen effluvium, as it has a strong genetic component and follows a distinct pattern of progression.
Explanation of Genetic Baldness
Genetic baldness is inherited from one’s parents and is primarily influenced by the presence of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone. DHT binds to receptors in the hair follicles, leading to miniaturization and eventual cessation of hair growth. The pattern of hair loss in men typically starts with a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, while women may experience diffuse thinning all over the scalp.
Hair Transplant Basics
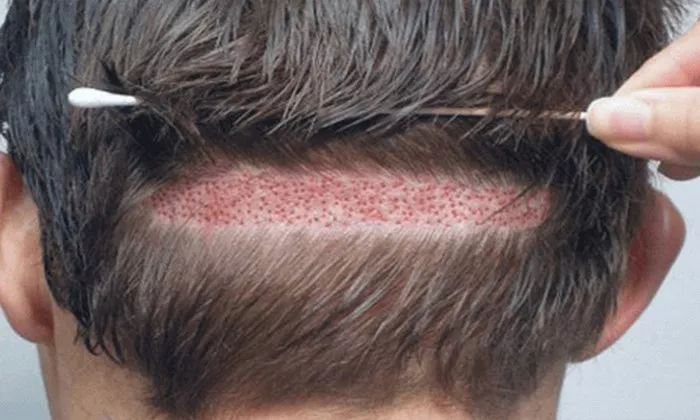
Hair transplant surgery is a widely recognized and effective treatment for genetic baldness. It involves the surgical relocation of hair follicles from the donor area, usually the back or sides of the scalp, to the balding or thinning areas. Two primary techniques are utilized in hair transplantation: Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT).
In FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area using a small punch tool and then implanted into the recipient site. FUE is minimally invasive and leaves tiny, almost imperceptible scars, making it a preferred choice for many patients.
FUT, on the other hand, involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, dissecting it into individual follicular units, and then implanting them into the recipient site. While FUT may leave a linear scar at the donor site, it can yield a higher number of grafts in a single session compared to FUE.
Effectiveness for Genetic Baldness
Numerous studies and clinical trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of hair transplants for genetic baldness. According to data published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, hair transplant procedures have shown success rates ranging from 80% to 90% in terms of graft survival and patient satisfaction.
One notable study conducted by Bernstein Medical Center for Hair Restoration and the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine followed patients who underwent hair transplant surgery over a five-year period. The results showed that 95% of participants experienced significant improvement in hair density and overall appearance.
Donor Hair Requirements
The success of a hair transplant largely depends on the availability of an adequate supply of donor hair. The donor area must have healthy, robust hair follicles that are resistant to the effects of DHT. In some cases, individuals with advanced hair loss may not have enough donor hair to achieve satisfactory results with a single transplant session. In such instances, multiple sessions or alternative donor sources, such as body hair, may be considered.
Limitations and Expectations
While hair transplants can effectively restore hair in balding or thinning areas, it’s essential for patients to have realistic expectations. A successful hair transplant can significantly improve the appearance and self-confidence of individuals with genetic baldness, but it may not always achieve a full head of hair. Factors such as the extent of hair loss, the quality of the donor hair, and individual healing responses can impact the final outcome.
It’s also important to note that hair transplant results are not immediate and may take several months to fully manifest. Some patients may require touch-up procedures or additional sessions to achieve their desired aesthetic goals.
Alternative Treatments
In addition to hair transplant surgery, several alternative treatments are available for genetic baldness. Medications such as minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia) can help slow down or halt the progression of hair loss by blocking the effects of DHT and promoting hair regrowth. These medications are often used in conjunction with hair transplant surgery to optimize results.
Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress levels, and avoiding harsh hair styling practices, can also support overall hair health and minimize further hair loss.
Long-Term Maintenance
Hair transplant surgery offers a permanent solution to genetic baldness, but it’s essential for patients to commit to long-term maintenance and care. Following the post-operative instructions provided by the surgeon, including proper wound care and avoiding activities that could disrupt the grafts, is crucial for optimal healing and graft survival.
Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are necessary to monitor progress and address any concerns that may arise. In some cases, patients may opt for additional procedures, such as touch-up sessions or hairline refinements, to further enhance their results over time.
In conclusion, hair transplant surgery is a highly effective treatment for genetic baldness, offering lasting results and significant improvements in hair density and appearance. With advancements in surgical techniques and ongoing research, hair transplantation continues to evolve as a safe and reliable solution for individuals seeking to restore their natural hairline and regain confidence in their appearance.
FAQs
Does hair transplant work if completely bald?
Hair transplant procedures can be effective for individuals who are completely bald, depending on various factors such as the availability of donor hair from other areas of the body and the expertise of the surgeon. However, extensive baldness may require multiple sessions and a comprehensive consultation with a qualified specialist to determine the feasibility and potential outcomes of the procedure.
Can you get a hair transplant if you have male pattern baldness?
Yes, hair transplant surgery is a viable option for individuals experiencing male pattern baldness. During the procedure, healthy hair follicles from donor areas (typically the back or sides of the head) are transplanted to the balding or thinning areas. However, the success of the transplant may vary depending on factors such as the extent of baldness, the quality of donor hair, and individual health considerations.
Will I go bald if my dad is?
While genetics play a significant role in hair loss, inheriting the genetic predisposition for baldness from your father does not guarantee that you will go bald. Genetic hair loss, or androgenetic alopecia, can be influenced by a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. However, not everyone with a family history of baldness will experience significant hair loss. It’s essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.
How to stop genetic balding?
While it’s not always possible to completely stop genetic balding, several strategies can help slow down its progression and promote healthy hair growth. These may include lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress levels, avoiding harsh hair treatments, and using FDA-approved medications like minoxidil and finasteride. Additionally, advanced treatments such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy and low-level laser therapy (LLLT) may also be beneficial in managing genetic balding. Consulting with a dermatologist or hair restoration specialist can provide personalized recommendations based on individual needs and preferences.