Hair loss can be a distressing experience for anyone, regardless of gender. While it’s commonly associated with men, women also face the challenge of thinning hair and balding patches. In recent years, hair transplant procedures have gained popularity as a solution for both men and women seeking to restore their hairline and regain confidence. However, the effectiveness of hair transplants for women, as well as the suitability criteria, procedure details, risks, costs, and alternative treatments, are essential aspects to consider before undergoing such a procedure.
Effectiveness of Hair Transplants for Women
Hair transplant procedures involve transplanting hair follicles from one part of the body, typically the back or sides of the scalp (donor area), to areas where hair loss has occurred (recipient area). While hair transplants are more commonly associated with men, they can also be effective for women experiencing pattern baldness, alopecia, or other forms of hair loss.
Success rates and long-term results of hair transplants in women vary depending on several factors, including the skill of the surgeon, the quality of donor hair, and the patient’s individual response to the procedure. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, hair transplant procedures have shown promising results in women, with many experiencing significant improvements in hair density and coverage.
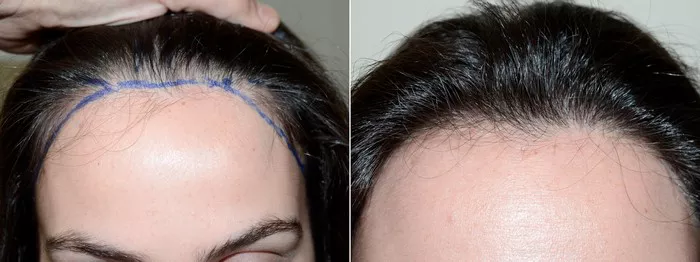
Statistical data on the effectiveness of hair transplants for women can be challenging to generalize due to the diversity of patients and the variability in outcomes. However, before-and-after photos can provide visual evidence of the potential results of the procedure. These photos often showcase noticeable improvements in hair density and natural-looking hairlines, contributing to increased confidence and satisfaction among patients.
Suitability Criteria
Not all women experiencing hair loss are suitable candidates for hair transplant procedures. Several factors determine eligibility, including the presence of healthy donor hair, the pattern of hair loss, and overall health considerations.
A woman with sufficient healthy donor hair, typically located at the back or sides of the scalp, is more likely to be a suitable candidate for a hair transplant. The pattern of hair loss also plays a crucial role, as women experiencing diffuse thinning or pattern baldness may benefit more from the procedure than those with extensive hair loss or scarring alopecia.
Additionally, candidates for hair transplants should be in good overall health and have realistic expectations about the outcomes of the procedure. Consulting with a qualified dermatologist or hair restoration specialist can help determine whether a woman is a suitable candidate for a hair transplant based on her individual circumstances.
Procedure Details
Hair transplant procedures for women typically involve two primary techniques: Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Microscopic Dissection of Extracted Epidermal Tissue (MDEE).
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): FUE involves harvesting individual hair follicles from the donor area using a small, circular punch tool. These follicles are then transplanted into the recipient area, where they establish new hair growth. FUE is known for its minimal scarring and shorter recovery time compared to traditional transplant methods.
Microscopic Dissection of Extracted Epidermal Tissue (MDEE): MDEE is a more intricate technique that involves dissecting tiny sections of skin containing hair follicles from the donor area under a microscope. These micrografts are then transplanted into the recipient area, allowing for precise placement and natural-looking results.
Regardless of the technique used, the hair transplant procedure typically takes several hours to complete and is performed under local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. Patients may experience some swelling, bruising, and minor discomfort in the days following the procedure, but these symptoms usually subside within a week.
Side Effects and Risks
Like any surgical procedure, hair transplants carry potential side effects and risks that patients should be aware of before undergoing treatment. Common side effects include:
1. Swelling and bruising: Some degree of swelling and bruising in the scalp area is normal after a hair transplant and typically resolves within a few days.
2. Pain and discomfort: Patients may experience mild pain or discomfort during the recovery period, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain medication.
3. Infection: While rare, there is a risk of infection at the donor or recipient sites following a hair transplant. Patients should follow post-procedure care instructions carefully to minimize this risk.
4. Scarring: Although newer techniques like FUE minimize scarring, some degree of scarring may still occur at the donor site. However, these scars are typically small and easily concealable with hair growth.
5. Unnatural-looking results: In some cases, hair transplants may result in an unnatural appearance if not performed by a skilled surgeon or if the patient’s expectations are unrealistic.
To mitigate these risks, patients should choose a board-certified dermatologist or hair restoration specialist with experience in performing hair transplant procedures. Additionally, following post-procedure care instructions, including keeping the scalp clean and avoiding strenuous activity, can help promote optimal healing and reduce the risk of complications.
Costs and Financing
The cost of a hair transplant for women can vary widely depending on factors such as the extent of hair loss, the technique used, the surgeon’s experience, and geographic location. On average, hair transplant procedures can range from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.
Since hair transplants are considered cosmetic procedures, they are typically not covered by health insurance plans. However, some clinics offer financing options or payment plans to help make the procedure more affordable for patients. It’s essential for individuals considering a hair transplant to inquire about pricing and financing options during their initial consultation with a hair restoration specialist.
Alternative Treatments
While hair transplants are an effective solution for many women experiencing hair loss, they may not be suitable or desired for everyone. Fortunately, several alternative treatments and approaches can help manage hair loss and promote hair growth:
1. Topical applications: Products containing minoxidil or other hair growth stimulants can be applied topically to the scalp to promote hair growth and prevent further thinning.
2. Medications: Oral medications such as finasteride may be prescribed to help slow or stop hair loss in women with androgenetic alopecia.
3. Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress levels, and avoiding harsh styling practices can help support overall hair health and reduce the risk of further hair loss.
4. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting a concentrated solution of the patient’s own platelets into the scalp to stimulate hair growth and improve hair density.
5. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT): LLLT devices emit low-level laser light to the scalp, which is believed to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth.
It’s essential for individuals considering alternative treatments for hair loss to consult with a dermatologist or hair restoration specialist to determine the most suitable approach based on their specific needs and goals.
In conclusion, hair transplant procedures can be an effective solution for women experiencing hair loss, providing natural-looking results and increased confidence. By understanding the effectiveness, suitability criteria, procedure details, risks, costs, and alternative treatments associated with hair transplants, women can make informed decisions about their hair restoration journey. Consulting with a qualified dermatologist or hair restoration specialist is key to achieving optimal outcomes and restoring a fuller, thicker head of hair.
FAQs
1. How long does a female hair transplant last?
A female hair transplant typically lasts a lifetime. The transplanted hair is usually resistant to the effects of DHT (dihydrotestosterone), the hormone responsible for hair loss, making it a permanent solution. However, it’s essential to note that the longevity of the results can vary depending on individual factors such as the quality of the donor hair, the technique used, and post-operative care.
2. Do hair transplants look natural for women?
Yes, modern hair transplant techniques, such as follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE), can provide natural-looking results for women. Skilled surgeons carefully place individual follicular units in a way that mimics the natural hair growth pattern, ensuring a seamless integration with existing hair. Additionally, advancements in technology and surgical techniques have improved the aesthetic outcomes of female hair transplants, leading to more natural-looking results.
3. Do women have to go bald for a hair transplant?
No, women do not have to go completely bald to undergo a hair transplant. Hair transplantation can effectively treat various degrees of hair loss, from minor thinning to more extensive balding. In fact, early intervention when hair loss is minimal can yield better results, as it allows for the preservation of existing hair and a more natural-looking outcome.
4. What happens 10 years after a hair transplant?
Ten years after a hair transplant, the majority of patients continue to enjoy the benefits of their procedure. The transplanted hair typically retains its characteristics and resists further hair loss caused by genetic factors. However, some patients may experience gradual thinning or hair loss in areas not treated during the initial transplant. Maintenance treatments or touch-up procedures may be recommended to address these changes and maintain optimal results over time. Regular follow-ups with a qualified hair restoration specialist can help monitor the progression of hair loss and adjust treatment plans as needed.