Hair loss is a common concern for many individuals, affecting both men and women of all ages. While some types of hair loss are localized or occur in specific patterns, diffuse hair loss presents a unique challenge due to its widespread nature. In this article, we will delve into what diffuse hair loss is, explore its causes, examine its signs and symptoms, discuss whether it is permanent or temporary, and outline preventive measures to mitigate its effects.
What is Diffuse Hair Loss?
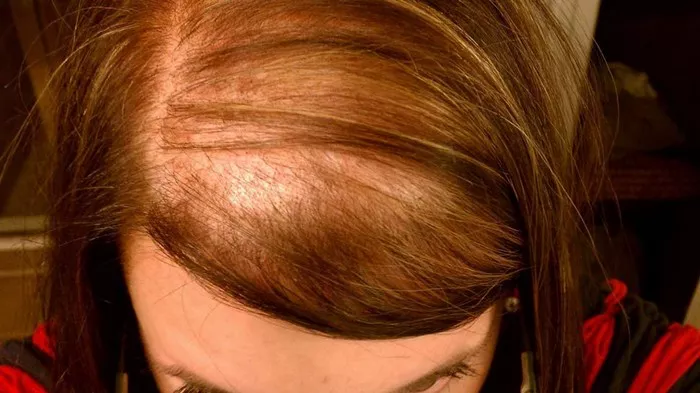
Diffuse hair loss, also known as diffuse alopecia or telogen effluvium, is a type of hair loss characterized by a uniform thinning of hair across the scalp. Unlike patterned hair loss, where bald patches or receding hairlines are evident, diffuse hair loss leads to a reduction in hair density throughout the scalp. This condition can be distressing for individuals as it can significantly impact their appearance and self-esteem.
What Causes Diffuse Hair Loss?
Several factors can contribute to diffuse hair loss, ranging from physiological to environmental influences. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial in determining appropriate treatment strategies. Some common causes of diffuse hair loss include:
1. Stress: Emotional or physical stressors such as illness, surgery, childbirth, or significant life events can trigger a condition known as telogen effluvium. This occurs when a large number of hair follicles prematurely enter the resting phase (telogen), leading to increased shedding and noticeable thinning of the hair.
2. Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as those experienced during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders, can disrupt the hair growth cycle and contribute to diffuse hair loss. Hormonal imbalances can affect the production of hair follicles and lead to increased shedding.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of essential nutrients, particularly vitamins and minerals crucial for hair growth, can impair the health of hair follicles and result in diffuse hair loss. Common deficiencies include iron, vitamin D, vitamin B12, and zinc.
4. Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune diseases (e.g., alopecia areata), scalp infections, and chronic illnesses (e.g., lupus, diabetes), can contribute to diffuse hair loss by disrupting normal hair growth cycles or causing inflammation of the scalp.
5. Medications and Treatments: Some medications, including chemotherapy drugs, antidepressants, and blood thinners, can have side effects that include hair loss. Radiation therapy, used to treat cancer, can also lead to hair thinning or baldness in the affected area.
6. Genetic Predisposition: While diffuse hair loss is often triggered by external factors, genetic predisposition can play a role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to this condition. Those with a family history of hair loss may be more likely to experience diffuse thinning.
7. Hair Care Practices: Excessive styling, frequent use of heated styling tools, harsh chemical treatments (e.g., bleaching, perming), and tight hairstyles (e.g., ponytails, braids) can damage the hair shaft and contribute to breakage and thinning over time.
Signs and Symptoms of Diffuse Hair Loss
Identifying the signs and symptoms of diffuse hair loss is essential for early detection and intervention. Some common indicators include:
- Noticeable thinning of hair across the entire scalp
- Increased shedding during brushing, showering, or styling
- Widening of the part line or visible scalp through the hair
- Reduced hair density and volume
- Changes in hair texture or quality (e.g., dryness, brittleness)
Individuals experiencing these symptoms should consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Is Diffuse Thinning Permanent or Temporary Hair Loss?
One of the most pressing concerns for individuals with diffuse hair loss is whether the condition is permanent or temporary. The answer largely depends on the underlying cause. In cases where diffuse hair loss is triggered by temporary factors such as stress, hormonal changes, or nutritional deficiencies, hair growth typically resumes once the underlying issue is addressed.
However, in some instances, diffuse hair loss may be chronic or progressive, particularly if it is related to genetic predisposition or underlying medical conditions. In such cases, managing the condition and preventing further hair loss may be the primary goal.
What Can be Done to Prevent Diffuse Hair Loss?
While it may not always be possible to prevent diffuse hair loss entirely, there are steps individuals can take to minimize its occurrence and promote healthy hair growth:
1. Maintain a Balanced Diet: Consuming a nutrient-rich diet that includes protein, iron, vitamins (particularly B-complex vitamins), and minerals (such as zinc and selenium) is essential for supporting healthy hair growth. Consider incorporating foods such as lean proteins, leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains into your meals.
2. Manage Stress: Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or seeking support from a therapist can help manage stress levels and minimize its impact on hair health.
3. Avoid Harsh Hair Care Practices: Limit the use of heated styling tools, harsh chemical treatments, and tight hairstyles that can damage the hair shaft and contribute to breakage. Opt for gentle hair care products and techniques that promote scalp health and minimize trauma to the hair follicles.
4. Address Underlying Health Conditions: If diffuse hair loss is linked to an underlying medical condition or hormonal imbalance, seeking appropriate medical treatment and management can help address the root cause and prevent further hair loss.
5. Be Gentle with Your Hair: Handle your hair with care, avoiding excessive brushing, pulling, or friction that can lead to breakage. Use a wide-tooth comb or a soft-bristled brush to detangle hair gently, and avoid vigorous towel drying or rubbing when wet.
6. Consult a Healthcare Professional: If you notice significant or persistent hair loss, consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan. They can help determine the underlying cause of your hair loss and recommend appropriate interventions.
In conclusion, diffuse hair loss is a common condition that can have a variety of underlying causes, ranging from stress and hormonal changes to medical conditions and genetic predisposition. By understanding the factors that contribute to diffuse hair loss and taking proactive steps to promote scalp health and hair growth, individuals can minimize its impact and maintain healthy, vibrant hair.
FAQs
Can hair grow back after diffuse thinning?
Yes, hair can grow back after diffuse thinning, but it largely depends on the underlying cause and how well it’s addressed. For some, adopting a healthier lifestyle, using specific hair treatments, or addressing medical conditions can stimulate regrowth. However, in cases where hair follicles have been permanently damaged, regrowth may be limited.
What is the best hair treatment for diffuse thinning?
The best hair treatment for diffuse thinning varies depending on individual factors such as the cause of thinning, overall health, and response to treatment. Options may include topical solutions like minoxidil, oral medications like finasteride, low-level laser therapy, PRP (platelet-rich plasma) therapy, and hair transplant surgery. Consulting with a dermatologist or trichologist can help determine the most suitable treatment plan.
Does diffuse thinning ever stop?
Diffuse thinning can sometimes stabilize or slow down with appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes. However, without intervention, it may continue to progress over time. Monitoring the condition and seeking professional advice can help manage diffuse thinning effectively.
What are the early stages of diffuse thinning?
In the early stages of diffuse thinning, you may notice an overall decrease in hair density, with scalp visibility increasing. Hair shedding may also increase, particularly during washing or brushing. Additionally, you may observe a widening part or a decrease in hair volume. If you suspect diffuse thinning, it’s advisable to seek evaluation from a healthcare professional or dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management plan.