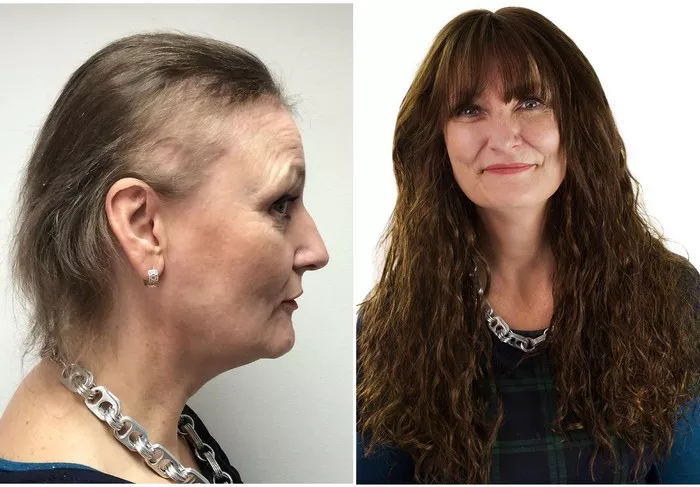
Hair loss is a prevalent concern among the elderly, often causing distress and impacting self-esteem. While it’s natural for hair to thin with age, excessive hair loss can be attributed to various factors. Understanding the causes and available treatments is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Common Causes of Hair Loss in Old Age
Several factors contribute to hair loss in old age, including:
1. Genetics: Hereditary factors play a significant role in determining hair loss patterns. Individuals with a family history of baldness are more likely to experience hair loss themselves.
2. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in menopause for women and declining testosterone levels for men, can lead to hair thinning and loss.
3. Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and scalp infections, can contribute to hair loss in old age.
4. Natural Aging Process: As individuals age, the rate of hair growth slows down, and hair follicles may shrink, resulting in thinner and less dense hair.
Gender-Specific Information
While some causes of hair loss are common to both genders, there are also gender-specific factors to consider:
1. Male Hair Loss:
Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair loss in men. It typically follows a predictable pattern, starting with a receding hairline and thinning at the crown. Genetics and the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) are primary contributors to male pattern baldness.
2. Female Hair Loss:
Women may experience hair thinning all over the scalp rather than specific patterns. Hormonal changes during menopause can significantly impact hair health, leading to gradual thinning. Additionally, conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can contribute to hair loss in women.
Treatment Options
Several treatment options are available to address hair loss in old age:
1. Over-the-Counter Remedies: Minoxidil, commonly known as Rogaine, is an over-the-counter topical solution approved by the FDA for both men and women. It can help stimulate hair growth and prevent further hair loss.
2. Prescription Medications: Finasteride, marketed as Propecia, is an oral medication approved for men with male pattern baldness. It works by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone into DHT, thereby reducing hair loss and promoting hair regrowth.
3. Hair Transplant Surgery: Hair transplant surgery involves transplanting hair follicles from areas of the scalp with healthy hair growth to balding or thinning areas. This surgical procedure can provide long-lasting results and restore a fuller head of hair.
4. Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can positively impact hair health. Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, managing stress levels, and avoiding harsh hair treatments can help maintain hair thickness and prevent further loss.
Preventive Measures
While it may not be possible to completely prevent hair loss in old age, certain measures can help slow down the process:
1. Nutritious Diet: Consuming a diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins can support healthy hair growth. Foods such as eggs, fish, nuts, and leafy greens contain essential nutrients for hair health.
2. Supplements: Biotin supplements are often recommended for promoting hair growth and maintaining hair strength. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
3. Gentle Hair Care Practices: Avoiding harsh hair treatments, such as frequent dyeing and styling with hot tools, can prevent damage to hair follicles and minimize hair loss.
4. Scalp Massage: Massaging the scalp regularly can improve blood circulation to the hair follicles, promoting hair growth and thickness.
When to See a Doctor
While mild hair loss is often a natural part of aging, certain signs may indicate underlying medical conditions or require professional intervention:
1. Sudden or Severe Hair Loss: If you notice a sudden increase in hair shedding or significant thinning, it’s essential to consult a dermatologist or healthcare provider to rule out underlying medical conditions.
2. Scalp Irritation or Inflammation: Persistent scalp itchiness, redness, or inflammation may indicate scalp conditions that require medical treatment.
3. Hair Loss in Patches: Hair loss occurring in discrete patches on the scalp may be a sign of alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition that causes hair loss.
4. Excessive Shedding After Pregnancy: Postpartum hair loss is common, but if hair shedding continues for an extended period or is severe, it’s advisable to seek medical advice.
In conclusion, hair loss in old age is a common concern with various underlying causes, including genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, and the natural aging process. Understanding these factors and exploring available treatment options can help individuals effectively manage hair loss and maintain healthy hair as they age. If experiencing significant or concerning hair loss, it’s essential to seek guidance from a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
FAQs
What foods prevent hair loss?
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can help promote healthy hair growth and prevent hair loss. Foods high in protein, such as lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes, are crucial for maintaining strong hair follicles. Incorporating fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins A, C, and E, as well as zinc and iron, can also support hair health. Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids found in foods like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds can help nourish the scalp and prevent dryness, which may contribute to hair loss.
Is it normal to lose hair in old age?
Yes, it is normal to experience some degree of hair loss as you age. Age-related hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is influenced by genetics, hormonal changes, and environmental factors. As people age, hair follicles shrink, leading to thinner and shorter hair strands. While it’s common for both men and women to experience some thinning of the hair with age, the rate and extent of hair loss can vary significantly among individuals.
What is the best vitamin for hair loss in an older woman?
For older women experiencing hair loss, biotin (vitamin B7) is often recommended as it plays a vital role in maintaining healthy hair, skin, and nails. Biotin helps strengthen the hair shaft and promote hair growth. Other vitamins and minerals beneficial for hair health in older women include vitamin D, iron, and zinc. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, as excessive intake of certain vitamins and minerals can have adverse effects.
What are the big 3 to prevent hair loss?
The “big 3” treatments for preventing hair loss typically include minoxidil, finasteride, and ketoconazole. Minoxidil, available as a topical solution or foam, is a vasodilator that increases blood flow to the scalp, promoting hair growth. Finasteride, taken orally, inhibits the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to hair loss. Ketoconazole, often used in medicated shampoos, has anti-inflammatory and anti-fungal properties that can help reduce scalp irritation and inflammation associated with hair loss. These treatments are commonly recommended for individuals experiencing male or female pattern baldness but should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.