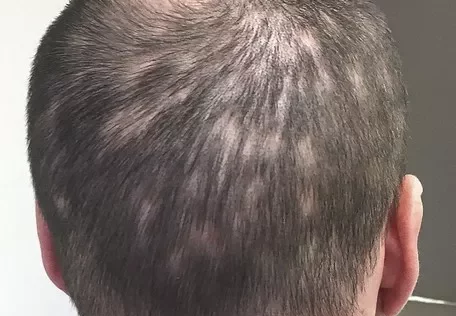
Scarring alopecia, also known as cicatricial alopecia, is a condition characterized by irreversible hair loss due to the destruction of hair follicles and subsequent replacement with scar tissue. This condition can significantly impact an individual’s physical appearance and emotional well-being. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of scarring alopecia is crucial for effective treatment and improved outcomes for affected individuals.
What is Scarring Alopecia?
Scarring alopecia is a type of hair loss characterized by the permanent destruction of hair follicles and their replacement with scar tissue. Unlike non-scarring alopecia, where the hair follicles remain intact and can potentially regrow hair, scarring alopecia leads to irreversible hair loss. The condition can affect people of all ages, genders, and ethnicities.
Scarring alopecia can manifest in various forms, including localized patches of hair loss or diffuse thinning across the scalp. In some cases, scarring alopecia may also affect other areas of the body with hair follicles, such as the eyebrows, eyelashes, beard, or pubic area.
What Causes Scarring Alopecia?
The exact cause of scarring alopecia is not fully understood, and it can result from a combination of genetic, immune, inflammatory, and environmental factors. Several potential triggers and underlying mechanisms have been proposed:
1. Autoimmune Disorders: In many cases, scarring alopecia is believed to be driven by autoimmune reactions, where the body’s immune system mistakenly targets hair follicles as foreign invaders, leading to their destruction. Conditions such as lichen planopilaris and discoid lupus erythematosus are examples of autoimmune-related scarring alopecia.
2. Inflammatory Conditions: Chronic inflammation within the scalp can damage hair follicles and lead to scarring alopecia. Inflammatory skin conditions like folliculitis decalvans and dissecting cellulitis of the scalp are associated with scarring alopecia.
3. Infectious Agents: Certain bacterial or fungal infections of the scalp can trigger inflammation and subsequent scarring alopecia if left untreated. Examples include bacterial folliculitis and fungal infections like tinea capitis.
4. Trauma or Injury: Physical trauma to the scalp, such as burns, injuries, or surgical procedures, can damage hair follicles and result in scarring alopecia. Chemical burns from harsh hair treatments or accidents involving hot objects can also lead to scarring.
5. Genetic Predisposition: There may be a genetic predisposition to developing certain types of scarring alopecia, although the specific genes involved are not yet fully identified. Family history of autoimmune disorders or other inflammatory conditions may increase the risk of developing scarring alopecia.
6. Environmental Factors: Exposure to environmental toxins, pollutants, or certain medications may contribute to the development or exacerbation of scarring alopecia in susceptible individuals.
It’s important to note that the underlying cause of scarring alopecia may vary from person to person, and in many cases, the exact trigger remains unknown.
What are the Symptoms of Scarring Alopecia?
The symptoms of scarring alopecia can vary depending on the underlying cause and the specific subtype of the condition. However, common signs and symptoms may include:
1. Progressive Hair Loss: Hair loss that occurs gradually over time and does not regrow. The loss of hair follicles leads to smooth, shiny patches of skin on the scalp or other affected areas.
2. Itching or Burning Sensation: Some individuals with scarring alopecia may experience itching, burning, or pain in the affected areas of the scalp.
3. Redness or Inflammation: Inflammatory changes such as redness, scaling, or swelling of the scalp may be present, particularly in cases associated with autoimmune or inflammatory conditions.
4. Thinning or Loss of Eyebrows, Eyelashes, or Body Hair: In addition to scalp involvement, scarring alopecia may also affect other areas with hair follicles, leading to thinning or loss of eyebrows, eyelashes, beard, or pubic hair.
5. Scalp Scarring: Upon closer examination, scarring or changes in the skin texture may be observed in the affected areas, indicating the presence of underlying scar tissue.
It’s essential to seek medical evaluation and diagnosis if experiencing any of these symptoms to determine the underlying cause and appropriate management.
How is Scarring Alopecia Diagnosed?
Diagnosing scarring alopecia typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a dermatologist or hair specialist. The diagnosis may include the following steps:
1. Medical History: The healthcare provider will inquire about the onset and progression of symptoms, any relevant medical conditions, family history of hair loss or autoimmune disorders, medications or treatments used, and exposure to potential triggers.
2. Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the scalp and affected areas will be conducted to assess the pattern and extent of hair loss, presence of inflammation or scarring, and any other associated skin changes.
3. Scalp Biopsy: A scalp biopsy may be performed to obtain a small sample of skin tissue from the affected area for microscopic examination. This helps confirm the presence of inflammation, scar tissue, and other characteristic changes associated with scarring alopecia.
4. Blood Tests: Blood tests may be ordered to assess for underlying autoimmune disorders, hormonal imbalances, or other systemic conditions that may contribute to hair loss.
5. Additional Tests: In some cases, additional tests such as fungal cultures, skin scrapings, or imaging studies may be recommended to rule out infectious causes or evaluate for structural abnormalities of the scalp.
Based on the findings of the diagnostic evaluation, the healthcare provider can make a definitive diagnosis of scarring alopecia and develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
Are There Different Types of Scarring Alopecia?
Scarring alopecia encompasses a diverse group of conditions, each with its own characteristic features, underlying mechanisms, and clinical presentation. Some common types of scarring alopecia include:
1. Lichen Planopilaris (LPP): Lichen planopilaris is an inflammatory condition characterized by small, red, itchy papules that affect the hair follicles, leading to scarring and permanent hair loss.
2. Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE): Discoid lupus erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the skin, including the scalp, leading to inflammation, scarring, and hair loss in the affected areas.
3. Folliculitis Decalvans: Folliculitis decalvans is a type of folliculitis that causes inflammation and destruction of hair follicles, resulting in scarring alopecia, often accompanied by pustules or crusted lesions on the scalp.
4. Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia (CCCA): CCCA is a form of scarring alopecia that predominantly affects women of African descent, characterized by progressive hair loss and scarring centered around the vertex of the scalp.
5. Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA): Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a subtype of scarring alopecia characterized by the gradual recession of the frontal hairline, often accompanied by eyebrow and eyelash loss, predominantly affecting postmenopausal women.
These are just a few examples of the many subtypes of scarring alopecia, each with its own distinct clinical features and management considerations.
Management and Treatment
The management of scarring alopecia aims to halt disease progression, alleviate symptoms, and preserve existing hair follicles to the extent possible. Treatment strategies may vary depending on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual response to therapy. Some common approaches to managing scarring alopecia include:
1. Topical and Oral Medications: Corticosteroids, either in topical formulations or oral tablets, are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response in autoimmune-related scarring alopecia. Other medications such as hydroxychloroquine, retinoids, and immunosuppressants may also be used in certain cases.
2. Intralesional Injections: Intralesional corticosteroid injections directly into the affected areas of the scalp can help reduce inflammation and promote hair regrowth in localized patches of scarring alopecia.
3. Topical Immunotherapy: Topical immunotherapy with agents such as diphencyprone (DPCP) or squaric acid dibutylester (SADBE) may be considered for select patients with refractory scarring alopecia to modulate the immune response and induce hair regrowth.
4. Hair Transplantation: In cases where significant scarring and hair loss have occurred, hair transplantation techniques such as follicular unit transplantation (FUT) or follicular unit extraction (FUE) may be considered to surgically implant healthy hair follicles into the affected areas.
5. Supportive Measures: In addition to medical treatments, supportive measures such as gentle scalp care, avoiding harsh chemicals or styling practices that may further damage hair follicles, and protecting the scalp from excessive sun exposure can help minimize symptoms and promote scalp health.
It’s important for individuals with scarring alopecia to work closely with a dermatologist or hair specialist to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to their specific needs and goals. Regular follow-up visits and monitoring are essential to assess treatment response, adjust therapy as needed, and address any concerns or complications that may arise.
In conclusion, scarring alopecia is a complex and challenging condition characterized by irreversible hair loss due to the destruction of hair follicles and replacement with scar tissue. While the exact cause of scarring alopecia remains elusive in many cases, advancements in research and understanding of the underlying mechanisms have led to improved diagnostic and treatment modalities. With early detection, appropriate intervention, and comprehensive management strategies, individuals affected by scarring alopecia can achieve better outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
FAQs
What are the effects of scarring alopecia?
Scarring alopecia, also known as cicatricial alopecia, results in permanent hair loss due to inflammation that damages hair follicles. This leads to irreversible scarring and bald patches on the scalp. Depending on the severity and extent of scarring, it can cause significant emotional distress and impact one’s self-esteem.
What’s the difference between scarring and nonscarring alopecia?
Scarring alopecia involves the destruction of hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss and scarring of the scalp. In contrast, nonscarring alopecia refers to hair loss without irreversible damage to the hair follicles, allowing for potential regrowth. While nonscarring alopecia conditions like alopecia areata may cause temporary hair loss, scarring alopecia results in permanent baldness.
Is scarring alopecia contagious?
No, scarring alopecia is not contagious. It is a result of autoimmune disorders, genetic predisposition, or other underlying medical conditions, rather than being spread through contact or exposure to affected individuals.
Who might be affected by scarring alopecia?
Scarring alopecia can affect individuals of any age, gender, or ethnicity. However, it is more commonly observed in adults and tends to be more prevalent among women than men. Certain medical conditions, such as lupus, lichen planus, and certain types of folliculitis, increase the risk of developing scarring alopecia.
How common is scarring alopecia?
Scarring alopecia is considered relatively rare compared to nonscarring forms of alopecia. However, its prevalence may be underestimated due to misdiagnosis or underreporting. The exact prevalence varies depending on geographic location and population demographics. Research suggests that scarring alopecia accounts for a small percentage of all cases of hair loss disorders.