Hair loss is a common concern that affects both men and women. While male pattern baldness is widely recognized, female hair loss, particularly in the form of a receding hairline, is less discussed but equally distressing for those experiencing it. Understanding what causes a female receding hairline, its appearance, risk factors, available treatments, and steps to address concerns is crucial for those affected. In this article, we delve into these aspects to provide comprehensive insights into female hairline recession.
What is a Female Receding Hairline and What Does it Look Like?
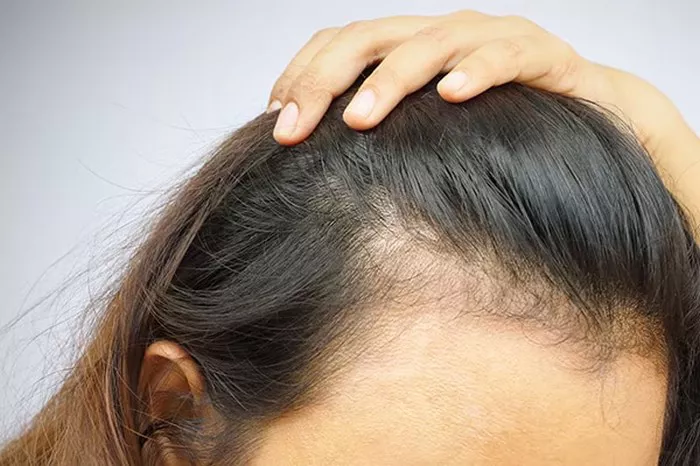
A receding hairline in women manifests as a gradual thinning of hair around the temples and forehead. Unlike male pattern baldness, which typically begins with a receding hairline at the temples, female hairline recession often starts with widening of the part and thinning at the crown. Over time, this can progress to a noticeable recession of the hairline, leading to a more pronounced forehead and less coverage of the scalp.
The appearance of a receding hairline can vary among individuals, with some experiencing minor thinning and others noticing significant recession. Additionally, the rate of hair loss and the extent of recession can be influenced by various factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, and lifestyle habits.
What Causes a Receding Hairline in Women?
Several factors contribute to female hairline recession, ranging from genetic predisposition to underlying health conditions. Understanding these causes is essential for developing effective treatment strategies. Some common causes include:
1. Genetics: Like many other forms of hair loss, female hairline recession can be hereditary. If you have a family history of thinning hair or receding hairline, you may be more susceptible to experiencing similar patterns of hair loss.
2. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or hormonal disorders like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can contribute to hair loss and hairline recession in women. Changes in estrogen and testosterone levels can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to shedding and thinning of hair.
3. Age: As women age, the hair growth cycle naturally slows down, leading to thinner, weaker hair strands. This age-related hair thinning can affect the density of hair around the temples and forehead, contributing to a receding hairline.
4. Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the body’s hormonal balance and contribute to hair loss. Stress-induced hair shedding, known as telogen effluvium, can affect the overall thickness and density of hair, including the hairline.
5. Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases (e.g., alopecia areata), and scalp conditions like seborrheic dermatitis, can cause hair loss and hairline recession in women.
6. Diet and Nutrition: Poor nutrition, deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals (e.g., iron, vitamin D, biotin), and crash dieting can impact hair health and contribute to hair loss.
7. Hairstyling Practices: Overuse of heat styling tools, tight hairstyles (e.g., ponytails, braids), and chemical treatments (e.g., perms, coloring) can damage the hair shaft and contribute to hair breakage and hairline recession over time.
Female Hairline Recession Risk Factors
While the causes of female hairline recession are multifactorial, certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of experiencing this condition. These risk factors include:
1. Family History: A family history of hair loss or receding hairline can increase your risk of developing similar patterns of hair loss.
2. Hormonal Imbalance: Fluctuations in hormone levels due to pregnancy, menopause, or hormonal disorders can predispose women to hair loss and hairline recession.
3. Age: Hair naturally thins with age, making older women more susceptible to hairline recession.
4. Medical Conditions: Underlying medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or autoimmune diseases, can contribute to hair loss and hairline recession.
5. Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the hair growth cycle and contribute to hair shedding and thinning, including around the hairline.
6. Nutritional Deficiencies: Poor diet and nutritional deficiencies can impact hair health and increase the risk of hair loss.
7. Hairstyling Habits: Overuse of heat styling tools, tight hairstyles, and harsh chemical treatments can damage the hair and lead to hair breakage and hairline recession.
Female Hairline Recession Treatment
Treatment options for female hairline recession vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some common treatment approaches include:
1. Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter minoxidil (Rogaine) can help stimulate hair growth and improve the appearance of a receding hairline in women. Prescription-strength minoxidil formulations may also be recommended by a healthcare provider.
2. Hormone Therapy: Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be prescribed to women experiencing hair loss due to hormonal imbalances, such as menopause or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
3. Nutritional Supplements: Supplements containing vitamins and minerals essential for hair health, such as biotin, iron, and vitamin D, may help support hair growth and prevent further hair loss.
4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting the patient’s own platelet-rich plasma into the scalp to stimulate hair growth and improve hair density.
5. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): LLLT devices, such as laser combs or helmets, emit low-level laser light to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth.
6. Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP): SMP is a non-surgical cosmetic procedure that involves tattooing the scalp to create the appearance of fuller hair.
7. Hair Transplant Surgery: In cases of advanced hairline recession, hair transplant surgery may be considered to restore hair growth and improve the appearance of the hairline.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider or a qualified hair loss specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs and preferences.
What to Do If You’re Worried About Your Receding Hairline
If you’re concerned about hairline recession or experiencing noticeable hair loss, consider taking the following steps:
1. Consult a Healthcare Provider: Schedule an appointment with a dermatologist or healthcare provider who specializes in hair loss to evaluate your condition and discuss potential treatment options.
2. Identify Underlying Causes: Work with your healthcare provider to identify any underlying medical conditions or lifestyle factors that may be contributing to your hair loss.
3. Explore Treatment Options: Discuss available treatment options, including topical treatments, hormone therapy, nutritional supplements, and cosmetic procedures, to determine the most suitable approach for your needs.
4. Practice Good Hair Care Habits: Adopt healthy hair care practices, such as using gentle shampoos, avoiding harsh chemical treatments, minimizing heat styling, and avoiding tight hairstyles that can pull on the hairline.
5. Seek Support: Don’t hesitate to seek support from friends, family, or a support group if you’re struggling with the emotional impact of hair loss. Talking to others who have experienced similar challenges can provide valuable support and reassurance.
In conclusion, female hairline recession is a common but often overlooked condition that can have significant emotional and psychological effects on affected individuals. By understanding the causes, risk factors, and treatment options for hairline recession in women, you can take proactive steps to address your concerns and restore confidence in your appearance. Remember to seek professional guidance and support to navigate your hair loss journey effectively.
FAQs
1. How to hide thinning hair in the front for women?
Thinning hair in the front can be distressing, but there are several strategies to conceal it effectively. One option is to try different hairstyles that add volume and camouflage thin areas. Consider opting for layered cuts or styles with side-swept bangs to create the illusion of fuller hair. Additionally, using volumizing products such as mousses or root-lifting sprays can help add thickness and texture to the hair. Another option is to experiment with hair accessories like headbands, scarves, or hairpieces to cover up thinning spots and draw attention away from them.
2. How to tell if a hairline is receding in females?
A receding hairline in women can manifest as the gradual thinning of hair along the forehead’s edges. Look for signs such as a widening part or sparse hair growth around the temples and frontal region. Additionally, pay attention to any changes in the shape of your hairline over time. If you notice your hairline moving further back or a more prominent “M” shape forming, it could indicate a receding hairline.
3. What does a normal female hairline look like?
A normal female hairline typically follows a gentle, rounded shape along the forehead without significant recession. It sits slightly above the brow bone and maintains a consistent density of hair across the frontal region. Unlike male hairlines, which commonly have a more pronounced “M” shape, female hairlines tend to be softer and less angular in appearance.
4. How can a woman get rid of a receding hairline?
Addressing a receding hairline in women often involves a multifaceted approach. Firstly, consult a healthcare professional to identify any underlying causes contributing to hair loss, such as hormonal imbalances or nutritional deficiencies. Depending on the diagnosis, treatment options may include topical minoxidil solutions, oral medications like finasteride, or procedures like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy or hair transplant surgery. Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques can promote overall hair health and potentially slow down or reverse the progression of a receding hairline.