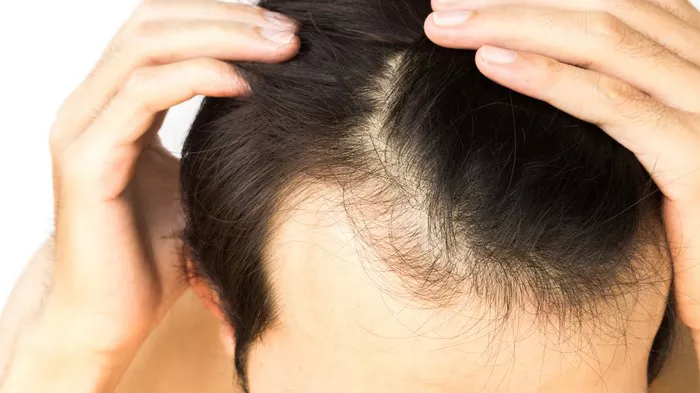
Hair shedding is a natural and inevitable part of the hair growth cycle. However, many people are often concerned about the amount of hair they lose on a daily basis and wonder if their shedding is within the normal range. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the factors that influence hair shedding, what constitutes normal shedding, when to be concerned, and tips for maintaining healthy hair.
The Hair Growth Cycle: An Overview
Before delving into the intricacies of hair shedding, it’s essential to understand the hair growth cycle. The hair growth cycle consists of three main phases:
1. Anagen Phase: This is the active growth phase of the hair follicle. During this phase, cells in the hair bulb divide rapidly, leading to the formation of new hair. The duration of the anagen phase varies depending on genetics, age, and other factors but typically lasts between two to seven years.
2. Catagen Phase: Following the anagen phase, the hair follicle enters the catagen phase, also known as the transitional phase. During this short phase lasting approximately two to three weeks, the hair follicle shrinks, and the hair detaches from the blood supply.
3. Telogen Phase: The telogen phase is the resting phase of the hair growth cycle. During this phase, the old hair remains in the follicle while new hair begins to grow underneath it. This phase lasts around three to four months.
After the telogen phase, the hair follicle re-enters the anagen phase, and the cycle repeats itself.
Factors Influencing Hair Shedding
Several factors can influence the rate of hair shedding, including:
1. Genetics: The tendency for hair shedding can be inherited. If you have family members who experience excessive shedding, you may be more prone to it as well.
2. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can affect the hair growth cycle and lead to increased shedding.
3. Stress: Physical or emotional stress can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to excessive shedding. This type of shedding, known as telogen effluvium, is often temporary and resolves once the stressor is removed.
4. Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of essential nutrients, such as iron, protein, and vitamins, can impair hair growth and increase shedding.
5. Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and scalp infections, can contribute to hair shedding.
6. Hair Care Practices: Overly aggressive hair care practices, such as excessive brushing, tight hairstyles, and frequent use of heat styling tools, can damage the hair shaft and lead to increased shedding.
What Is Considered Normal Hair Shedding?
It’s important to differentiate between normal hair shedding and excessive shedding. On average, it is normal to lose between 50 to 100 hairs per day. However, this number can vary depending on individual factors such as hair density, length, and growth cycle.
To determine if your shedding is within the normal range, you can perform a simple hair shedding test. Gently grasp a small section of hair between your fingers and run your fingers through it from the base to the ends. If you have less than 10% of the hairs in that section come out, your shedding is likely within the normal range.
When to Be Concerned
While some degree of hair shedding is normal, certain signs may indicate excessive shedding or underlying issues:
1. Noticeable Thinning: If you notice a significant decrease in hair density or widening of your part line, it may be a sign of excessive shedding or hair loss.
2. Increased Shedding Over Time: If you consistently notice more hair loss than usual over a prolonged period, it may indicate a problem.
3. Scalp Conditions: Scalp conditions such as itching, redness, or flakiness accompanied by increased shedding may warrant further evaluation.
4. Sudden Hair Loss: Rapid and significant hair loss, especially if accompanied by other symptoms such as fatigue or weight changes, may indicate an underlying medical condition and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
If you experience any of these signs, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Hair
While some factors influencing hair shedding, such as genetics and hormonal changes, are beyond your control, there are steps you can take to promote healthy hair and minimize shedding:
1. Follow a Balanced Diet: Ensure your diet includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, to support healthy hair growth.
2. Practice Gentle Hair Care: Avoid overly aggressive hair care practices such as excessive brushing, tight hairstyles, and harsh chemical treatments that can damage the hair shaft and lead to increased shedding.
3. Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to help minimize the impact of stress on hair shedding.
4. Use Hair Care Products Wisely: Choose hair care products that are gentle and suitable for your hair type. Avoid products containing harsh chemicals that can strip the hair of its natural oils and lead to increased shedding.
5. Protect Your Hair: Minimize heat styling and use heat protectant products when necessary. Additionally, protect your hair from environmental damage by wearing a hat or scarf outdoors.
6. Seek Professional Advice: If you’re experiencing excessive shedding or hair loss, consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist for proper evaluation and treatment options.
Conclusion
Hair shedding is a natural part of the hair growth cycle, and on average, it is normal to lose between 50 to 100 hairs per day. However, several factors can influence the rate of shedding, and excessive shedding may be a sign of underlying issues such as hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, or medical conditions. By understanding the factors that influence hair shedding and adopting healthy hair care practices, you can promote optimal hair health and minimize shedding. If you’re concerned about your shedding or hair loss, don’t hesitate to seek professional advice for proper evaluation and treatment.
FAQs
What factors can influence hair shedding?
Several factors can influence the rate of hair shedding, including genetics, hormonal changes, stress, nutritional deficiencies, medical conditions, and hair care practices.
What can I do to minimize hair shedding and promote healthy hair growth?
To promote healthy hair growth and minimize shedding, follow a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, practice gentle hair care, manage stress, use hair care products wisely, protect your hair from environmental damage, and seek professional advice if you’re experiencing excessive shedding or hair loss.
Are there any specific hair care products or treatments that can help reduce shedding?
While there are no specific products or treatments guaranteed to reduce shedding for everyone, using gentle hair care products suitable for your hair type and avoiding harsh chemicals and heat styling can help minimize shedding and promote overall hair health.
Is hair shedding the same as hair loss?
Hair shedding refers to the natural process of hairs falling out as part of the hair growth cycle, whereas hair loss refers to a decrease in hair density or baldness that may result from various factors, including genetics, medical conditions, or hormonal imbalances.