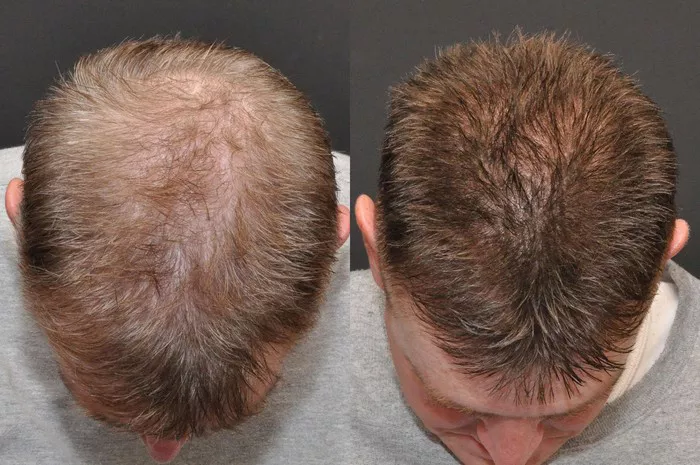
Hair transplantation is a significant and increasingly popular solution for individuals suffering from hair loss. This surgical procedure offers the promise of a fuller head of hair, restoring confidence and appearance. However, one of the most common concerns post-transplant is the shedding phase. Understanding when shedding stops after a hair transplant and what to expect during this period is crucial for patients. This article delves into the intricacies of the shedding phase, factors influencing it, and provides a timeline for what patients can anticipate in the months following their surgery.
Understanding the Hair Transplant Process
Before diving into the shedding phase, it’s important to have a basic understanding of the hair transplant process. Hair transplantation involves extracting hair follicles from a donor area (usually the back or sides of the head) and implanting them into the balding or thinning areas of the scalp. There are two primary methods of hair transplantation:
1. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): In this method, a strip of scalp is removed from the donor area, and the follicles are then extracted and transplanted.
2. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): This method involves individually extracting follicles from the donor area and then transplanting them to the recipient site.
Both methods aim to achieve natural-looking hair growth, but the post-operative experience, including shedding, can vary slightly between the two.
The Shedding Phase Explained
Why Does Shedding Occur?
Shedding after a hair transplant is a normal part of the healing process. Known as “shock loss” or “telogen effluvium,” this phenomenon occurs because the transplanted hair follicles go into a resting phase due to the trauma of the surgery. This resting phase causes the hair strands to fall out, but the follicles remain intact and healthy.
Timeline of Shedding Post-Transplant
The shedding phase typically begins around 2 to 4 weeks after the hair transplant procedure. Patients may notice hair falling out in the shower, on their pillow, or while combing their hair. This can be alarming, but it is a normal and expected part of the recovery process.
Factors Influencing the Shedding Phase
Several factors can influence the duration and intensity of the shedding phase:
1. Individual Healing Response: Each person’s body heals differently, which can affect how quickly the shedding phase occurs and resolves.
2. Hair Transplant Technique: The method used (FUT or FUE) can influence the shedding timeline. FUE, being less invasive, might lead to a quicker recovery and potentially less intense shedding.
3. Post-Operative Care: Following post-operative care instructions meticulously can impact the shedding process. Proper care can minimize trauma to the scalp and promote faster healing.
When Does Shedding Stop?
Typical Duration of the Shedding Phase
The shedding phase usually lasts between 1 to 3 months. By the end of the third month post-transplant, most of the transplanted hairs that were going to shed will have fallen out.
New Hair Growth
After the shedding phase, the follicles enter a new growth cycle. New hair growth typically begins around 3 to 4 months post-transplant. Initially, the new hair may be fine and light, but it will thicken and darken over time. By the 6-month mark, noticeable hair growth should be evident, with continued improvement over the next year.
Long-Term Expectations
Full hair growth can take up to 12 to 18 months post-transplant. Patience is crucial during this period as the hair follicles establish themselves and produce healthy hair.
Managing the Shedding Phase
Post-Operative Care Tips
Proper post-operative care can help manage the shedding phase and promote quicker recovery:
1. Follow Doctor’s Instructions: Adhering to the care instructions provided by the surgeon is essential. This includes taking prescribed medications, avoiding strenuous activities, and protecting the scalp from sun exposure.
2. Gentle Hair Care: Avoid harsh shampoos and vigorous hair washing. Use gentle, sulfate-free shampoos and avoid scratching or rubbing the scalp.
3. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can impair healing and negatively affect hair growth.
4. Stay Hydrated and Maintain a Healthy Diet: Proper nutrition and hydration support overall health and can aid in the healing process.
Dealing with Anxiety and Expectations
It’s natural for patients to feel anxious about the shedding phase. Understanding that this is a temporary and normal part of the process can help alleviate some of the stress. Setting realistic expectations and being patient is crucial. Consulting with the surgeon for regular follow-ups can also provide reassurance.
FAQs About Shedding After Hair Transplant
Is Shedding After a Hair Transplant Permanent?
No, shedding after a hair transplant is not permanent. It is a temporary phase where the transplanted hairs fall out to make way for new growth.
Can Anything Be Done to Prevent Shedding?
Shedding is a natural response to the trauma of surgery and cannot be entirely prevented. However, following post-operative care instructions can help manage and potentially minimize the intensity of shedding.
Will All Transplanted Hair Shed?
Not all transplanted hair will shed. While a significant amount of hair may fall out, some transplanted hairs might remain and continue to grow.
What If Shedding Continues Beyond Three Months?
If shedding persists beyond three months, it’s advisable to consult with the surgeon. While extended shedding can sometimes occur, it’s essential to rule out any underlying issues.
Conclusion
The shedding phase after a hair transplant is a normal and expected part of the recovery process. Understanding when shedding stops and what to anticipate can help alleviate concerns and set realistic expectations. Most patients will experience shedding between 2 to 4 weeks post-surgery, with the phase lasting up to three months. New hair growth typically begins around 3 to 4 months post-transplant, with continued improvement over the next year. Proper post-operative care and patience are essential for achieving the best results. By following the guidelines provided and maintaining realistic expectations, patients can look forward to enjoying the full benefits of their hair transplant.