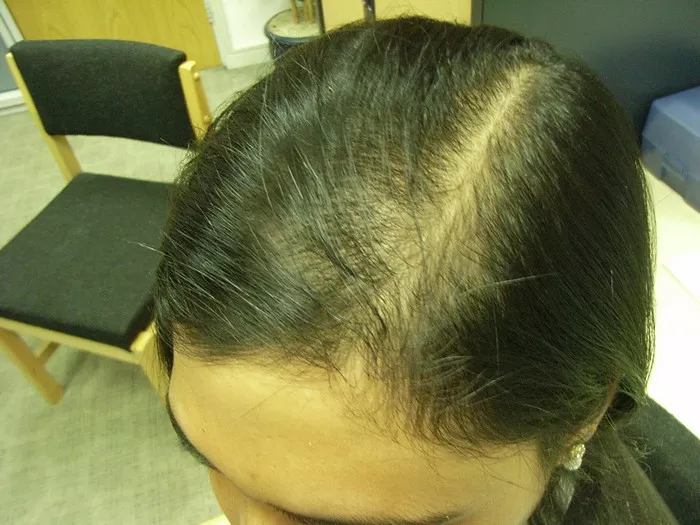
Autoimmune hair loss, most commonly known as alopecia areata, is a condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss. Unlike other types of hair loss, such as androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness), autoimmune hair loss can affect anyone regardless of age, gender, or ethnicity. Understanding its causes and symptoms is crucial for effectively managing and potentially stopping the progression of this condition.
Causes of Autoimmune Hair Loss
The exact cause of autoimmune hair loss remains unclear, but several factors are believed to contribute to its onset:
1. Genetic Predisposition: Family history plays a significant role in the likelihood of developing alopecia areata. Certain genes related to the immune system might make an individual more susceptible.
2. Immune System Dysregulation: The body’s immune system, which typically protects against viruses and bacteria, mistakenly targets hair follicles. This attack causes inflammation and subsequent hair loss.
3. Environmental Triggers: Stress, trauma, viral infections, or other environmental factors can trigger or exacerbate autoimmune responses, leading to hair loss.
4. Other Autoimmune Disorders: Individuals with other autoimmune conditions, such as thyroid disease, rheumatoid arthritis, or vitiligo, are at higher risk of developing alopecia areata.
Symptoms of Autoimmune Hair Loss
Autoimmune hair loss manifests in various ways:
- Patchy Hair Loss: The most common presentation is sudden, round patches of hair loss on the scalp.
- Total Hair Loss: In severe cases, individuals may experience total scalp hair loss (alopecia totalis) or complete body hair loss (alopecia universalis).
- Nail Changes: Some people may notice changes in their nails, such as pitting, ridges, or brittleness.
- Regrowth and Relapse: Hair may regrow in affected areas, but it can also fall out again, leading to a cycle of regrowth and loss.
Diagnosing Autoimmune Hair Loss
Proper diagnosis is essential for effective management. A healthcare professional, typically a dermatologist, will perform the following:
Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough medical history and physical examination help identify the pattern and extent of hair loss and check for associated symptoms or other autoimmune conditions.
Scalp Biopsy
A scalp biopsy involves taking a small sample of scalp tissue for microscopic examination. This helps confirm the diagnosis by revealing characteristic changes in hair follicles caused by an autoimmune attack.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can identify underlying autoimmune conditions or deficiencies, such as thyroid dysfunction or anemia, that might contribute to hair loss.
Treatment Options for Autoimmune Hair Loss
There is no definitive cure for autoimmune hair loss, but several treatment options can help manage the condition, promote hair regrowth, and reduce the frequency of relapses.
Topical Treatments
- Corticosteroids: Topical corticosteroids are often the first line of treatment. They reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response in the affected area, promoting hair regrowth.
- Minoxidil: While primarily used for androgenetic alopecia, minoxidil can also be effective in stimulating hair growth in cases of alopecia areata.
- Anthralin: A synthetic tar-like substance, anthralin is applied to the scalp to modulate the immune response and stimulate hair regrowth.
Intralesional Corticosteroid Injections
For more localized and severe patches of hair loss, intralesional corticosteroid injections directly into the affected areas can be highly effective. This method delivers a concentrated dose of medication to suppress the immune attack on hair follicles.
See Also: How to Stop Hair Loss After Gastric Bypass Surgery
Systemic Treatments
- Oral Corticosteroids: In cases of widespread hair loss, oral corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce systemic inflammation. However, their long-term use is limited due to potential side effects.
- Immunosuppressive Agents: Medications such as methotrexate or cyclosporine can suppress the overall immune response. These are typically reserved for severe or refractory cases due to their potential side effects.
- JAK Inhibitors: A newer class of medications, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, has shown promising results in treating alopecia areata by targeting specific pathways involved in the immune response.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves exposing the scalp to ultraviolet light. It can modulate the immune response and promote hair regrowth. This treatment is often combined with other therapies for enhanced effectiveness.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
- Nutritional Supplements: Ensuring adequate intake of vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D, zinc, and biotin, can support overall hair health.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress, a known trigger for autoimmune responses.
- Acupuncture: Some individuals find relief through acupuncture, which may help balance the immune system and reduce inflammation.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Hair Regrowth
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes can support hair regrowth and overall well-being:
Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants supports immune function and hair health. Key nutrients include:
- Protein: Essential for hair structure and growth.
- Iron: Deficiency can lead to hair loss; include sources like lean meats, beans, and spinach.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, they promote scalp health and reduce inflammation.
- Vitamins A, C, D, and E: Crucial for healthy hair growth; found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
Regular Exercise
Exercise improves blood circulation, including to the scalp, and helps reduce stress, which can be a trigger for autoimmune responses.
Scalp Care
Gentle scalp care is important to avoid further irritation or damage:
- Use Mild Shampoos: Avoid harsh chemicals and choose products designed for sensitive scalps.
- Avoid Heat Styling: Minimize the use of hair dryers, straighteners, and curling irons to prevent damage.
- Protect the Scalp: Wear hats or scarves to protect the scalp from sun exposure and cold weather.
Mental Health Support
Coping with hair loss can be emotionally challenging. Seeking support from mental health professionals, support groups, or counseling can help manage the psychological impact and improve overall quality of life.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
Research into the mechanisms of autoimmune hair loss is ongoing, with promising developments on the horizon. Future directions include:
Genetic Studies
Advancements in genetic research are uncovering specific genes associated with alopecia areata, providing insights into its underlying causes and potential targets for new treatments.
Biological Therapies
Biological therapies, including targeted monoclonal antibodies, are being explored for their potential to modulate the immune system more precisely and effectively than traditional immunosuppressive drugs.
Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine, including stem cell therapy, aims to restore hair follicles and promote hair regrowth by harnessing the body’s natural healing processes.
Personalized Medicine
As our understanding of the genetic and molecular basis of autoimmune hair loss improves, personalized treatment approaches tailored to an individual’s specific genetic and immunological profile may become a reality.
Conclusion
Stopping autoimmune hair loss involves a multifaceted approach that includes medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and psychological support. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, a combination of therapies tailored to the individual’s needs can effectively manage the condition and promote hair regrowth. Ongoing research and advancements in understanding the mechanisms behind autoimmune hair loss hold promise for more targeted and effective treatments in the future.
Living with autoimmune hair loss can be challenging, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can manage their symptoms, improve their quality of life, and regain their confidence. If you suspect you have autoimmune hair loss, consult a healthcare professional to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific condition.