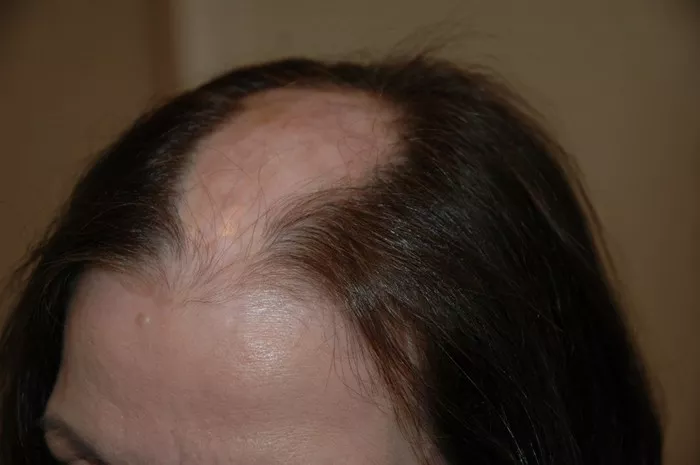
Scarring alopecia, also known as cicatricial alopecia, is a diverse group of rare disorders that destroy hair follicles, replace them with scar tissue, and cause permanent hair loss. Understanding how to stop scarring alopecia from spreading is crucial for anyone affected by this condition, as early and appropriate interventions can help manage symptoms and prevent further hair loss. This article delves into the various aspects of scarring alopecia, including its types, causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and, most importantly, strategies to halt its progression.
Types of Scarring Alopecia
Scarring alopecia can be broadly classified into primary and secondary types.
Primary Scarring Alopecia
In primary scarring alopecia, the hair follicle is the primary target of the inflammatory process. This category includes conditions such as:
1. Lichen Planopilaris (LPP): A form of lichen planus that affects the scalp, leading to patchy hair loss and scarring.
2. Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA): A variant of LPP, primarily affecting postmenopausal women, characterized by a band-like pattern of hair loss along the frontal hairline.
3. Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia (CCCA): Common in African American women, it starts at the crown and spreads outward.
4. Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE): A chronic autoimmune condition affecting the skin and scalp, resulting in scarring and hair loss.
5. Folliculitis Decalvans: A form of chronic scalp inflammation leading to scarring and hair loss.
Secondary Scarring Alopecia
Secondary scarring alopecia occurs when external factors like infections, injuries, or neoplasms destroy the hair follicle. These can be due to:
1. Severe Infections: Such as bacterial, fungal, or viral infections that cause significant inflammation and scarring.
2. Trauma: Including burns, surgical scars, or physical injury to the scalp.
3. Neoplasms: Tumors or cancers that affect the scalp.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of scarring alopecia is essential in preventing its spread. Although the exact cause often remains unknown, several contributing factors have been identified:
1. Autoimmune Reactions: Many forms of scarring alopecia, such as LPP and FFA, are believed to be linked to autoimmune reactions where the body mistakenly attacks its own hair follicles.
2. Genetic Predisposition: There is evidence suggesting a genetic component, particularly in conditions like CCCA.
3. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal imbalances, especially in postmenopausal women, have been linked to conditions like FFA.
4. Infections: Both bacterial and fungal infections can lead to follicular damage and subsequent scarring.
5. Environmental Factors: UV radiation and other environmental triggers can exacerbate conditions like DLE.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of scarring alopecia early can significantly affect the outcome. Common symptoms include:
1. Redness and Scaling: The affected area of the scalp may become red and scaly.
2. Itching and Pain: These symptoms often accompany the inflammatory process.
3. Hair Loss: The most noticeable symptom, with hair falling out in patches.
4. Follicular Pustules: In some cases, small pustules or pimples may form around hair follicles.
5. Scarring: As the condition progresses, the scalp becomes smooth and shiny due to scarring.
Diagnostic Methods
Diagnosis of scarring alopecia typically involves:
1. Clinical Examination: A thorough scalp examination by a dermatologist.
2. Trichoscopy: A non-invasive technique using a dermatoscope to examine the scalp and hair follicles.
3. Scalp Biopsy: A small sample of scalp tissue is taken for microscopic examination to confirm the diagnosis and identify the specific type of scarring alopecia.
4. Blood Tests: To check for underlying autoimmune or infectious conditions.
Effective Strategies to Stop Scarring Alopecia from Spreading
Once diagnosed, the primary goal is to halt the progression of scarring alopecia. This requires a multi-faceted approach combining medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and ongoing management.
Medical Treatments
1. Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Corticosteroids, either topical or systemic, are commonly used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response. Topical corticosteroids can be applied directly to the scalp, while oral corticosteroids may be prescribed for more severe cases.
2. Immunosuppressive Agents: Drugs such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, and mycophenolate mofetil are used to suppress the immune system in severe cases of autoimmune-related scarring alopecia.
3. Hydroxychloroquine: An antimalarial drug that has anti-inflammatory properties, often used in conditions like DLE and LPP.
4. Antibiotics: Both topical and oral antibiotics may be used to treat or prevent infections that contribute to follicular destruction.
5. Antifungal Medications: In cases where fungal infections are present, antifungal treatments can be effective.
6. Retinoids: Topical retinoids like tretinoin can help reduce hyperkeratosis and follicular plugging.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
1. Gentle Hair Care: Avoid harsh hair treatments, tight hairstyles, and excessive use of heat styling tools to reduce trauma to the scalp.
2. Sun Protection: Use sunscreen or wear hats to protect the scalp from UV radiation, especially in conditions like DLE.
3. Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support overall hair and scalp health.
4. Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate autoimmune conditions, so practices like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can be beneficial.
See Also: How to Stop Hair Fall Due to Typhoid: A Comprehensive Guide
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
While conventional medical treatments are primary, some patients may find relief with complementary therapies:
1. Essential Oils: Oils like rosemary and tea tree oil have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. However, they should be used with caution and ideally under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
2. Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine practice may help reduce stress and improve overall wellbeing.
3. Nutritional Supplements: Supplements like biotin, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids can support hair health, though they should be used with a healthcare provider’s guidance.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular follow-up with a dermatologist is crucial to monitor the condition and adjust treatments as necessary. This includes:
1. Routine Scalp Examinations: To assess the effectiveness of treatments and check for new areas of inflammation.
2. Trichoscopic Evaluations: Periodic trichoscopic exams can provide detailed insights into the condition of the hair follicles.
3. Photographic Records: Taking regular photos of the scalp can help track changes over time and provide visual evidence of treatment efficacy.
Preventing Recurrence
Even after successful treatment, vigilance is required to prevent recurrence. Strategies include:
1. Continuing Preventative Treatments: Long-term, low-dose treatments may be necessary to keep the condition under control.
2. Avoiding Known Triggers: Identifying and avoiding factors that trigger flare-ups, such as certain hair products or UV exposure.
3. Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle: Continuing a healthy diet, stress management practices, and gentle hair care routines.
Conclusion
Stopping scarring alopecia from spreading requires a comprehensive and proactive approach. Early diagnosis, appropriate medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring are key to managing this challenging condition. By understanding the types, causes, symptoms, and effective strategies, individuals can take control of their health and work towards preserving their hair and scalp health. As with any medical condition, collaboration with healthcare professionals is essential for tailored treatment and optimal outcomes.