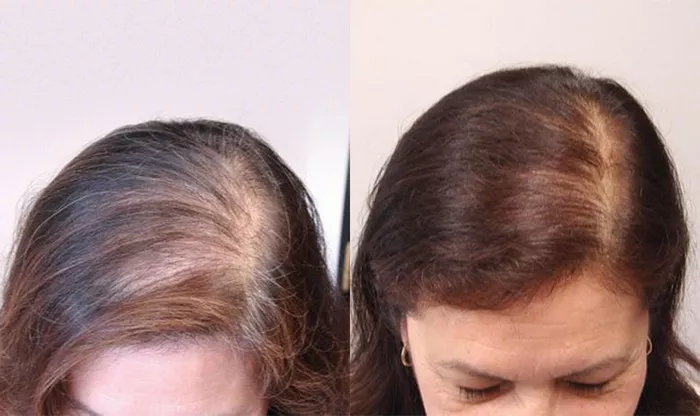
Sepsis, a life-threatening condition caused by the body’s extreme response to infection, can have numerous long-term health implications. One of the less discussed but equally distressing after-effects of sepsis is hair loss. For individuals recovering from this severe illness, losing hair can add emotional strain to an already challenging recovery process. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of why hair loss occurs after sepsis and offer effective strategies to mitigate this issue.
Understanding the Link Between Sepsis and Hair Loss
The Impact of Sepsis on the Body
Sepsis triggers a systemic inflammatory response that can cause widespread damage to tissues and organs. During sepsis, the body prioritizes vital organ function, often at the expense of other systems, including hair follicles. This shift in resources can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle.
Telogen Effluvium: A Common Culprit
Hair loss after sepsis is frequently attributed to a condition known as telogen effluvium. This condition occurs when a significant stressor, such as severe infection or trauma, pushes a large number of hair follicles into the resting (telogen) phase of the hair growth cycle. After a few months, these resting hairs fall out, leading to noticeable thinning and hair loss.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Hair Health
Sepsis can also lead to nutritional deficiencies, as the body utilizes more nutrients to combat infection and recover from the illness. Deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron, zinc, and biotin, can significantly impact hair health and contribute to hair loss.
Strategies to Stop Hair Loss After Sepsis
1. Nutritional Support and Supplementation
Ensure a Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for hair health. Focus on foods high in vitamins A, C, D, E, and B-complex, as well as minerals like iron, zinc, and selenium. Protein is also vital, as hair is primarily composed of keratin, a protein.
Consider Supplements: If dietary intake is insufficient, supplements can help bridge the gap. Biotin, in particular, is known for promoting hair growth. Other helpful supplements include vitamin D, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation.
2. Gentle Hair Care Practices
Avoid Harsh Treatments: Limit the use of chemical treatments, such as dyes and perms, which can further stress and damage hair. Opt for gentle, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners to avoid stripping hair of natural oils.
Minimize Heat Styling: Excessive heat from styling tools can weaken hair strands. Allow hair to air dry when possible, and use heat protectant products if styling is necessary.
Be Gentle When Brushing: Use a wide-toothed comb or a brush with soft bristles to reduce hair breakage. Avoid brushing hair when wet, as it is more prone to damage.
3. Stress Management Techniques
Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation: Stress can exacerbate hair loss, so incorporating stress-reducing practices like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
Seek Support: Joining a support group or talking to a therapist can help manage the emotional toll of recovering from sepsis and dealing with hair loss.
4. Medical Treatments and Therapies
Topical Treatments: Minoxidil (Rogaine) is a popular over-the-counter treatment that can stimulate hair growth. Apply it to the scalp as directed to see improvements over several months.
Prescription Medications: In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications like finasteride (Propecia) for men to promote hair growth. Consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the suitability of these treatments.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting a concentration of the patient’s own platelets into the scalp to stimulate hair growth. This treatment has shown promise in promoting hair regrowth.
See Also: How to Stop Hair Loss After Weight Loss Surgery
5. Lifestyle Modifications
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can improve overall circulation, including to the scalp, promoting healthier hair growth.
Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for overall health and recovery. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to support the body’s healing processes.
Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and hair. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep hair follicles hydrated.
Monitoring Progress and When to Seek Help
Track Changes and Improvements
Keep a journal to document any changes in your hair growth and health. Note the effectiveness of different strategies and any new symptoms that arise. This record can help identify patterns and effective treatments.
Consult Healthcare Professionals
If hair loss persists despite following these strategies, consult a dermatologist or a trichologist (a specialist in hair and scalp conditions). They can perform a thorough evaluation and recommend more targeted treatments.
Explore Advanced Treatments
For severe cases, advanced treatments like hair transplantation may be considered. This procedure involves transplanting healthy hair follicles from one part of the scalp to the thinning areas. Discuss the potential benefits and risks with a specialist.
Conclusion
Recovering from sepsis is a challenging journey, and dealing with hair loss can add to the emotional burden. Understanding the underlying causes of hair loss post-sepsis and implementing effective strategies can help mitigate this distressing side effect. By focusing on nutrition, gentle hair care practices, stress management, and seeking appropriate medical treatments, individuals can support their hair’s health and promote regrowth. Patience and consistency are key, and with the right approach, it is possible to restore and maintain healthy hair after sepsis.