Hair loss can be a distressing experience, leading many to explore various hair restoration options. Two of the most popular methods are Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). While both techniques aim to restore hair, they differ significantly in their approach, procedure, recovery, and results. This article will delve into the fundamental differences between FUT and FUE hair transplants, helping you make an informed decision about which method might be best for you.
Understanding Hair Transplantation
What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves moving hair follicles from one part of the body (the donor site) to the bald or thinning area (the recipient site). This technique is commonly used to treat male pattern baldness but can also address hair loss in women and other types of hair loss due to trauma or medical conditions.
The Importance of Hair Follicles
Hair follicles are tiny structures in the skin that produce hair. Each follicle contains a sebaceous gland, hair bulb, and a small muscle called the arrector pili. In hair transplantation, healthy hair follicles are harvested from areas with dense hair growth (usually the back or sides of the scalp) and transplanted to areas with thinning or no hair.
FUT Hair Transplant
Procedure
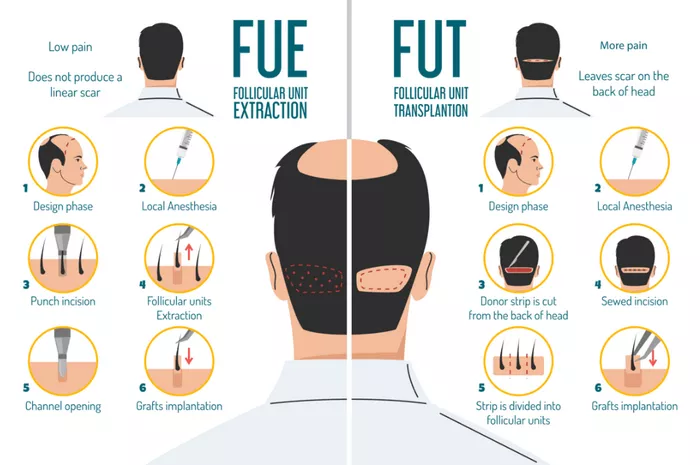
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), also known as the strip method, involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area. This strip is then dissected into individual follicular units under a microscope. These units are meticulously implanted into the recipient area.
Step-by-Step Process
1. Preparation: The scalp is cleaned and numbed with local anesthesia.
2. Donor Area Harvesting: A strip of scalp is surgically removed from the donor area, typically from the back of the head.
3. Dissection: The strip is dissected into individual follicular units, containing one to four hairs each.
4. Recipient Site Creation: Tiny incisions are made in the recipient area where the follicular units will be implanted.
5. Implantation: The follicular units are carefully placed into the incisions, following the natural hair growth pattern.
Advantages of FUT
High Yield of Grafts: FUT can harvest a large number of grafts in a single session, making it suitable for extensive hair restoration.
Efficient Use of Donor Hair: The strip method ensures a high survival rate of transplanted follicles.
Lower Cost: Generally, FUT is less expensive than FUE due to the shorter duration of the procedure.
Disadvantages of FUT
Linear Scar: FUT leaves a linear scar at the donor site, which can be visible if the hair is worn short.
Longer Recovery Time: The recovery period is typically longer due to the larger incision and sutures required.
Potential for More Pain and Discomfort: Patients may experience more pain and discomfort during the healing process compared to FUE.
FUE Hair Transplant
Procedure
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) involves extracting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area using a tiny punch tool. These follicles are then implanted into the recipient area.
Step-by-Step Process
1. Preparation: The scalp is cleaned and numbed with local anesthesia.
2. Extraction: Individual hair follicles are harvested using a micro-punch tool, which creates tiny circular incisions around each follicle.
3. Recipient Site Creation: Tiny incisions are made in the recipient area.
4. Implantation: The extracted follicles are implanted into the recipient area, following the natural hair growth pattern.
Advantages of FUE
No Linear Scar: FUE does not leave a linear scar, making it ideal for individuals who prefer to wear their hair short.
Faster Recovery Time: The recovery period is usually shorter, with less discomfort and a lower risk of complications.
Minimally Invasive: The procedure is less invasive, with tiny incisions that heal quickly and leave minimal scarring.
Disadvantages of FUE
Longer Procedure Time: FUE can be time-consuming, especially for large areas of hair loss, as each follicle is extracted individually.
Higher Cost: Due to the meticulous nature of the procedure, FUE is generally more expensive than FUT.
Limited Graft Yield: FUE may not be as efficient in harvesting a large number of grafts in a single session compared to FUT.
Comparing FUT and FUE
Scarring
FUT: Leaves a linear scar at the donor site, which can be noticeable with short hairstyles.
FUE: Results in tiny, dot-like scars that are less visible and easier to conceal, even with short hair.
Recovery Time
FUT: Typically involves a longer recovery period due to the larger incision and sutures.
FUE: Offers a shorter recovery time, with less discomfort and a quicker return to normal activities.
Cost
FUT: Generally less expensive due to the shorter duration of the procedure.
FUE: More expensive due to the labor-intensive nature of individually extracting each follicle.
Graft Quality and Quantity
FUT: Can yield a higher number of grafts in a single session, making it suitable for extensive hair restoration.
FUE: May provide fewer grafts per session, but the quality of each graft can be very high due to the precision of the extraction process.
See Also: How Long Until FUE Grafts Are Secure: What You Need to Know
Suitability for Different Patients
FUT: Ideal for patients requiring a large number of grafts and those who do not mind a linear scar.
FUE: Suitable for patients who prefer minimal scarring, shorter recovery times, and those who require fewer grafts.
Choosing the Right Method
Factors to Consider
1. Extent of Hair Loss: The degree of hair loss can influence the choice between FUT and FUE. Extensive hair loss might be better addressed with FUT, while smaller areas can be effectively treated with FUE.
2. Scarring Concerns: If visible scarring is a concern, FUE might be the preferable option due to its minimal scarring.
3. Budget: Consider the cost differences between the two procedures and choose one that fits your budget.
4. Recovery Time: If a quicker recovery is a priority, FUE may be more suitable.
5. Hair Style Preference: Those who prefer to wear their hair short might favor FUE to avoid a visible linear scar.
Consultation with a Specialist
It is essential to consult with a hair transplant specialist to determine the most suitable method for your specific needs. A specialist can evaluate your hair loss, donor area, and overall health to recommend the best approach.
Conclusion
Both FUT and FUE hair transplants offer effective solutions for hair restoration, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the differences between the two methods can help you make an informed decision based on your individual needs and preferences. Whether you prioritize a higher graft yield, minimal scarring, shorter recovery time, or cost, there is a hair transplant method that can meet your expectations. Consulting with a qualified hair transplant specialist is the first step toward achieving the best possible results and restoring your confidence.