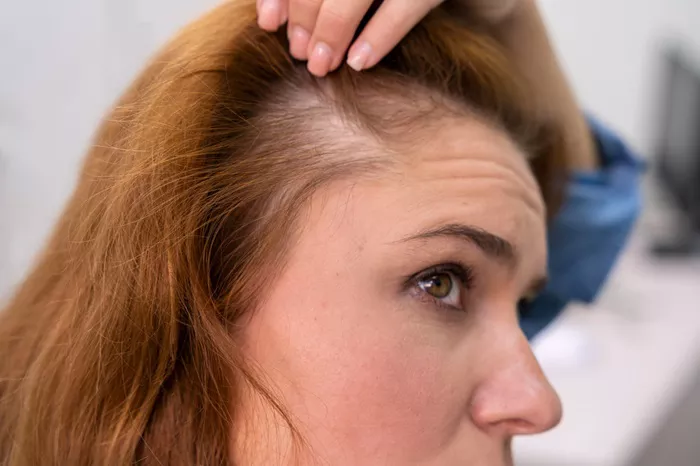
Hair loss is a common concern affecting millions of people worldwide. For those seeking a permanent solution, hair transplantation has become a popular option. However, a critical question that arises is: Does a hair transplant stop hair loss completely? This article aims to explore this question in detail, addressing how hair transplants work, their effectiveness in stopping hair loss, and what you can expect post-procedure.
Understanding Hair Loss
The Causes of Hair Loss
Hair loss, or alopecia, can occur due to various reasons, including genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, and lifestyle factors. The most common form of hair loss in both men and women is androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness. This condition is primarily genetic and leads to the progressive thinning of hair over time.
How Hair Loss Progresses
In androgenetic alopecia, hair follicles gradually shrink, leading to thinner and shorter hair. Over time, the follicles may stop producing new hair altogether. This process is progressive, meaning that without intervention, hair loss will continue over time.
What is a Hair Transplant?
The Basics of Hair Transplantation
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure in which hair follicles are removed from one part of the body, usually the back or sides of the scalp (donor area), and transplanted to the balding or thinning areas (recipient area). The two main techniques used in hair transplants are Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
How Hair Transplants Work
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): In FUT, a strip of scalp is removed from the donor area. This strip is then divided into individual hair follicles, which are implanted into the thinning or bald areas.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): In FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area using a specialized tool. These follicles are then implanted into the recipient area.
Both techniques aim to redistribute hair from denser areas to areas of thinning or baldness, resulting in a fuller head of hair.
Does a Hair Transplant Stop Hair Loss?
The Role of Transplanted Hair
Transplanted hair is usually taken from areas of the scalp that are resistant to the effects of hormones that cause hair loss, such as the back and sides of the head. Because these hair follicles are genetically programmed to resist balding, they typically continue to grow in their new location for a lifetime.
The Limits of Hair Transplantation
While hair transplants can restore hair to balding areas, they do not stop the overall progression of genetic hair loss. Non-transplanted hair, especially in areas prone to androgenetic alopecia, may continue to thin and fall out over time. This means that while the transplanted hair is permanent, the surrounding hair may still be subject to hair loss.
The Importance of Post-Transplant Care
After a hair transplant, it’s crucial to follow your doctor’s recommendations for hair care and any prescribed treatments. This may include medications like minoxidil or finasteride to slow the progression of hair loss in non-transplanted areas and to maintain overall hair density.
Hair Transplants vs. Hair Loss Treatments
Combining Treatments
For many individuals, a combination of hair transplantation and medical treatments offers the best results. While the transplant addresses the immediate issue of hair loss by filling in bald spots, treatments like minoxidil or finasteride can help maintain the surrounding hair and slow the progression of hair loss.
Expectations and Realities
Understanding what a hair transplant can and cannot do is vital. While it provides a long-lasting solution for bald areas, it doesn’t cure the underlying condition of hair loss. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider and maintaining a hair care regimen are essential for the best long-term results.
Who is a Good Candidate for a Hair Transplant?
Assessing Hair Loss Severity
A good candidate for a hair transplant is someone who has sufficient hair in the donor area to be transplanted to the balding areas. The severity of hair loss and the pattern of balding are key factors in determining candidacy.
Age and Timing Considerations
Hair transplants are often more successful in individuals who have stabilized their hair loss, typically in their late 20s or older. Younger individuals with early-stage hair loss may not be ideal candidates, as their hair loss may continue to progress, requiring additional treatments.
See also: Is FUE Hair Transplant Painful: Things You Need To Know
The Procedure: What to Expect
Pre-Procedure Consultation
Before undergoing a hair transplant, you’ll have a consultation with a specialist to discuss your goals, assess your hair loss, and determine the best treatment plan. The specialist will examine your scalp, discuss your medical history, and possibly conduct a scalp biopsy or blood tests.
The Day of the Procedure
On the day of the procedure, you’ll receive local anesthesia to numb the scalp. The procedure can take several hours, depending on the number of follicles being transplanted. During the procedure, you can typically read, watch TV, or even nap.
Recovery and Aftercare
After the procedure, your scalp may be tender, and you might need to wear bandages for a few days. Most patients can return to work within a week, but it’s important to follow your doctor’s aftercare instructions carefully, which may include taking prescribed medications and avoiding certain activities.
The Results: What to Expect
Initial Results
Transplanted hair will usually start to grow within a few months. Initially, the transplanted hair may fall out, but this is a normal part of the process known as “shock loss.” New hair growth typically begins around three to four months after the procedure.
Long-Term Results
The final results of a hair transplant can take up to a year to become fully visible. The transplanted hair will continue to grow naturally, and because it comes from areas resistant to hair loss, it is usually permanent.
Caring for Your Hair Post-Transplant
Maintaining Hair Health
Post-transplant care is crucial for maintaining the health and longevity of your transplanted hair. Use gentle hair care products, avoid harsh chemicals, and protect your scalp from excessive sun exposure.
Ongoing Hair Loss Management
To prevent further hair loss in non-transplanted areas, continue using any prescribed hair loss treatments. Regular check-ups with your hair specialist can help monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Conclusion
A hair transplant is an effective way to restore hair in balding areas, providing a natural-looking solution that can last a lifetime. However, it’s important to understand that a hair transplant does not stop the overall process of hair loss. While the transplanted hair is permanent, other areas of your scalp may continue to experience thinning. Combining a hair transplant with ongoing hair loss treatments and proper care is the best way to maintain a full, healthy head of hair over the long term.
By setting realistic expectations and following a comprehensive treatment plan, you can achieve the best possible results from your hair transplant. Whether you’re considering a hair transplant or are already on the journey, staying informed and proactive is key to managing hair loss effectively.