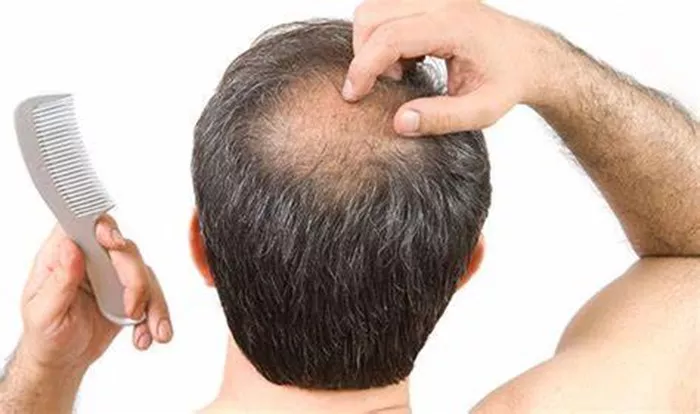
Genetic hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common form of hair loss affecting both men and women. It’s a condition that is largely influenced by genetics, and while it cannot be completely stopped, there are various treatments and strategies available that can help slow down the process, manage the symptoms, and even restore hair in some cases. This article will delve into the causes of genetic hair loss, the available treatment options, and lifestyle changes that can help manage the condition.
Understanding Genetic Hair Loss
What Is Genetic Hair Loss?
Genetic hair loss is a hereditary condition that leads to the gradual thinning of hair and, in many cases, eventual baldness. In men, it is often referred to as male pattern baldness, and in women, as female pattern hair loss. The condition is caused by the sensitivity of hair follicles to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of the male hormone testosterone. This sensitivity leads to the miniaturization of hair follicles, resulting in shorter and finer hair strands until the follicles eventually stop producing hair altogether.
Who Is Affected by Genetic Hair Loss?
Genetic hair loss can affect both men and women, though it manifests differently. In men, hair loss typically starts with a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, eventually leading to baldness on the top of the head while the sides and back remain unaffected. In women, the pattern is more diffuse, with general thinning across the scalp but usually without complete baldness.
Can Genetic Hair Loss Be Stopped?
While genetic hair loss cannot be completely stopped, its progression can be slowed down, and in some cases, hair regrowth can be stimulated. The key to managing genetic hair loss lies in early intervention and consistent treatment.
Treatments for Genetic Hair Loss
1. Medications
There are several medications available that can help slow down or manage genetic hair loss. These medications are most effective when started early in the hair loss process.
Minoxidil (Rogaine):Minoxidil is an over-the-counter topical treatment that is applied directly to the scalp. It works by increasing blood flow to the hair follicles, which can help to prolong the growth phase of the hair cycle and encourage hair regrowth. Minoxidil is available in various strengths and is suitable for both men and women. It is most effective in the early stages of hair loss, and consistent use is necessary to maintain results.
Finasteride (Propecia):Finasteride is an oral prescription medication that works by blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT, the hormone responsible for follicle miniaturization in genetic hair loss. By reducing DHT levels, finasteride can slow down hair loss and, in some cases, even promote regrowth. Finasteride is typically prescribed for men, as it can have side effects that are not suitable for women, particularly those who are pregnant or may become pregnant.
Dutasteride (Avodart):Dutasteride is another oral medication that is similar to finasteride but is more potent in inhibiting DHT production. It is sometimes prescribed for men who do not respond to finasteride or who experience significant hair loss. Like finasteride, dutasteride is not recommended for use in women of childbearing age due to potential risks.
2. Hair Transplant Surgery
For individuals with advanced hair loss, hair transplant surgery may be an option. This procedure involves taking hair follicles from a donor area (typically the back or sides of the scalp) and transplanting them to the thinning or balding areas. There are two main types of hair transplant procedures:
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT):FUT involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area, from which individual hair follicles are harvested and then transplanted to the balding areas. This method leaves a linear scar but allows for the transplantation of a large number of follicles in one session.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE):FUE involves harvesting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area using a small punch tool. These follicles are then transplanted to the balding areas. FUE is less invasive than FUT and does not leave a linear scar, but it can be more time-consuming and may require multiple sessions for extensive hair loss.
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy is a non-surgical treatment that involves drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting the platelet-rich plasma into the scalp. Platelets contain growth factors that can stimulate hair growth and improve hair thickness. PRP therapy is often used in conjunction with other hair loss treatments to enhance results.
4. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT involves the use of low-level lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. This treatment is non-invasive and can be done at home using laser caps or combs, or in a clinical setting. LLLT is believed to increase blood flow to the scalp and improve cellular activity in hair follicles.
5. Microneedling
Microneedling involves the use of a device with fine needles to create micro-injuries in the scalp. These micro-injuries trigger the body’s natural healing response, which includes the production of collagen and the release of growth factors that can stimulate hair growth. Microneedling is often combined with topical treatments, such as minoxidil, to enhance their effectiveness.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Genetic Hair Loss
1. Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins is essential for maintaining healthy hair. Nutritional deficiencies can exacerbate hair loss, so it’s important to ensure that your diet includes the following:
Protein: Hair is made up of keratin, a type of protein. Consuming adequate protein from sources like lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes is crucial for hair health.
Iron: Iron deficiency can lead to hair thinning. Include iron-rich foods such as spinach, red meat, and beans in your diet.
Zinc: Zinc plays a role in hair tissue growth and repair. Foods like nuts, seeds, and shellfish are good sources of zinc.
Biotin: Biotin (vitamin B7) is known for its role in hair growth. Eggs, nuts, and whole grains are rich in biotin.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These healthy fats help nourish the hair follicles. Fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds are excellent sources of omega-3s.
2. Stress Management
Chronic stress can contribute to hair loss by disrupting the hair growth cycle. Practicing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, exercise, and adequate sleep, can help reduce the impact of stress on your hair.
3. Gentle Hair Care Practices
Harsh hair care practices can worsen hair loss. To protect your hair:
Avoid Over-Washing: Washing your hair too frequently can strip it of natural oils, leading to dryness and breakage. Aim to wash your hair 2-3 times a week.
Use Mild Shampoos: Choose shampoos that are free of sulfates and other harsh chemicals that can damage hair.
Avoid Heat Styling: Excessive use of heat styling tools can weaken hair and cause it to break. If you must use heat, apply a heat protectant spray first.
Be Gentle When Brushing: Use a wide-toothed comb or a soft-bristle brush to avoid pulling or breaking your hair.
Early Intervention Is Key
The Importance of Starting Treatment Early
The earlier you address genetic hair loss, the more effective treatments are likely to be. If you notice signs of thinning hair or a receding hairline, it’s important to consult with a dermatologist or a hair specialist as soon as possible. Early intervention can help slow down the progression of hair loss and preserve the hair you have.
Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
Genetic hair loss is a progressive condition, meaning that even after successful treatment, ongoing maintenance may be necessary. Regular check-ups with a hair specialist can help monitor the condition and adjust treatments as needed.
See also: Is There a Way to Stop Genetic Hair Loss?
Conclusion
While there is no definitive way to stop genetic hair loss entirely, a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and early intervention can help manage the condition and preserve hair for as long as possible. Whether you choose medications, hair transplant surgery, or non-invasive therapies like PRP and LLLT, the key is to start early and be consistent with your treatment plan. By taking proactive steps, you can slow down the progression of genetic hair loss and maintain a fuller head of hair for years to come.