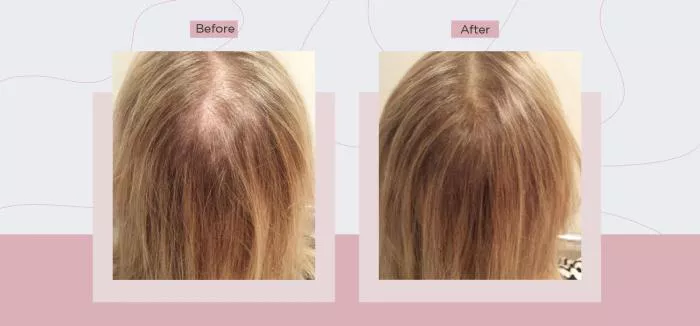
Thinning hair is a common concern that affects millions of people worldwide, regardless of age or gender. The causes of thinning hair can vary widely, from genetic predisposition to lifestyle factors, but the impact on self-esteem and confidence is often profound. Fortunately, there are effective ways to treat thinning hair, ranging from lifestyle changes to medical interventions. This article explores the best approaches to managing and treating thinning hair, providing actionable advice to help you restore and maintain healthy hair.
Understanding Thinning Hair
What Causes Thinning Hair?
Thinning hair can be triggered by several factors, including:
Genetics: Hereditary hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of thinning hair. This condition is passed down from family members and affects both men and women.
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal imbalances, such as those experienced during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders, can lead to thinning hair.
Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of essential vitamins and minerals, particularly iron, zinc, and biotin, can weaken hair and lead to thinning.
Stress: Physical or emotional stress can disrupt the hair growth cycle, causing more hairs to enter the resting phase and eventually fall out.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as alopecia areata, scalp infections, and autoimmune diseases, can contribute to hair thinning.
Medications: Some medications, including those used to treat cancer, depression, and high blood pressure, can cause hair thinning as a side effect.
Hair Care Practices: Overuse of heat styling tools, chemical treatments, and tight hairstyles can damage the hair shaft and follicles, leading to thinning.
Identifying Thinning Hair
Thinning hair may not be immediately noticeable, especially if you have a lot of hair to begin with. However, some signs can help you identify if your hair is thinning:
Widening Part: If your hair part is becoming more visible or is widening, this could be a sign of thinning hair.
Reduced Hair Volume: You may notice a decrease in the overall volume of your hair, making it appear flatter and less full.
Increased Hair Shedding: Finding more hair in your brush, on your pillow, or in the shower drain can indicate that you are losing more hair than usual.
Visible Scalp: If your scalp is becoming more visible, particularly at the crown or temples, this could be a sign of thinning hair.
Best Ways to Treat Thinning Hair
1. Nutritional Support: Feed Your Hair from Within
A well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for healthy hair growth. Here are some dietary recommendations to support thinning hair:
Protein: Hair is primarily made up of a protein called keratin. Ensure your diet includes adequate protein from sources like lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes.
Iron: Iron deficiency is a common cause of hair thinning, particularly in women. Include iron-rich foods such as red meat, spinach, and lentils in your diet.
Zinc: Zinc plays a vital role in hair tissue growth and repair. Foods like nuts, seeds, and shellfish are excellent sources of zinc.
Biotin: Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, is essential for hair health. Eggs, nuts, and whole grains are good dietary sources of biotin.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids help maintain a healthy scalp and reduce inflammation. Fatty fish like salmon, as well as flaxseed and walnuts, are rich in omega-3s.
Vitamins A, C, and E: These vitamins have antioxidant properties that protect hair follicles from damage. Incorporate fruits, vegetables, and nuts into your diet to ensure you’re getting these essential vitamins.
2. Topical Treatments: Direct Care for the Scalp
Topical treatments can be applied directly to the scalp to promote hair growth and prevent further thinning. Some effective options include:
Minoxidil: Minoxidil is a well-known over-the-counter treatment for thinning hair. It’s available in both liquid and foam forms and is applied directly to the scalp. Minoxidil helps to increase blood flow to the hair follicles, encouraging hair growth and slowing down hair loss. It is one of the most widely used treatments for androgenetic alopecia and can be effective in both men and women.
Essential Oils: Certain essential oils, such as rosemary, peppermint, and lavender, have been shown to promote hair growth. These oils can be diluted with a carrier oil and massaged into the scalp to stimulate hair follicles and improve scalp health.
Scalp Massages: Regular scalp massages increase blood circulation to the hair follicles, promoting hair growth. You can use your fingertips or a scalp massaging tool to gently massage the scalp for a few minutes each day.
Corticosteroid Creams: For those experiencing hair thinning due to inflammatory scalp conditions, corticosteroid creams or ointments can help reduce inflammation and prevent further hair loss. These treatments are typically prescribed by a dermatologist.
3. Hair Care Routine: Treat Your Hair with Care
Adopting a gentle hair care routine is essential for preventing further damage and promoting healthy hair growth. Consider the following tips:
Avoid Over-Washing: Washing your hair too frequently can strip it of its natural oils, leading to dryness and breakage. Aim to wash your hair 2-3 times a week, depending on your hair type.
Use Gentle Shampoos and Conditioners: Choose sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners that are formulated for thinning hair. These products are less likely to cause irritation or damage to the scalp and hair.
Minimize Heat Styling: Excessive use of heat styling tools, such as flat irons, curling irons, and blow dryers, can weaken the hair shaft and contribute to thinning. When using heat, apply a heat protectant spray and use the lowest heat setting possible.
Be Gentle When Brushing: Use a wide-tooth comb or a brush with soft bristles to gently detangle your hair. Start at the ends and work your way up to avoid pulling and breaking the hair.
Avoid Tight Hairstyles: Hairstyles that pull on the hair, such as ponytails, braids, and buns, can cause traction alopecia, a form of hair loss caused by tension on the hair follicles. Opt for looser styles that don’t strain your hair.
4. Medical Treatments: Seek Professional Help
For those experiencing significant hair thinning, medical treatments may be necessary to promote hair growth and prevent further loss. Some options include:
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting the platelet-rich plasma into the scalp. The growth factors in PRP can stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. PRP therapy is often recommended for individuals with androgenetic alopecia and other forms of hair thinning.
Hair Transplant Surgery: Hair transplant surgery involves removing hair follicles from one part of the scalp (usually the back or sides) and transplanting them to areas with thinning or no hair. This procedure is typically recommended for individuals with significant hair loss who have not responded to other treatments.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): LLLT is a non-invasive treatment that uses low-level lasers to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. This treatment is painless and can be performed in a clinic or at home using a laser cap or comb.
Prescription Medications: For individuals with androgenetic alopecia, prescription medications like finasteride (for men) and spironolactone (for women) may be recommended. These medications work by blocking the effects of androgens (male hormones) on the hair follicles, slowing down hair loss and promoting regrowth.
5. Lifestyle Changes: Promote Overall Health
Healthy hair starts with a healthy lifestyle. Making positive changes to your daily habits can have a significant impact on the health of your hair:
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to hair thinning by disrupting the hair growth cycle. Implement stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity to reduce stress levels and support hair health.
Get Enough Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for overall health, including hair health. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to allow your body to repair and regenerate cells, including hair follicles.
Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is key to maintaining healthy hair and scalp. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your hair hydrated from the inside out.
Quit Smoking: Smoking has been linked to hair thinning and hair loss. The toxins in cigarette smoke can damage hair follicles and reduce blood flow to the scalp. Quitting smoking can improve your overall health and support healthy hair growth.
6. Hair Supplements: Boost Hair Growth
In addition to a healthy diet, hair supplements can provide extra support for thinning hair. Some popular supplements for hair health include:
Biotin: Biotin supplements are widely used to support hair growth and strengthen hair. Biotin deficiency can lead to hair thinning, so supplementing with biotin may help improve hair health.
Collagen: Collagen supplements provide the amino acids needed to produce keratin, the protein that makes up hair. Collagen can help strengthen hair and improve its elasticity.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 supplements, such as fish oil, can help reduce inflammation and support a healthy scalp, promoting hair growth.
Multivitamins: A high-quality multivitamin can ensure that you’re getting all the essential nutrients needed for healthy hair growth, including vitamins A, C, D, and E, as well as zinc and iron.
See also: The Ultimate Guide to the Best Treatments for Hair Thinning
Conclusion
Treating thinning hair requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying causes and promotes overall hair health. By combining a nutritious diet, gentle hair care practices, topical treatments, and medical interventions when necessary, you can effectively manage thinning hair and restore its fullness and vitality. Remember, it’s essential to be patient and consistent with your hair care routine, as hair growth takes time. If you’re experiencing significant hair loss or are unsure of the best course of action, consult with a dermatologist or hair specialist for personalized advice and treatment options.