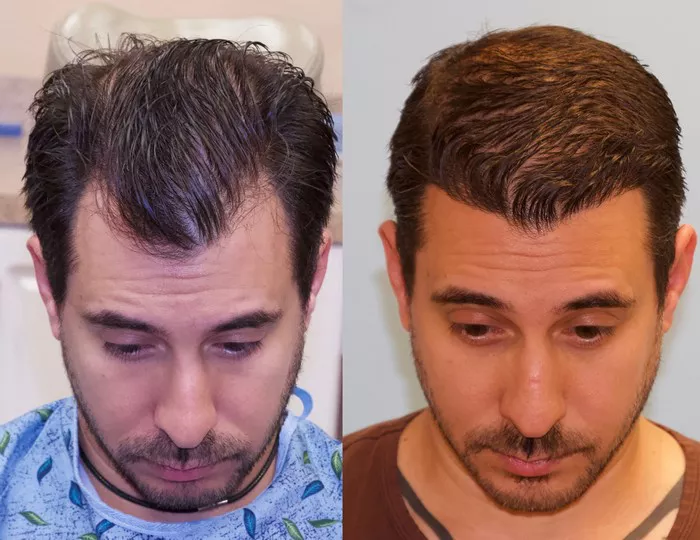
Hair transplants are a popular and effective solution for individuals experiencing hair loss. The procedure involves transferring hair follicles from one part of the scalp to areas where hair thinning or baldness has occurred. To ensure optimal results and minimize complications, patients need to follow specific post-operative care instructions. One critical aspect often discussed is smoking—its impact on healing and when it is safe to resume smoking after a hair transplant. This article provides an in-depth look at how smoking affects hair transplant recovery and offers guidelines on when you can safely return to smoking.
Understanding Hair Transplant Surgery
What Is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves moving hair follicles from a donor area, usually the back or sides of the scalp, to the thinning or balding areas. There are two primary techniques used:
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): This method involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, dissecting it into individual follicular units, and implanting them into the recipient site.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): FUE involves extracting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area and transplanting them to the recipient area.
Both techniques aim to restore natural-looking hair and improve density in areas affected by hair loss.
The Healing Process After a Hair Transplant
After a hair transplant, the scalp goes through several stages of healing:
Initial Healing (Days 1-7): This phase involves immediate recovery from the surgery. The transplanted area may be red, swollen, and tender. Crusts and scabs may form around the grafts.
Post-Operative Healing (Weeks 2-4): The scalp continues to heal, and the initial discomfort subsides. The transplanted hair follicles begin to settle into their new location, and some shedding of the transplanted hair may occur.
Hair Growth Phase (Months 2-6): New hair growth starts as the transplanted follicles enter the anagen (growth) phase. The hair initially may be fine or thin but gradually becomes thicker over time.
Mature Hair Growth (6-12 Months): The transplanted hair reaches its full density and texture. By this time, most of the transplanted hair should have grown in fully.
The Impact of Smoking on Healing
How Smoking Affects the Body’s Healing Process
Smoking has well-documented negative effects on the body’s healing process, which can be particularly concerning after a surgical procedure like a hair transplant. Here’s how smoking impacts healing:
Reduced Blood Flow: Smoking causes blood vessels to constrict, reducing blood flow and oxygen supply to tissues. This diminished blood flow can impair the healing process and increase the risk of complications.
Impaired Immune Response: Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes can weaken the immune system, making the body less effective at fighting off infections and healing wounds.
Delayed Wound Healing: The toxic substances in smoke can hinder cellular repair and prolong the healing process. This can be detrimental in the context of a hair transplant, where the scalp needs to heal quickly for the best results.
Increased Risk of Complications: Smokers are at a higher risk for complications such as infection and poor graft survival. These risks can negatively affect the outcome of the hair transplant.
Specific Concerns for Hair Transplant Patients
For hair transplant patients, smoking can have specific adverse effects on both the transplanted hair follicles and the surrounding scalp:
Graft Survival: Adequate blood flow is essential for the survival of the transplanted hair follicles. Smoking can reduce the chances of successful grafts by impairing blood circulation to the scalp.
Post-Operative Infection: The risk of infection is higher for smokers, which can complicate the healing process and impact the results of the transplant.
Aesthetic Results: Poor healing and increased risk of complications can lead to less satisfactory aesthetic results, affecting the density and appearance of the newly transplanted hair.
Guidelines for Smoking After a Hair Transplant
When Can You Resume Smoking?
Given the negative impact of smoking on the healing process, it is crucial to adhere to specific guidelines regarding when you can resume smoking after a hair transplant:
Immediate Post-Operative Period (First 7 Days): It is strongly recommended to avoid smoking during the first week after the procedure. This period is crucial for initial healing, and smoking during this time can significantly hinder recovery.
Initial Recovery Phase (Weeks 2-4): While the immediate risk of smoking may decrease slightly after the first week, it is still advisable to avoid smoking during the early recovery phase. The scalp continues to heal, and smoking can impede the progress made in the initial stages.
Long-Term Considerations (Beyond 4 Weeks): By the end of the first month, the healing process will be well underway, but the scalp may still be vulnerable. If you choose to resume smoking, do so cautiously and be aware of the potential impacts on the final results of the hair transplant.
Tips for Smokers Considering a Hair Transplant
If you are a smoker planning to undergo a hair transplant, consider the following tips to minimize the impact of smoking on your recovery:
Quit Smoking Before the Procedure: Ideally, quitting smoking several weeks before the hair transplant can improve your overall healing capacity and reduce risks. Aim to stop smoking at least 4-6 weeks prior to the procedure.
Consult Your Surgeon: Discuss your smoking habits with your hair transplant surgeon. They can provide personalized advice based on your health and the specifics of your procedure.
Follow Post-Operative Instructions: Adhere to all post-operative care instructions provided by your surgeon. This includes recommendations related to smoking and other factors that can influence healing.
Consider Nicotine Alternatives: If quitting smoking entirely is challenging, consider using nicotine replacement therapies or other alternatives to reduce the impact of smoking on your recovery.
Potential Alternatives and Considerations
Smoking Cessation Support
If you are concerned about the effects of smoking on your hair transplant and overall health, seeking support to quit smoking can be beneficial. Various resources and programs are available to help individuals quit smoking, including:
Counseling and Support Groups: Professional counseling and support groups can provide guidance and encouragement for quitting smoking.
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT): NRT products, such as patches, gums, and lozenges, can help reduce nicotine cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Prescription Medications: Medications like varenicline (Chantix) and bupropion (Zyban) can assist with smoking cessation by reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Alternative Hair Restoration Methods
If smoking or other factors make it challenging to achieve optimal results with a hair transplant, consider exploring alternative hair restoration methods:
Non-Surgical Treatments: Options such as minoxidil (Rogaine) and low-level laser therapy (LLLT) can help promote hair growth without surgery. These treatments may be suitable for individuals who are unable or unwilling to undergo a hair transplant.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting your own platelet-rich plasma into the scalp to stimulate hair growth. This non-surgical option can complement hair transplant procedures or serve as an alternative.
See also: Can Hair Loss from Smoking Be Reversed?
Conclusion
Smoking can significantly impact the healing process and outcomes of a hair transplant. To ensure the best results from your hair transplant surgery, it is crucial to follow recommended guidelines regarding smoking. Avoid smoking during the initial recovery period, ideally quit before the procedure, and consult with your surgeon for personalized advice.
The negative effects of smoking on blood flow, immune response, and wound healing can jeopardize the success of your hair transplant and affect the final aesthetic results. By taking proactive steps to minimize smoking or quit altogether, you can improve your chances of achieving a successful hair transplant and enjoy the benefits of restored, healthy hair.