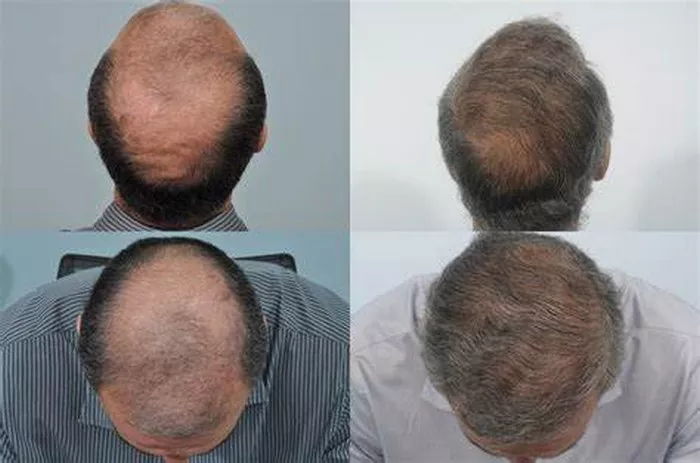
Hair thinning is a common concern for many individuals, and the desire to have thicker, fuller hair is a prevalent one. Understanding whether thin hair can grow back thicker involves exploring the causes of hair thinning, potential treatments, and lifestyle changes that can support hair health. This comprehensive guide delves into these aspects to provide a thorough understanding of how thin hair can potentially regain its thickness.
1. Understanding Hair Thinning
1.1 What Causes Hair Thinning?
Hair thinning can result from various factors, including genetic predisposition, hormonal changes, and lifestyle choices. Identifying the underlying cause of thinning hair is crucial for determining effective treatment strategies.
1.1.1 Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition is one of the most common causes of hair thinning. Conditions such as androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness) affect both men and women, leading to progressive thinning of the hair. This type of hair loss is hereditary and typically occurs due to the influence of androgens (male hormones).
1.1.2 Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes, such as those experienced during pregnancy, menopause, or due to thyroid disorders, can impact hair growth. Hormonal imbalances can lead to temporary or permanent thinning of the hair.
1.1.3 Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of essential nutrients, such as iron, zinc, and vitamins, can contribute to hair thinning. Nutritional deficiencies can weaken hair follicles and impede healthy hair growth.
1.1.4 Stress and Lifestyle Factors
Stress, both physical and emotional, can impact hair health by disrupting the hair growth cycle. Poor lifestyle choices, such as inadequate sleep, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption, can also contribute to hair thinning.
2. Can Thin Hair Grow Back Thicker?
2.1 Factors Influencing Hair Thickness
Several factors influence whether thin hair can grow back thicker. These include the underlying cause of thinning, the effectiveness of treatments, and individual variations in hair growth response.
2.1.1 Hair Follicle Health
The health of hair follicles plays a crucial role in hair thickness. Healthy hair follicles can produce thicker hair strands. Treatments that improve follicle health may support the growth of thicker hair.
2.1.2 Hair Growth Cycle
The hair growth cycle affects how hair grows and sheds. Intervening in the cycle with appropriate treatments can potentially impact hair thickness. For example, promoting the anagen (growth) phase can encourage thicker hair growth.
2.1.3 Treatment Response
Individual responses to hair treatments vary. Factors such as genetics, age, and overall health can influence the effectiveness of treatments aimed at improving hair thickness.
3. Treatments for Thicker Hair
3.1 Medical Treatments
3.1.1 Minoxidil
Minoxidil is an over-the-counter topical treatment that can stimulate hair growth and increase hair thickness. It is commonly used for androgenetic alopecia and is available in various formulations.
3.1.2 Finasteride
Finasteride is a prescription oral medication that reduces levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to hair thinning. By inhibiting DHT, finasteride can help promote thicker hair growth in individuals with androgenetic alopecia.
3.1.3 Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s own blood into the scalp. The growth factors in PRP can stimulate hair follicles and promote thicker hair growth.
3.2 Non-Medical Treatments
3.2.1 Hair Transplant Surgery
Hair transplant surgery involves relocating hair follicles from one area of the scalp to another. This procedure can provide a more permanent solution for thinning hair by transplanting healthy follicles that can grow thicker hair in the recipient area.
3.2.2 Topical Products and Serums
Various topical products and serums contain ingredients designed to support hair health and promote thickness. These products may include biotin, caffeine, and botanical extracts that nourish the scalp and hair follicles.
3.3 Lifestyle and Home Remedies
3.3.1 Scalp Massage
Regular scalp massage can improve blood circulation to the hair follicles, promoting nutrient delivery and encouraging hair growth. Adding essential oils, such as rosemary or peppermint, can enhance the benefits.
3.3.2 Nutritional Supplements
Taking nutritional supplements that provide essential vitamins and minerals can support overall hair health. Supplements such as biotin, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids can contribute to healthier, thicker hair.
3.3.3 Healthy Hair Care Practices
Adopting gentle hair care practices, such as using sulfate-free shampoos and avoiding excessive heat styling, can help prevent further thinning and support hair thickness.
4. Preventing Further Hair Thinning
4.1 Addressing Underlying Causes
Identifying and addressing the underlying causes of hair thinning is essential for preventing further loss. For example, managing hormonal imbalances, improving nutrition, and reducing stress can help mitigate hair thinning.
4.2 Stress Management
Implementing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, exercise, and relaxation practices, can help reduce the impact of stress on hair health. Managing stress effectively can support overall well-being and hair growth.
4.3 Regular Hair Care
Maintaining a consistent and healthy hair care routine can prevent further damage and support hair thickness. Regular washing, conditioning, and gentle handling of hair can contribute to its overall health.
5. Realistic Expectations
5.1 Understanding Limitations
While treatments and lifestyle changes can improve hair thickness, it is important to have realistic expectations. Not all individuals will experience the same results, and some degree of hair thinning may persist despite interventions.
5.2 Embracing Individual Variation
Hair growth and thickness vary among individuals based on genetics, age, and overall health. Embracing individual differences and focusing on achievable improvements can help manage expectations and satisfaction with hair care efforts.
6. Consulting with Professionals
6.1 Dermatologists and Trichologists
Consulting with dermatologists or trichologists can provide personalized guidance on managing hair thinning and promoting thickness. These professionals can conduct assessments, recommend treatments, and offer expert advice.
6.2 Hair Transplant Surgeons
For individuals considering surgical options, consulting with a qualified hair transplant surgeon can provide information on the suitability of hair transplant procedures and potential outcomes.
See also: Which Shampoo Is Best for Thinning Hair?
Conclusion
Thin hair can potentially grow back thicker, but the success of this process depends on various factors, including the underlying cause of thinning, the effectiveness of treatments, and individual responses. By understanding the causes of hair thinning, exploring available treatments, and adopting healthy lifestyle practices, individuals can work towards achieving thicker, fuller hair.
This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights into the possibility of thickening thin hair and offers practical recommendations for improving hair health. Whether through medical treatments, lifestyle changes, or professional consultations, addressing hair thinning requires a multifaceted approach to achieve the best possible outcomes.