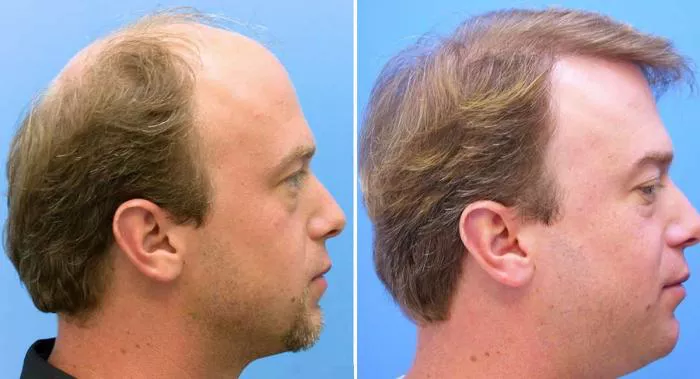
Hair transplantation has gained immense popularity over the years as a solution to combat hair loss and restore hair in balding areas. While many people are familiar with the idea of hair transplants, the process of how transplanted hair grows is less commonly understood. In this article, we will explore the growth stages of transplanted hair, the factors affecting its success, and how to care for transplanted hair after the procedure. This guide is designed to meet the search intent of those who are considering or have already undergone a hair transplant and want to know what to expect during the hair regrowth journey.
What is Hair Transplantation?
Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure where hair follicles are removed from one part of the body, typically the back or sides of the scalp (known as the donor area), and transplanted into the balding or thinning areas (recipient area). The two most common hair transplant techniques are:
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): Involves removing a strip of skin with hair follicles from the donor area and implanting the follicles into the recipient area.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): Involves extracting individual hair follicles and implanting them one by one into the recipient area. This method is less invasive and leaves minimal scarring compared to FUT.
After the procedure, patients can expect hair to regrow in the treated areas, but the process is not immediate. Understanding the stages of transplanted hair growth is crucial for managing expectations and ensuring proper aftercare.
Stages of Transplanted Hair Growth
Transplanted hair goes through distinct stages before full regrowth is achieved. These stages are similar to the natural hair growth cycle, but there are some unique elements to the process after a hair transplant.
1. Dormancy Phase (First 1–4 Weeks Post-Transplant)
Immediately after the hair transplant procedure, the transplanted hair follicles enter a dormant phase. During this time, the transplanted hairs may remain in place for the first couple of weeks before shedding. This initial shedding is completely normal and happens because the hair follicles are adjusting to their new environment.
Shedding: Within 1 to 3 weeks after the transplant, the hair in the transplanted follicles typically sheds. This shedding phase, known as telogen effluvium, is a natural part of the process. It can be alarming, but it’s important to remember that the follicles are still intact beneath the scalp and are preparing to enter the next growth phase.
2. Resting Phase (1–3 Months Post-Transplant)
After the shedding phase, the hair follicles enter a resting phase. This phase can last anywhere from 1 to 3 months, during which no visible hair growth occurs. The transplanted follicles remain dormant as they adapt to their new location.
Healing: During the resting phase, the scalp continues to heal from the transplant. Any redness, swelling, or scabbing from the procedure will subside, and the skin in the recipient area will start to look more normal. This phase requires patience, as it may seem like nothing is happening on the surface, but the follicles are gradually preparing to produce new hair.
3. Early Growth Phase (3–6 Months Post-Transplant)
Around 3 to 4 months after the hair transplant, the early growth phase begins. New hairs start to emerge from the transplanted follicles. These new hairs may be fine, thin, and lighter in color initially, but they will gradually thicken and darken over time.
Growth Pattern: The hair growth in this phase may be uneven, with some areas growing faster than others. It is common to see sporadic hair growth at first, but this will improve as the hair follicles establish themselves.
Texture: New hairs can appear curly or wiry in the beginning, which is temporary. As the hair matures, it will take on the normal texture of the patient’s natural hair.
4. Maturation Phase (6–12 Months Post-Transplant)
The maturation phase typically starts around 6 months after the hair transplant. During this phase, the transplanted hair follicles become fully functional, and the hair starts to grow more consistently.
Thickening: The hair shafts thicken, and the overall density of the transplanted area improves. By the 9-month mark, most patients will see a significant improvement in hair coverage.
Consistency: The color and texture of the hair will normalize, blending seamlessly with the patient’s natural hair.
5. Final Results (12–18 Months Post-Transplant)
By the time 12 to 18 months have passed since the transplant, patients should see the final results of their procedure. At this point, the hair will have reached its full density, and the appearance will be natural.
Full Growth: The transplanted hair will have the same growth patterns as natural hair, including the ability to grow and be cut, styled, and colored just like the rest of the hair on the scalp.
Permanent Results: The hair that grows from the transplanted follicles is permanent and should not fall out in the future, as these follicles are resistant to the effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the hormone responsible for hair loss.
Factors That Affect Transplanted Hair Growth
While the growth stages of transplanted hair are generally predictable, several factors can affect the outcome and speed of growth. Understanding these factors can help patients manage their expectations and take steps to maximize their results.
1. Quality of Donor Hair
The success of a hair transplant largely depends on the quality of the donor hair. Hair taken from the back and sides of the scalp is typically more resistant to hair loss, making it ideal for transplantation. If the donor hair is thin or sparse, it can affect the overall density of the transplant.
2. The Surgeon’s Skill
The experience and skill of the surgeon performing the hair transplant can significantly influence the final results. A skilled surgeon will ensure that the follicles are carefully transplanted in a way that mimics the natural growth patterns of the patient’s hair. This includes considering the angle, direction, and density of the transplanted follicles.
3. Patient’s Age and Health
Younger patients and those in good health tend to experience faster and more robust hair growth after a transplant. Health conditions like diabetes, poor circulation, or scalp infections can delay healing and affect the success of the transplant. It’s important for patients to follow pre- and post-operative instructions to minimize risks and promote healthy regrowth.
4. Aftercare Routine
Proper aftercare is critical to the success of a hair transplant. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions carefully to ensure the newly transplanted follicles have the best chance of thriving. Key aftercare tips include:
Avoiding Touching or Scratching: The scalp will be sensitive after the transplant, and it’s important to avoid scratching or touching the area to prevent dislodging the grafts.
Gentle Washing: Follow the surgeon’s advice on how to wash the hair without causing trauma to the transplanted area.
Avoiding Sun Exposure: Direct sunlight can damage the scalp and affect healing. Patients should protect their scalp with hats or stay indoors during the early recovery period.
Common Myths About Transplanted Hair Growth
Myth 1: Transplanted Hair Falls Out Permanently
Many people are concerned when their transplanted hair sheds after the procedure. However, this is completely normal and temporary. Shedding is part of the telogen phase, and the hair will grow back stronger.
Myth 2: Results Are Immediate
Hair growth after a transplant takes time, and immediate results should not be expected. It takes up to 12 to 18 months for full results to appear, so patience is essential.
Myth 3: Transplanted Hair Requires Special Maintenance
Once the transplanted hair has fully grown in, it does not require any special treatment compared to natural hair. Regular washing, conditioning, and styling routines are all that’s needed to maintain the health of the transplanted hair.
How to Care for Transplanted Hair
1. Follow Post-Operative Instructions
Immediately after the transplant, it’s crucial to follow the specific instructions provided by the surgeon. This includes keeping the scalp clean, avoiding physical strain, and taking any prescribed medications.
2. Use Gentle Hair Products
After the transplant, it’s important to use mild, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners to avoid irritating the scalp. Avoid any harsh chemicals or treatments that could damage the new follicles.
3. Protect Your Scalp
During the healing phase, avoid direct sunlight and harsh environmental factors. Wearing a hat or using sunscreen on the scalp can protect the newly transplanted follicles.
4. Stay Hydrated and Eat a Balanced Diet
Maintaining proper hydration and a diet rich in vitamins and minerals is essential for hair health. Nutrients like biotin, vitamin E, and zinc are known to promote hair growth and can support the overall success of the transplant.
See also: How to Maintain Hair After a Hair Transplant?
Conclusion
Transplanted hair goes through several stages of growth, from an initial shedding phase to full maturation over the course of 12 to 18 months. Patience is key during this process, as the final results take time to develop. Factors like the quality of donor hair, the skill of the surgeon, and proper aftercare all play important roles in the success of a hair transplant. By understanding the growth stages and following recommended care routines, patients can enjoy a natural-looking, long-lasting solution to hair loss.