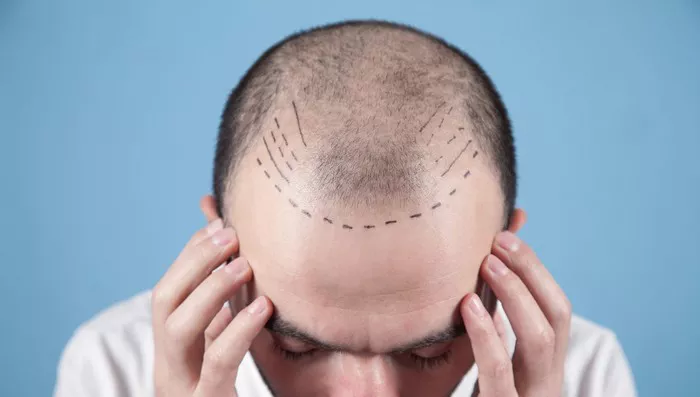
Hair transplant surgery has emerged as a popular solution for individuals dealing with hair loss. One of the most frequently asked questions among potential candidates is, “Where does the hair for a hair transplant come from?” Understanding the sources of donor hair, the techniques involved, and the overall process can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their hair restoration journey. This article delves into the origins of hair used in transplants, the types of donor hair, and the science behind hair restoration.
1. Introduction
Hair loss can have a profound impact on self-esteem and confidence, prompting many to seek solutions such as hair transplants. However, understanding where the hair for these procedures comes from is crucial for anyone considering this option. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the sources of donor hair, the techniques used in hair transplantation, and what potential candidates should know before undergoing the procedure.
2. Understanding Hair Loss
Before diving into the specifics of hair transplant sources, it’s important to understand the types and causes of hair loss that lead individuals to seek out these procedures.
2.1 Types of Hair Loss
Several types of hair loss can affect individuals, including:
Androgenetic Alopecia: Often referred to as male or female pattern baldness, this is the most common form of hair loss, characterized by thinning hair and receding hairlines.
Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune condition that causes patchy hair loss, which can affect both men and women.
Telogen Effluvium: A temporary form of hair loss triggered by stress, illness, or hormonal changes, where hair follicles enter a resting phase prematurely.
Traction Alopecia: Caused by prolonged tension on the hair follicles from styles like tight braids or ponytails.
2.2 Causes of Hair Loss
Hair loss can result from a variety of factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, medications, and lifestyle choices. Understanding these causes can help individuals determine the best course of action for treatment.
3. What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves relocating hair follicles from a donor site to an area of the scalp that is thinning or bald. The goal is to restore hair growth in these regions, resulting in a fuller, natural-looking head of hair.
3.1 Definition and Overview
Hair transplantation is primarily performed on individuals experiencing androgenetic alopecia, although it can also be effective for other forms of hair loss. The procedure involves two main steps: harvesting the donor hair and transplanting it into the recipient area.
3.2 The Purpose of Hair Transplants
The primary purpose of a hair transplant is to restore hair in areas where it has been lost or thinned. This can lead to improved self-confidence and an enhanced appearance, making it a popular choice for many individuals.
4. Sources of Donor Hair
The hair used for transplants can come from various sources. Understanding these sources is essential for candidates considering a hair restoration procedure.
4.1 The Donor Area
The most common source of donor hair is the patient’s own scalp. The area at the back of the head is typically utilized for this purpose due to its resistance to hair loss. This region contains hair follicles that are genetically programmed to remain healthy even in individuals experiencing baldness.
Characteristics: Hair from the donor area is often thicker and healthier, making it ideal for transplantation.
4.2 Hair from Other Areas of the Body
In some cases, hair from other parts of the body may be used, especially if the scalp does not have enough healthy hair. This can include:
Facial Hair: Beard or chest hair may be used for individuals lacking sufficient scalp donor hair.
Body Hair: Hair from the arms or legs can be harvested in certain situations, particularly for FUE techniques.
Using body hair requires careful consideration, as the texture and growth patterns can differ from scalp hair.
4.3 Hair from Donors
Inrare cases, hair from a deceased donor or a living donor may be used. This option is less common and typically reserved for specific circumstances, such as patients with extensive hair loss who have no suitable donor sites.
5. Techniques for Harvesting Donor Hair
The method used to harvest donor hair can influence the overall results of the transplant. There are several techniques, each with its pros and cons.
5.1 Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, which is then dissected into individual follicular units for transplantation. This method allows for the harvesting of a large number of grafts in a single session.
Advantages: FUT can provide a greater number of grafts and is often more cost-effective for extensive hair loss.
Disadvantages: The procedure leaves a linear scar in the donor area, which may be visible if the hair is cut short.
5.2 Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a minimally invasive technique where individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area using a specialized tool. This method leaves tiny, round scars rather than a linear one.
Advantages: FUE has a quicker recovery time and no visible linear scar, making it a popular choice for many patients.
Disadvantages: The process can be more time-consuming and expensive compared to FUT, particularly for larger grafts.
5.3 Robotic Hair Restoration
Robotic hair restoration uses advanced technology to assist in the FUE process, improving accuracy and efficiency. This method offers the benefits of FUE while potentially reducing the overall time of the procedure.
Advantages: Increased precision and reduced human error during the extraction process.
Disadvantages: The availability of robotic systems can be limited, and costs may be higher than traditional methods.
6. Factors Influencing the Choice of Donor Hair
When considering donor hair for a transplant, several factors come into play that can affect the choice of hair and the overall success of the procedure.
6.1 Hair Type and Texture
The type and texture of the hair play a critical role in determining the most suitable donor hair. For example:
Straight vs. Curly: Curly hair may provide better coverage due to its natural volume, while straight hair may be easier to style.
Thickness: Thicker hair strands can give the appearance of fuller hair, which may be preferred for certain patients.
6.2 Donor Hair Quality
The quality of the donor hair significantly impacts the results of the transplant. Healthy, strong hair follicles are more likely to survive the transplantation process and produce new hair.
6.3 Compatibility with Recipient Area
It is essential for the donor hair to match the recipient area in terms of color, texture, and growth pattern. This compatibility ensures that the transplanted hair blends seamlessly with the existing hair.
7. Conclusion
Understanding where the hair for a hair transplant comes from is essential for anyone considering this life-changing procedure. By knowing the sources of donor hair, the techniques involved, and the factors influencing the choice of donor hair, individuals can make informed decisions about their hair restoration options. Hair transplants can offer a new lease on life for those struggling with hair loss, restoring not just hair but also confidence and self-esteem.
This comprehensive guide has explored the journey of hair used in transplants, equipping potential candidates with the knowledge they need to embark on their hair restoration journey confidently. Whether you are dealing with genetic hair loss or the effects of an underlying condition, a hair transplant may provide the solution you’ve been searching for.