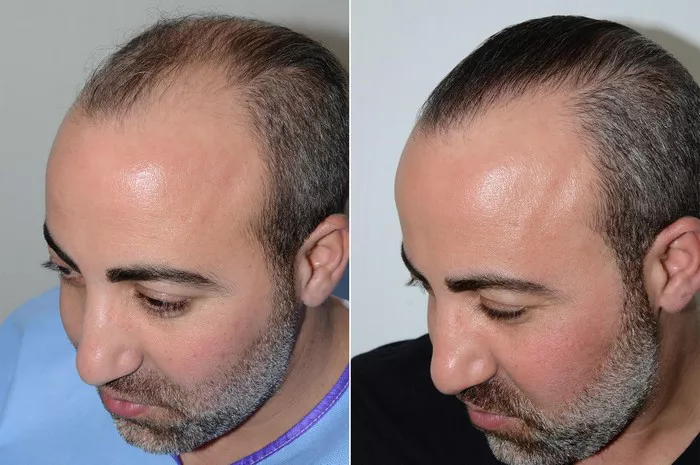
Hair transplants have become a popular and effective solution for individuals facing hair loss, offering a permanent way to restore a fuller head of hair. But one of the most frequently asked questions is, “How long will a hair transplant last?” In this article, we will explore the longevity of hair transplants, factors that affect the durability of results, and what to expect post-surgery.
Understanding the Hair Transplant Process
Before diving into how long a hair transplant lasts, it’s important to understand the procedure itself. Hair transplants work by relocating hair follicles from a donor area—usually the back or sides of the head—to areas experiencing thinning or balding. The follicles transplanted in these areas are genetically resistant to balding, which makes the results long-lasting.
There are two primary techniques used in hair transplants:
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): This method involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, which is then divided into individual follicular units and implanted into the recipient area.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): In this technique, individual follicles are harvested directly from the donor area and transplanted to the balding area. It’s less invasive and leaves minimal scarring compared to FUT.
Both methods offer natural-looking and permanent results, but how long these results last depends on various factors.
The Lifespan of a Hair Transplant
Permanent Nature of Transplanted Hair
The transplanted hair is taken from areas of the scalp that are typically not affected by androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness), meaning the follicles are resistant to the hormone DHT (dihydrotestosterone). Since these hairs are genetically predisposed to resist balding, they continue to grow for a lifetime, even after being transplanted to balding areas.
Initial Shedding Phase
One of the first things that happen after a hair transplant is a phenomenon called “shock loss” or shedding. Around two to four weeks after the surgery, the newly transplanted hairs will fall out. This is a natural part of the process and should not be cause for concern. It happens because the hair follicles temporarily enter a dormant phase.
New Hair Growth
New hair growth typically begins around three to four months after the procedure. At first, the hair may be fine and thin, but it will thicken over time. Full results are generally seen between 12 to 18 months after the transplant, at which point the hair will have grown and matured to match the surrounding hair.
Do Hair Transplants Last Forever?
In general, yes—hair transplants offer a permanent solution to hair loss. However, the transplanted hair will last indefinitely, but that doesn’t necessarily mean you won’t experience hair loss in other areas of your scalp. Here’s what to expect:
The transplanted follicles will continue to grow hair for the rest of your life because they are resistant to the hormone DHT, which causes balding.
Non-transplanted hair may continue to thin or fall out if you’re genetically predisposed to hair loss.
To manage this, some individuals may require additional treatments or medications such as minoxidil or finasteride to prevent further thinning or to address any future hair loss in untreated areas.
See Also: Understanding Hair Grafts: How Do Hair Grafts Work
Factors That Influence the Longevity of a Hair Transplant
Several factors play a role in how long your hair transplant lasts and how satisfied you are with the results. Below are some key influences:
1. Age
Age can impact the long-term success of a hair transplant. Younger patients (in their 20s or early 30s) may still experience significant hair loss after their transplant as the pattern of their balding hasn’t fully stabilized. In contrast, older individuals who have already lost a significant amount of hair are often better candidates since their hair loss has likely slowed or stopped.
2. Genetic Predisposition
The success of your hair transplant also depends on your genetic predisposition to hair loss. Individuals who are genetically inclined to continue losing hair may experience thinning in non-transplanted areas as they age. However, the transplanted hair should remain intact because of its DHT resistance.
3. Hair Transplant Technique
The technique used during the hair transplant can influence the longevity of the results. While both FUT and FUE methods are effective, FUE has a slightly lower graft survival rate because individual follicles are more susceptible to damage during extraction.
4. Surgeon’s Expertise
The skill and experience of the surgeon performing the transplant play a crucial role in the success and longevity of the procedure. An experienced surgeon knows how to handle the delicate grafts, ensure natural placement, and minimize damage, which increases the chances of the transplanted hair lasting a lifetime.
5. Aftercare and Maintenance Proper post-surgery care is critical to ensur
e the longevity of the results. Your surgeon will provide detailed instructions on how to care for your scalp after the transplant. This will likely include avoiding direct sunlight, refraining from heavy exercise, and using specialized hair care products. Following these guidelines will promote proper healing and graft survival.
Can You Lose Transplanted Hair?
While transplanted hair is generally permanent, it’s possible to experience hair loss in the following situations:
Shock Loss: This temporary shedding happens within the first few weeks post-surgery but should not affect long-term growth.
Health Conditions: Some underlying health conditions or lifestyle factors, such as poor diet or stress, can impact hair growth and cause thinning, including in transplanted areas.
Trauma to the Scalp: Physical trauma or conditions like scarring alopecia can cause hair loss, even in transplanted areas.
Aging: Although the transplanted hair is DHT-resistant, hair naturally becomes finer and thinner as we age. This won’t lead to full hair loss, but it might result in a change in hair texture or thickness over time.
The Role of Medications and Follow-up Treatments
To maintain the health of both transplanted and non-transplanted hair, many patients choose to continue using hair loss medications. Finasteride and minoxidil are two common medications that can help slow down hair loss and improve the overall density of hair. These treatments can be especially beneficial for younger individuals or those with a family history of aggressive hair loss.
In some cases, patients might consider Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy as a follow-up treatment. PRP involves injecting a concentration of platelets from your own blood into the scalp to stimulate hair growth and improve the quality of both transplanted and native hair.
How to Maximize the Lifespan of Your Hair Transplant
There are several steps you can take to ensure the longevity of your hair transplant:
1. Choose an Experienced Surgeon
Selecting a board-certified and experienced hair transplant surgeon is critical. A skilled surgeon will not only give you natural-looking results but also ensure that the transplanted follicles are handled properly and placed in a way that maximizes their survival.
2. Follow Post-Op Care Instructions
The aftercare phase is just as important as the surgery itself. Make sure to follow all the instructions provided by your surgeon, including how to wash your scalp, when to resume physical activities, and how to protect your scalp from sunlight.
3. Consider Hair Loss Medication
Medications like minoxidil or finasteride can be helpful for maintaining the overall health of your hair. Consult your doctor about whether these treatments are right for you.
4. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
A well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support healthy hair growth. Additionally, managing stress and avoiding smoking can promote better hair health and longevity.
5. Be Prepared for Future Treatments
Some patients may require follow-up hair transplants if hair loss continues in untreated areas. Having realistic expectations about this possibility will help you plan for the future.
Realistic Expectations: What to Know Before Getting a Hair Transplant
While hair transplants offer a permanent solution to hair loss, it’s important to have realistic expectations. The transplanted hair will last a lifetime, but you might need future treatments if your non-transplanted hair continues to thin.
Results can vary depending on the severity of your hair loss, your age, and your genetics. Consulting with a qualified surgeon will give you a clearer picture of what to expect in your specific case.
The Cost of a Hair Transplant and its Longevity
Hair transplants are a significant investment, and the cost can vary depending on factors like the number of grafts, the surgeon’s experience, and the location of the clinic. On average, hair transplants can cost anywhere from $4,000 to $15,000.
However, considering the longevity of the results—potentially lasting a lifetime—the cost can be seen as a one-time investment in your appearance and confidence.
Conclusion: Is a Hair Transplant Worth It?
If you’re looking for a permanent solution to hair loss, a hair transplant is one of the most reliable and long-lasting options available. The transplanted hair follicles are resistant to the effects of balding, which means they will continue to grow for a lifetime.
However, the longevity of your hair transplant results depends on factors like your age, genetics, the expertise of your surgeon, and how well you care for your scalp post-surgery. By choosing a skilled surgeon and following the right aftercare routine, you can enjoy the benefits of a full head of hair for many years to come.
In the end, a hair transplant is a long-term investment in yourself—offering not only restored hair but also renewed confidence.
You Might Be Interested In
The Ideal Age for a Hair Transplant: When is the Right Time?
How Many Hair Transplants Can I Have?