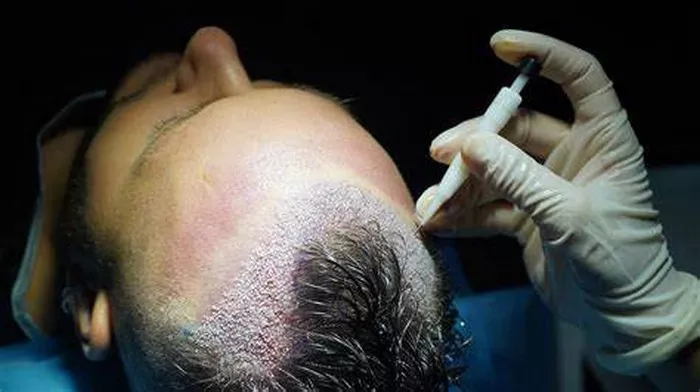
Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, prompting many to seek effective solutions. Among the most popular methods are Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). This article explores the intricacies of these two hair transplant techniques, comparing their procedures, benefits, drawbacks, and suitability to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding Hair Loss
1. Causes of Hair Loss
Before diving into the specifics of hair transplants, it’s crucial to understand the common causes of hair loss, which include:
Genetics: The most prevalent cause, often referred to as androgenetic alopecia.
Hormonal Changes: Conditions like pregnancy, menopause, and thyroid issues can lead to hair loss.
Medical Conditions: Certain illnesses, such as alopecia areata or scalp infections, can contribute.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential vitamins and minerals can affect hair health.
Stress: High levels of stress can trigger temporary hair loss.
2. Psychological Impact
Hair loss can lead to significant emotional distress, affecting self-esteem and overall quality of life. Many individuals consider hair transplants as a way to regain confidence and improve their appearance.
Overview of Hair Transplant Techniques
Hair transplant techniques aim to restore hair by relocating hair follicles from a donor site (usually the back of the head) to the balding areas. The two primary methods are FUE and FUT.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
1. What is FUE?
FUE is a minimally invasive hair transplant technique that involves extracting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area. This method eliminates the need for a linear incision, resulting in less scarring.
2. The FUE Procedure
Consultation: A thorough evaluation by a hair transplant specialist to determine suitability.
Preparation: The donor area is shaved and cleaned, and local anesthesia is administered.
Extraction: Using a specialized punch tool, individual follicles are extracted. This process can take several hours, depending on the number of follicles needed.
Implantation: The extracted follicles are then meticulously implanted into the recipient area, ensuring natural hair growth patterns.
3. Benefits of FUE
Minimal Scarring: Since no linear incision is made, the risk of noticeable scarring is significantly reduced.
Faster Recovery: Patients often experience quicker recovery times, allowing for a return to normal activities sooner.
Natural Results: The precision of follicle extraction and implantation results in a natural-looking hairline.
4. Drawbacks of FUE
Longer Procedure Time: FUE can take longer than FUT due to the meticulous nature of extracting individual follicles.
Cost: Generally, FUE is more expensive than FUT due to the advanced technology and time required.
Limited Graft Availability: For patients needing a large number of grafts, FUE may require multiple sessions.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
1. What is FUT?
FUT, also known as strip harvesting, involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area, which contains hair follicles. The strip is then dissected into individual follicular units for transplantation.
2. The FUT Procedure
Consultation: Similar to FUE, an evaluation is conducted to determine if the patient is a good candidate.
Preparation: The donor area is shaved, and local anesthesia is applied.
Strip Harvesting: A strip of scalp is surgically removed from the donor area. The edges are then stitched together.
Graft Preparation: The strip is dissected into individual follicular units under a microscope.
Implantation: The prepared grafts are implanted into the recipient area, following the natural hair growth pattern.
3. Benefits of FUT
Higher Graft Yield: FUT can often yield more grafts in a single session, making it suitable for patients with extensive hair loss.
Cost-Effective: Generally, FUT is less expensive than FUE due to the simpler extraction process.
Less Time on the Table: The initial harvesting phase is quicker compared to the meticulous individual extraction in FUE.
4. Drawbacks of FUT
Linear Scarring: FUT leaves a linear scar at the donor site, which may be visible if the hair is cut short.
Longer Recovery: Recovery may take longer due to the surgical incision, and patients may experience more discomfort post-surgery.
Restricted Activity: Patients may need to avoid strenuous activities for a longer period post-surgery.
Comparing FUE and FUT
1. Scarring
FUE: Minimal, point-like scars.
FUT: Linear scar that may be more noticeable.
2. Recovery Time
FUE: Quicker recovery, typically within a few days.
FUT: Longer recovery, usually taking a week or more.
3. Graft Availability
FUE: May require multiple sessions for large graft numbers.
FUT: Typically provides more grafts in a single session.
4. Cost
FUE: Generally more expensive.
FUT: More budget-friendly.
Who Should Choose FUE?
FUE is ideal for:
Individuals who prefer minimal scarring and quicker recovery.
Patients with shorter hair or those who want to wear their hair short.
People who have previously undergone hair transplant procedures and wish to fill in gaps.
Who Should Choose FUT?
FUT may be suitable for:
Patients with extensive hair loss needing a significant number of grafts.
Individuals who don’t mind a linear scar and have longer hair to cover it.
Those seeking a more cost-effective solution for hair restoration.
Post-Procedure Care
1. Immediate Care
Following either procedure, patients should expect some redness and swelling. Proper aftercare is essential to promote healing:
Avoid touching or scratching the treated area.
Follow the surgeon’s instructions regarding washing and caring for the scalp.
2. Long-Term Care
Hair Washing: Use gentle shampoos and avoid vigorous scrubbing.
Sun Protection: Protect the scalp from direct sunlight, especially during the initial healing phase.
Nutritional Support: A balanced diet can aid in the healing process and promote hair growth.
Expected Results
1. Hair Growth Timeline
After the transplant, patients can expect:
Initial Shedding: Some transplanted hairs may fall out within the first few weeks, a normal part of the process.
Growth Resumption: New hair growth typically starts around three to four months post-procedure.
Full Results: Final results may take up to 12 months to become fully apparent.
2. Realistic Expectations
While hair transplants can significantly improve appearance, results can vary based on individual factors, including hair type, density, and adherence to post-operative care.
Conclusion
Choosing between FUE and FUT hair transplant techniques depends on individual circumstances, including hair loss extent, budget, and personal preferences. Both methods offer effective solutions for hair restoration, each with its own set of advantages and challenges. Consulting with a qualified hair transplant specialist can help you determine the best approach for your specific needs, leading to a successful outcome and renewed confidence. By understanding these techniques, you can make an informed decision about your journey towards restoring your hair and self-esteem.
Related topics:
- What Is DHI Hair Transplant? A Complete Guide
- The Right Age for a Hair Transplant: Timing Your Decision
- Natural Ways to Regrow Edges: A Comprehensive Guide