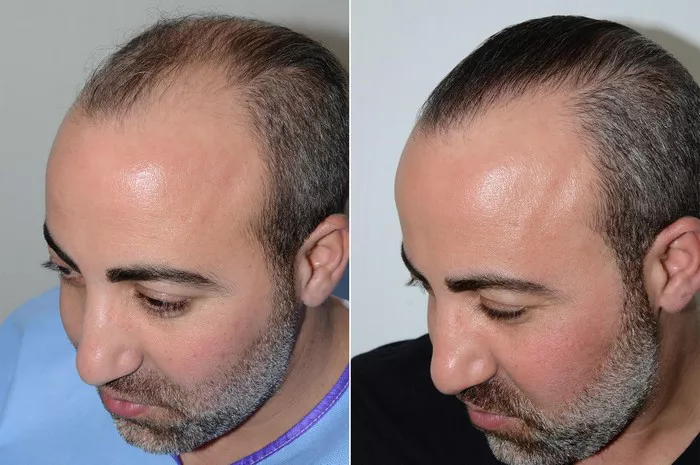
An M-shaped hairline, often characterized by a distinct peak in the center with receding sides, raises questions for many individuals regarding its implications for hair health. While some may see it as a sign of aging or balding, it’s essential to understand the context of hairlines and the factors that influence them. This article will explore the nature of M-shaped hairlines, their association with balding, and the various causes and treatments available.
Understanding Hairlines
The Anatomy of Hairlines
Hairlines can vary widely among individuals, influenced by genetics, age, and overall health. They are categorized into several shapes, including straight, widow’s peak, and M-shaped. The M-shaped hairline is particularly common in men but can also appear in women.
Characteristics of an M-Shaped Hairline
An M-shaped hairline is defined by:
Distinct Peaks: The hairline forms a pronounced peak in the center, resembling the letter “M.”
Receding Sides: The sides of the hairline gradually recede, often creating a “V” shape.
This pattern can become more pronounced over time and is often associated with male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia.
Causes of an M-Shaped Hairline
1. Genetic Factors
Genetics plays a significant role in determining hairline shape and hair loss patterns. If there is a family history of baldness, individuals may be more prone to developing an M-shaped hairline as they age.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly androgens like testosterone, can influence hair growth. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone, is a primary factor in hair loss for both men and women. Elevated DHT levels can lead to hair follicle miniaturization, contributing to a receding hairline.
3. Aging
As individuals age, hair naturally thins, and hairlines may recede. The M-shaped hairline can become more noticeable as the density of hair decreases, leading many to interpret this change as balding.
4. Health Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or autoimmune diseases, can impact hair growth. These conditions may lead to hair thinning and changes in hairline shape.
Is an M-Shaped Hairline a Sign of Balding?
1. Contextual Factors
While an M-shaped hairline can be associated with balding, it is not an absolute indicator. Several contextual factors must be considered:
Age: Younger individuals may develop an M-shaped hairline without experiencing significant balding.
Hair Density: If the overall hair density remains high, an M-shaped hairline may not indicate advanced balding.
Family History: A family history of varied hairline shapes may suggest that not all M-shaped hairlines lead to balding.
2. Distinguishing Between Normal Variation and Balding
It’s crucial to differentiate between a naturally occurring M-shaped hairline and one that signals impending baldness. Monitoring the progression over time can provide insight:
Consistency: If the hairline has been stable for years, it may be a natural trait.
Change Over Time: Rapid changes, such as increased thinning or noticeable recession, can indicate balding.
Assessing Hair Loss: Signs to Look For
1. Thinning Hair
If the hair density in the crown or temples decreases significantly, it may be a sign of balding rather than just an M-shaped hairline.
2. Bald Spots
The presence of bald spots or patches on the scalp can indicate more severe hair loss and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
3. Shedding
Increased hair shedding, particularly in the shower or during styling, can signal hair loss. Noticing clumps of hair or excessive hair loss on pillows can be concerning.
4. Family Patterns
Understanding family history can help gauge the likelihood of developing baldness. If male or female relatives have experienced similar patterns, it may increase your chances.
Options for Addressing an M-Shaped Hairline
1. Lifestyle Changes
Healthy lifestyle choices can promote better hair health:
Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports hair health. Nutrients like biotin, zinc, and vitamins A, C, and E are crucial.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can contribute to hair loss. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and exercise can help mitigate stress.
2. Non-Surgical Treatments
Several non-surgical options can help address hair loss:
Minoxidil (Rogaine)
Description: An over-the-counter topical treatment applied to the scalp.
Effectiveness: Minoxidil can help stimulate hair growth and slow down hair loss for some individuals.
Finasteride (Propecia)
Description: A prescription oral medication that reduces DHT levels.
Effectiveness: Finasteride can slow hair loss and, in some cases, promote regrowth.
3. Hair Transplant Surgery
For individuals with significant hair loss, hair transplant surgery can provide a more permanent solution:
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
Procedure: Involves removing a strip of scalp and transplanting hair follicles to balding areas.
Pros and Cons: Effective for extensive hair loss but leaves a linear scar.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
Procedure: Individual hair follicles are extracted and transplanted.
Pros and Cons: Less invasive with no linear scar, but typically more expensive.
4. Scalp Micropigmentation
This non-surgical technique involves tattooing tiny dots on the scalp to create the illusion of hair follicles. It can effectively enhance the appearance of a receding hairline.
Psychological Impact of an M-Shaped Hairline
1. Self-Esteem and Confidence
Hair loss can have a profound impact on self-esteem and confidence. Individuals may feel less attractive or younger as their hairlines change.
2. Social Perceptions
Societal standards of beauty often equate a full head of hair with youthfulness. This perception can contribute to feelings of inadequacy in individuals with receding hairlines.
3. Coping Mechanisms
It’s essential to develop healthy coping mechanisms for dealing with hair loss:
Support Groups: Connecting with others experiencing similar issues can provide emotional support.
Professional Counseling: Seeking professional help can aid in addressing feelings of anxiety or depression related to hair loss.
Preventive Measures
1. Regular Scalp Care
Maintaining a healthy scalp can promote hair health. Regular washing, gentle brushing, and avoiding harsh products can help maintain the scalp’s environment.
2. Avoiding Heat and Chemical Damage
Minimizing the use of heat styling tools and harsh chemicals can prevent damage to hair and promote healthier growth.
3. Regular Check-Ups
Consulting with a dermatologist or trichologist can help monitor hair health and address any underlying conditions contributing to hair loss.
Conclusion
An M-shaped hairline can signify potential balding, but it is not a definitive indicator. Understanding the various factors influencing hairline shape, monitoring changes over time, and exploring available options can empower individuals facing this concern. From lifestyle changes to medical treatments, there are numerous avenues to address hair loss and promote confidence. Ultimately, seeking professional guidance and support can lead to effective solutions tailored to individual needs.
Related topics:
- How to Regrow Your Hairline Naturally: Effective Strategies
- Can You Get a New Hairline? Exploring Options and Techniques
- How Long Does a Hairline Transplant Last? Insights and Care