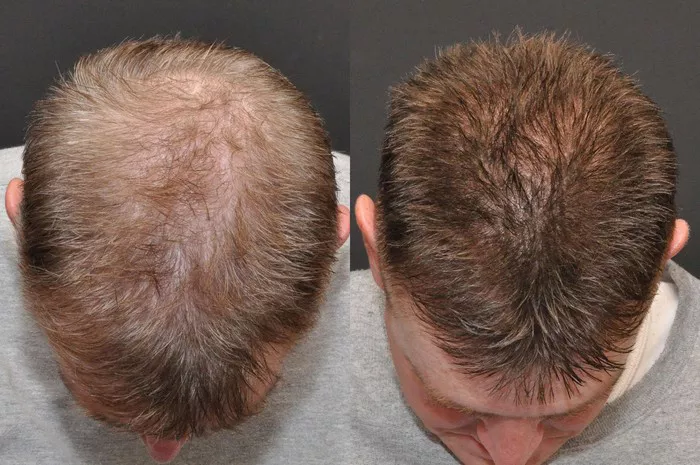
Alopecia, characterized by hair loss that can vary in severity and type, affects millions of people worldwide. For those grappling with this condition, a hair transplant may seem like a promising solution. However, questions often arise regarding its effectiveness for various forms of alopecia. This comprehensive article explores the relationship between hair transplants and alopecia, discussing how the procedure works, its suitability for different types of alopecia, potential outcomes, and considerations for individuals contemplating this surgical intervention.
1. Understanding Alopecia: Types and Causes
Alopecia encompasses several forms of hair loss, each with distinct characteristics and causes. Understanding these variations is crucial for determining whether a hair transplant is an appropriate treatment option.
Androgenetic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness)
Description: The most common form of hair loss, affecting both men and women. It is characterized by a gradual thinning of hair, often starting at the temples or crown.
Causes: Genetic predisposition and hormonal factors, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Alopecia Areata
Description: An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss.
Causes: The exact cause is unknown, but genetic and environmental factors may play a role.
Alopecia Totalis and Universalis
Description: More severe forms of alopecia areata, resulting in total hair loss on the scalp (totalis) or throughout the body (universalis).
Causes: Similar to alopecia areata, with an autoimmune component.
Traction Alopecia
Description: Hair loss caused by prolonged tension on the hair follicles, often from tight hairstyles.
Causes: Repetitive pulling on hair strands over time.
Cicatricial Alopecia
Description: Scarring alopecia, where inflammation damages hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss.
Causes: Autoimmune conditions or skin disorders.
Understanding the type of alopecia is essential, as it significantly influences the effectiveness of hair transplant surgery.
2. How Hair Transplants Work
Hair transplants involve relocating hair follicles from a donor site (usually the back or sides of the scalp) to the thinning or balding areas. There are two primary methods for performing hair transplants:
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
Procedure: Individual hair follicles are extracted using a specialized tool and then transplanted to the desired area.
Benefits: Minimally invasive, with less visible scarring and a quicker recovery time.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
Procedure: A strip of scalp containing hair follicles is surgically removed, and individual follicular units are transplanted.
Benefits: Can harvest a larger number of follicles in one session, making it suitable for extensive hair loss.
Understanding these methods helps evaluate their effectiveness for different alopecia types.
3. Hair Transplants for Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia is the most suitable type of alopecia for hair transplant surgery due to its predictable nature and the presence of donor hair.
Success Rates
Research Findings: Numerous studies indicate high success rates, with over 90% of patients experiencing significant hair regrowth after surgery.
Longevity: Transplanted hair is generally permanent, as the follicles are resistant to DHT.
Ideal Candidates
Individuals in the early to moderate stages of hair loss are typically the best candidates.
Adequate donor hair supply is essential for successful transplantation.
4. Hair Transplants for Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata presents a unique challenge for hair transplants due to its unpredictable nature.
Success Rates and Considerations
Variable Results: While some patients may experience success, others may see little to no improvement due to the autoimmune nature of the condition.
Regrowth Potential: Hair may regrow in untreated areas, making transplants less effective or necessary.
Ideal Candidates
Individuals with stable alopecia areata (those not experiencing active hair loss) may be better candidates.
Consultation with a dermatologist is crucial for assessing the condition’s stability.
5. Hair Transplants for Alopecia Totalis and Universalis
Transplanting hair in cases of totalis or universalis is generally not recommended due to the comprehensive nature of hair loss.
Challenges and Limitations
Lack of Donor Hair: These conditions often result in a complete lack of donor hair, making transplantation impractical.
Unpredictable Results: Even if donor hair is available, the autoimmune response may hinder growth in transplanted areas.
Alternative Treatments
Patients may consider other treatments, such as corticosteroid injections, topical immunotherapy, or other medical options.
6. Hair Transplants for Traction Alopecia
Traction alopecia may benefit from hair transplants if caught early enough.
Success Rates
Positive Outcomes: Transplants can effectively restore hair in areas affected by traction alopecia, especially if the damage is not permanent.
Preventive Measures: Adjusting hairstyles to reduce tension is crucial for long-term success.
Ideal Candidates
Individuals with early-stage traction alopecia, where hair follicles are still viable, are good candidates.
7. Hair Transplants for Cicatricial Alopecia
Cicatricial alopecia poses significant challenges for hair transplant candidates.
Considerations for Transplantation
Permanent Damage: The scarring process can permanently destroy hair follicles, making transplantation ineffective.
Assessment: A thorough evaluation by a dermatologist is essential to assess the condition and potential for hair regrowth.
Alternative Treatments
Treatments aimed at reducing inflammation or managing the underlying condition may be more appropriate.
8. Factors Influencing Hair Transplant Success
Numerous factors can impact the success of hair transplant surgery, regardless of the type of alopecia.
Age and Gender
Younger patients often experience better outcomes due to healthier hair follicles.
Gender may also play a role, as hormonal factors can affect hair growth patterns.
Overall Health
Good overall health improves healing and recovery, making it essential to address any medical conditions before surgery.
Surgeon Expertise
Choosing a qualified, experienced surgeon is crucial for achieving optimal results. Researching credentials and past work can help ensure a successful procedure.
9. Preparing for a Hair Transplant
Preparation is key to a successful hair transplant experience.
Pre-Procedure Consultation
A thorough evaluation by a hair restoration specialist will help determine the suitability of the procedure for your specific type of alopecia.
Discussing Expectations
Patients should have realistic expectations regarding potential outcomes, recovery time, and costs involved.
10. Post-Procedure Care and Recovery
Understanding what to expect after a hair transplant is vital for recovery.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Patients should follow their surgeon’s aftercare instructions carefully, which may include avoiding strenuous activities and following a specific hair care regimen.
Monitoring Results
Hair growth may take several months to become noticeable, with full results typically visible within 6 to 12 months.
11. Long-Term Outcomes and Maintenance
Long-term care and maintenance can enhance the success of a hair transplant.
Regular Follow-Ups
Scheduling regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon can help monitor progress and address any concerns.
Maintaining Scalp Health
Using gentle hair care products and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to the longevity of transplanted hair.
12. Conclusion
Hair transplants can be an effective solution for certain types of alopecia, particularly androgenetic alopecia. However, the success of the procedure varies depending on the type of hair loss, individual health factors, and proper pre- and post-operative care. By understanding the nuances of each alopecia type and consulting with a qualified specialist, individuals can make informed decisions about their hair restoration options. With the right approach, a hair transplant can lead to restored confidence and a fuller head of hair for those struggling with hair loss.
Related topics:
- Does FUE Leave Scars? Understanding Follicular Unit Extraction
- Understanding Post-Transplant Numbness: Duration and Recovery
- Essential Post-Hair Transplant Care: Steps for Best Results