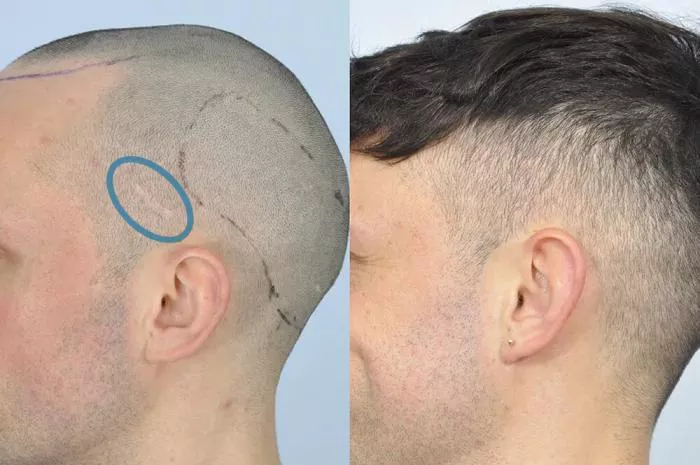
Hair loss can be a distressing issue for many individuals, affecting self-confidence and overall quality of life. Fortunately, advancements in medical technology have led to effective solutions like hair transplants. For those considering this procedure, a common question is whether the transplanted hair actually grows. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the science behind hair transplants, the factors that influence hair growth, and what patients can expect from the procedure.
Understanding Hair Transplants
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure designed to restore hair to areas of the scalp where it has thinned or fallen out. The process involves removing hair follicles from a donor site, typically the back or sides of the scalp, and transplanting them to the recipient site, usually the top or front of the head. The goal is to create a natural-looking hairline and increase hair density.
There are two primary methods of hair transplantation:
Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT): Also known as strip surgery, this method involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area and dissecting it into individual follicular units. These units are then implanted into the recipient area.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): This technique involves extracting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area using a small punch tool. The follicles are then implanted into the recipient area.
Both methods are effective, but FUE is often preferred for its minimal scarring and faster recovery time.
The Science Behind Hair Growth
To understand why transplanted hair grows, it’s essential to delve into the biology of hair follicles. Hair follicles are miniaturized structures in the skin that produce hair. Each follicle contains stem cells that are responsible for hair growth. These stem cells are programmed to produce hair in cycles, consisting of growth (anagen), regression (catagen), and rest (telogen) phases.
When hair follicles are transplanted, they retain their genetic programming and continue to produce hair in the new location. This is because the donor area, typically the back and sides of the scalp, contains follicles that are resistant to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is a primary cause of hair loss. By transplanting these DHT-resistant follicles to the recipient area, the hair continues to grow naturally.
Factors Influencing Hair Growth After Transplant
Several factors can influence the success of hair growth after a transplant:
- Genetic Factors: The genetic makeup of the donor follicles plays a significant role in their ability to grow in the new location. Follicles from the donor area are chosen because they are genetically programmed to resist hair loss, ensuring that they continue to grow even in areas prone to balding.
- Technique and Skill of the Surgeon: The expertise of the surgeon performing the transplant is crucial. Proper extraction and implantation techniques ensure that the follicles are not damaged and are placed at the correct angle and depth for optimal growth.
- Post-Operative Care: Following the surgeon’s post-operative instructions is essential for successful hair growth. This includes avoiding strenuous activities, protecting the scalp from direct sunlight, and using prescribed medications to prevent infection and promote healing.
- Nutrition and Lifestyle: A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, such as proteins, vitamins, and minerals, supports hair growth. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including managing stress and getting adequate sleep, can positively impact the results of a hair transplant.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or autoimmune diseases, can affect hair growth. Patients with these conditions should consult their doctor to manage any underlying issues that could impact the success of the transplant.
The Timeline for Hair Growth After Transplant
Understanding the timeline for hair growth after a transplant can help set realistic expectations and reduce anxiety. Here’s a general overview of what patients can expect:
- First Week: Immediately after the procedure, the scalp may be swollen and tender. Patients may experience some discomfort and itching, but these symptoms usually subside within a week. It’s important to follow post-operative care instructions carefully during this period.
- Two to Four Weeks: Within the first few weeks, the transplanted hair will typically fall out. This is a normal part of the process and does not indicate failure. The hair follicles are still active and will begin to regrow in the coming months.
- Three to Six Months: New hair growth usually begins around three months after the transplant. Initially, the hair may be fine and soft, but it will gradually thicken and become more robust.
- Six to Twelve Months: By six to twelve months, most patients will see significant hair growth. The hair should be fully grown and integrated into the scalp, creating a natural-looking result.
- One Year and Beyond: After one year, the final results of the hair transplant should be visible. The transplanted hair will continue to grow and behave like natural hair, requiring regular maintenance and care.
Tips for Maximizing Hair Growth After Transplant
To maximize the chances of successful hair growth after a transplant, patients can take several steps:
- Follow Post-Operative Instructions: Adhere to the surgeon’s post-operative care guidelines, including avoiding strenuous activities, protecting the scalp from direct sunlight, and using prescribed medications.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals to support hair growth. Foods high in biotin, vitamin E, and omega-3 fatty acids are particularly beneficial.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact hair growth. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get enough restorative sleep each night, as sleep is essential for overall health and hair growth.
- Avoid Harmful Habits: Refrain from smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as these habits can impede the healing process and affect hair growth.
- Use Scalp Treatments: Some patients find that using scalp treatments, such as minoxidil or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, can enhance hair growth and thickness.
Conclusion
Hair transplants are a highly effective solution for restoring hair and improving the appearance of those affected by hair loss. The transplanted hair does indeed grow, thanks to the genetic resistance of the donor follicles and the skill of the surgeon. By understanding the science behind hair growth, following post-operative care instructions, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, patients can achieve natural-looking and long-lasting results. If you’re considering a hair transplant, consult with a qualified hair restoration specialist to discuss your options and determine the best course of treatment for your needs.