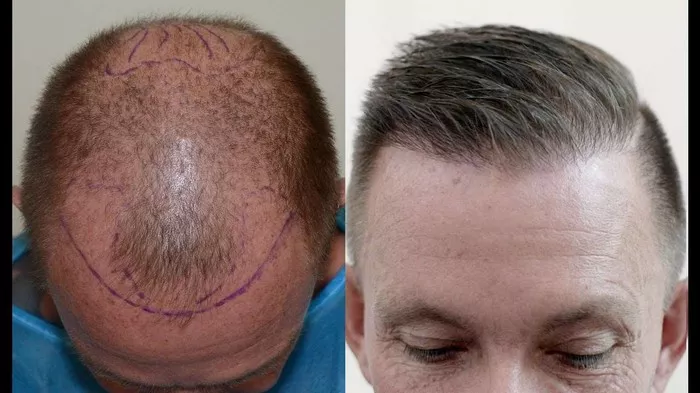
Hair transplantation has become one of the most popular solutions for hair loss, offering individuals a chance to restore hair that looks and feels natural. However, a question that commonly arises is: Will transplanted hair last forever? Understanding the long-term viability of transplanted hair involves examining multiple factors, such as the genetic characteristics of donor hair, the techniques used, and the effects of aging and lifestyle.
In this comprehensive article, we’ll delve into the longevity of transplanted hair, factors influencing its durability, and what individuals can expect from this investment over time. We will also discuss the role of ongoing care and whether additional procedures might be necessary to maintain the desired results.
Understanding Hair Transplantation: How Does It Work?
To understand if transplanted hair will last forever, it’s essential to first know the basics of hair transplantation. The procedure typically involves the transfer of hair follicles from one part of the scalp (usually the back and sides of the head) to the balding or thinning areas. The two primary techniques used are Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT).
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
Procedure: In FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted from the donor area and implanted one by one into the recipient area. This technique minimizes scarring and allows for a more natural look.
Advantages: FUE is less invasive than FUT, leaves tiny, almost invisible scars, and has a quicker recovery time. It also provides flexibility in choosing the best follicles to transfer, which contributes to the durability of the results.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
Procedure: In FUT, a strip of scalp is removed from the donor area, and hair follicles are dissected from this strip before being transplanted. This technique is known for its efficiency in treating larger areas of hair loss.
Advantages: FUT allows for the transplantation of a large number of follicles in a single session, making it an effective solution for individuals needing extensive coverage. However, FUT leaves a linear scar, which might be a consideration for those who prefer shorter hairstyles.
Both FUE and FUT are effective for creating a long-lasting solution to hair loss, but understanding their differences helps in assessing the procedure’s impact on hair longevity.
The Genetics of Donor Hair: Why It Matters
The durability of transplanted hair primarily hinges on the genetic characteristics of the donor hair. Here’s why this is crucial to understanding whether transplanted hair can last forever.
Resistance to DHT
Hair follicles in the back and sides of the scalp are genetically resistant to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the hormone responsible for hair loss in androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness). Because DHT affects the hair follicles in the frontal and crown areas, it does not impact the follicles in the donor region as strongly.
Result: This genetic resistance makes transplanted hair less likely to fall out due to DHT, meaning it has a higher chance of lasting longer than the hair that originally occupied the thinning areas.
Permanent Hair Follicles
The donor hair used in hair transplants consists of permanent hair follicles, which means that they retain their original properties even after being moved to a new location.
Result: Once transplanted, these follicles continue to grow and behave like they did in their original location, maintaining the same growth cycles and resistance to hormonal changes.
However, it’s essential to remember that while donor hair is generally more resistant to hair loss, it is not immune to the effects of aging and other factors.
Factors Influencing the Longevity of Transplanted Hair
While transplanted hair has a strong potential for lasting long-term, several factors can affect its overall lifespan. These include aging, ongoing hair loss, health conditions, lifestyle choices, and the skill of the surgeon.
The Natural Aging Process
As we age, our hair undergoes natural changes, such as reduced density and slower growth rates. This aging process affects both transplanted and non-transplanted hair.
Result: Although transplanted hair remains relatively stable, it may thin slightly as part of the natural aging process. This change is typically gradual and less noticeable than pattern baldness but can still affect the overall appearance.
Progressive Hair Loss in Untreated Areas
Hair transplantation does not prevent further hair loss in untreated areas of the scalp. Patients experiencing pattern baldness may continue to lose hair around the transplanted areas, creating the need for additional treatments or touch-ups.
Solution: Many individuals opt for follow-up procedures to maintain consistency in hair density and achieve a more uniform look over time.
Health and Lifestyle Factors
Several health and lifestyle factors can impact the longevity of transplanted hair. Poor nutrition, stress, smoking, and certain medications can weaken hair follicles over time, including transplanted ones.
Tip: Maintaining a balanced diet, minimizing stress, and following a healthy lifestyle can help preserve the strength and health of your transplanted hair, maximizing its lifespan.
Surgeon’s Skill and Experience
The skill and experience of the surgeon significantly affect the success and longevity of a hair transplant. Proper graft placement, handling, and density can all contribute to the natural look and durability of the transplanted hair.
Importance of Choosing an Experienced Surgeon: An experienced surgeon understands how to angle and place each graft to mimic natural hair growth patterns, ensuring long-lasting and aesthetically pleasing results.
What Patients Can Expect Over Time: Short-Term vs. Long-Term Results
Hair transplantation results don’t appear overnight; the process requires patience and realistic expectations. Here’s what you can generally expect in terms of short-term and long-term results.
Short-Term Results (0–12 Months)
Initial Shedding (0–3 Months): It’s normal for transplanted hair to shed within the first few weeks, a process known as shock loss. This temporary shedding is a sign that the grafts are adapting to their new location.
Growth Phase (3–12 Months): After the shedding phase, new hair growth begins. The transplanted hair will start to emerge, showing steady growth over the following months. By the 12-month mark, most patients see the full results of their transplant.
Long-Term Results (1 Year and Beyond)
Stability and Maintenance: Once transplanted hair has fully grown, it remains relatively stable due to its genetic resistance to hair loss. Many patients enjoy long-lasting results that require minimal maintenance.
Potential for Additional Procedures: Some patients choose to undergo touch-up procedures as they age or if they experience further hair loss in untreated areas. This approach helps maintain the overall look and density of the hair.
Can Transplanted Hair Ever Fall Out? Understanding the Limits
Although transplanted hair is designed to last a lifetime, there are circumstances where it may thin or fall out over the years.
Aging and Thinning
As previously mentioned, aging can cause gradual thinning, even in transplanted hair. This thinning is a natural part of the aging process and does not necessarily indicate hair loss.
Health Conditions
Certain health conditions, such as autoimmune disorders or scalp infections, can affect hair growth, including transplanted hair. In these cases, the follicles may become damaged or fall out due to underlying health issues.
Mechanical Damage
Frequent pulling or trauma to the transplanted area can weaken the follicles, causing them to fall out. Avoiding tight hairstyles and minimizing friction on the scalp can help protect the hair.
Maximizing the Lifespan of Your Transplanted Hair
With proper care and maintenance, transplanted hair can last for decades. Here are some tips to ensure your transplanted hair remains healthy and vibrant over time:
Follow Post-Operative Care Instructions
Your surgeon will provide specific instructions for post-operative care, including how to wash and care for your scalp during the initial healing phase. Following these guidelines can help protect the newly transplanted follicles and promote optimal growth.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly biotin, zinc, and iron, can strengthen hair and improve its appearance. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to healthier hair growth.
Use Gentle Hair Care Products
Using mild shampoos and conditioners designed for hair transplants can help protect your hair and prevent unnecessary breakage. Avoid harsh chemicals or treatments that could damage the hair over time.
Schedule Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with your surgeon can help monitor the health of your transplanted hair and detect any potential issues early on. They can also advise on additional treatments if needed.
Conclusion
While transplanted hair is considered permanent, factors such as aging, health, and lifestyle can influence its longevity. Transplanted hair is more resistant to hormonal changes and tends to last longer than non-transplanted hair in individuals with genetic hair loss. However, natural thinning can still occur over time, and untreated areas may continue to lose hair, creating a need for follow-up procedures.
In general, hair transplantation is a durable and effective solution for hair loss, providing a long-lasting improvement that boosts confidence and self-esteem. With proper care, the transplanted hair will remain for many years, offering a fuller, natural-looking appearance that enhances overall quality of life.
- What to Expect Two Months After a Hair Transplant?
- Hair Transplants and Alopecia: Do They Really Work?
- When Can I Use Clippers After Hair Transplant