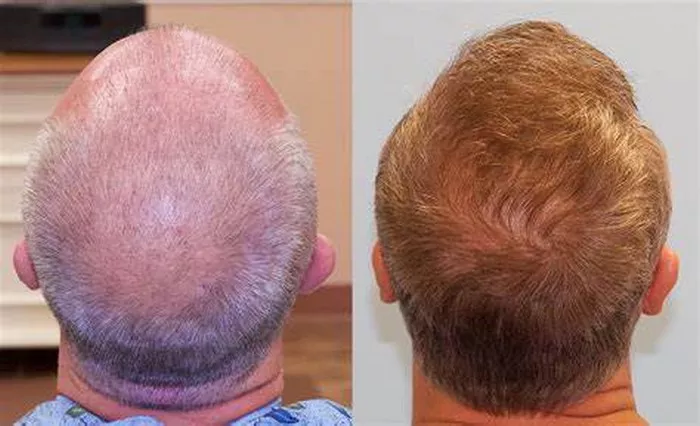
Hair thinning is a common concern that affects millions of people worldwide. Whether it’s due to genetics, hormonal changes, stress, or lifestyle factors, the loss of hair density can significantly impact self-esteem and confidence. The good news is that there are numerous strategies and treatments available to help recover thinning hair. This article will delve into the causes of hair thinning, provide actionable steps to address the issue, and offer expert advice to help you achieve healthier, fuller hair.
Understanding Hair Thinning
What is Hair Thinning?
Hair thinning, also known as hair loss or alopecia, refers to a reduction in the thickness and density of hair on the scalp. Unlike complete hair loss, where entire strands fall out and do not regrow, hair thinning involves a gradual decrease in hair volume, often making the scalp more visible.
Common Causes of Hair Thinning
Genetics:
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Also known as male or female pattern baldness, this is the most common form of hair loss and is influenced by genetic factors.
- Hereditary Patterns: If hair thinning runs in your family, you are more likely to experience it.
Hormonal Changes:
- Androgens: Hormones like dihydrotestosterone (DHT) can shrink hair follicles, leading to thinner hair.
- Menopause: Hormonal changes during menopause can cause hair thinning in women.
Nutritional Deficiencies:
- Iron Deficiency: Lack of iron can lead to anemia, which can cause hair thinning.
- Protein Deficiency: Insufficient protein intake can affect hair growth and density.
- Vitamin D: Low levels of vitamin D have been linked to hair thinning.
Medical Conditions:
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can cause hair thinning.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like alopecia areata, where the immune system attacks hair follicles, can lead to patchy hair loss.
Stress:
- Physical Stress: Severe illnesses, surgeries, or injuries can trigger temporary hair thinning.
- Emotional Stress: Chronic stress can also affect hair growth and density.
Lifestyle Factors:
- Poor Diet: A diet lacking essential nutrients can contribute to hair thinning.
- Excessive Styling: Frequent use of heat tools, tight hairstyles, and harsh chemical treatments can damage hair and lead to thinning.
- Smoking and Alcohol: These habits can negatively impact hair health.
Diagnosing Hair Thinning
When to Seek Professional Help
If you notice significant hair thinning, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional or a dermatologist. They can help diagnose the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatments. Here are some signs that indicate you should seek professional help:
- Rapid Hair Loss: If you’re losing hair at an unusually fast rate.
- Patchy Hair Loss: If you notice bald patches or areas where hair is missing.
- Persistent Itching or Scalp Irritation: If your scalp feels itchy, irritated, or painful.
- Changes in Hair Texture: If your hair becomes noticeably thinner, finer, or more brittle.
Diagnostic Tests
- Scalp Examination: A dermatologist will visually examine your scalp to assess the extent of hair thinning and look for signs of inflammation or infection.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can check for nutritional deficiencies, thyroid disorders, and other medical conditions that may be contributing to hair thinning.
- Pull Test: This test involves gently pulling on a small section of hair to determine how many hairs come out and whether they are in the growing, resting, or shedding phase.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a scalp biopsy may be necessary to examine the hair follicles and rule out certain conditions.
Treatment Options for Hair Thinning
Medical Treatments
Minoxidil (Rogaine):
How It Works: Minoxidil is a topical solution that promotes hair growth by increasing blood flow to the scalp and extending the growth phase of hair follicles.
Effectiveness: It is effective for both men and women and can be used to treat androgenetic alopecia.
Usage: Apply the solution to the scalp twice daily. Results may take several months to become noticeable.
Finasteride (Propecia):
How It Works: Finasteride is an oral medication that blocks the conversion of testosterone to DHT, reducing the shrinkage of hair follicles.
Effectiveness: It is primarily used for men with male pattern baldness and has been shown to slow hair loss and promote regrowth.
Usage: Take one tablet daily. Results may take several months to become noticeable.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
How It Works: PRP therapy involves extracting a small amount of your blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and injecting it back into the scalp.
Effectiveness: Platelets release growth factors that can stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth.
Usage: Typically, multiple sessions are required, spaced several weeks apart.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT):
How It Works: LLLT devices emit low-level laser light that stimulates hair follicles and promotes hair growth.
Effectiveness: Studies have shown that LLLT can improve hair density and thickness.
Usage: Use the device according to the manufacturer’s instructions, typically several times a week.
Non-Medical Treatments
Scalp Massages:
Benefits: Regular scalp massages can improve blood circulation, reduce stress, and stimulate hair follicles.
Technique: Use your fingertips to massage the scalp in circular motions for a few minutes each day.
Essential Oils:
Popular Oils: Rosemary, lavender, and peppermint oils are commonly used to promote hair growth and improve scalp health.
Application: Dilute the essential oils in a carrier oil (like coconut or jojoba oil) and apply to the scalp before bedtime. Leave it on overnight and wash it out in the morning.
Hair Growth Serums and Treatments:
Ingredients: Look for serums containing biotin, niacin, and other hair-strengthening ingredients.
Usage: Apply the serum to the scalp and hair roots as directed by the product instructions.
Lifestyle Changes
Balanced Diet:
Key Nutrients: Ensure your diet includes plenty of protein, iron, zinc, and vitamins A, C, and E.
Supplements: Consider taking supplements if you have specific deficiencies. Consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Stress Management:
Relaxation Techniques: Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga to reduce stress.
Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to improve overall health and reduce stress levels.
Avoid Harsh Chemicals and Heat:
Hair Care: Use gentle, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners. Avoid harsh chemical treatments like perms and relaxers.
Heat Styling: Minimize the use of heat styling tools and use them on low settings when necessary.
Healthy Scalp Practices:
Cleansing: Keep your scalp clean and free of buildup by washing your hair regularly with a mild shampoo.
Exfoliation: Use a scalp exfoliant once a week to remove dead skin cells and improve circulation.
Home Remedies for Hair Thinning
1. Aloe Vera
- Benefits: Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory properties and can soothe an irritated scalp. It also promotes hair growth and improves hair texture.
- Application: Apply fresh aloe vera gel to the scalp and leave it on for 30 minutes before washing it out.
2. Onion Juice
- Benefits: Onion juice contains sulfur, which can stimulate hair growth and improve blood circulation.
- Application: Extract the juice from fresh onions and apply it to the scalp. Leave it on for 20-30 minutes before washing it out.
3. Egg Mask
- Benefits: Eggs are rich in protein and biotin, which are essential for hair growth and strength.
- Application: Beat two eggs and apply the mixture to your hair and scalp. Leave it on for 20-30 minutes before washing it out.
4. Coconut Oil
- Benefits: Coconut oil is deeply moisturizing and can help strengthen hair strands and prevent breakage.
- Application: Warm a small amount of coconut oil and massage it into your scalp and hair. Leave it on overnight and wash it out in the morning.
Preventive Measures
Early Intervention
- Early Signs: Pay attention to early signs of hair thinning, such as increased shedding, smaller hair diameter, and visible scalp.
- Action: Start treatment as soon as you notice these signs to prevent further hair loss and promote regrowth.
Regular Check-ups
- Health Monitoring: Schedule regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor your overall health and address any underlying conditions that may affect hair growth.
- Dietary Review: Have a registered dietitian review your diet to ensure you are getting all the necessary nutrients for healthy hair.
Protective Hairstyles
- Avoid Tight Styles: Tight hairstyles like ponytails, braids, and buns can put tension on hair follicles and lead to hair breakage and thinning.
- Loose Styles: Opt for loose, gentle hairstyles that do not pull on the hair.
Conclusion
Hair thinning can be a challenging issue, but with the right approach, you can recover and maintain healthy, fuller hair. Understanding the causes of hair thinning and seeking professional help when necessary can guide you toward effective treatments. Incorporating medical treatments, non-medical therapies, and lifestyle changes can help you achieve the best results. By taking a comprehensive and proactive approach, you can address hair thinning and boost your confidence and well-being. So, don’t let hair thinning hold you back—take action today to regain your full, luscious locks.
- When Do You Start Losing Hair During Chemo?
- Telogen Effluvium: When It Starts and What to Expect
- What Is the Best Hair Restoration Method