Hair transplant surgery is a life-changing procedure that can restore confidence and improve appearance for individuals experiencing hair loss. However, one of the most common concerns among potential patients is whether the procedure is painful. Understanding the pain management strategies and what to expect during and after the surgery can help alleviate anxiety and ensure a smoother experience. This article will explore the pain levels associated with hair transplant procedures, the anesthesia used, and practical tips for managing discomfort.
Understanding Hair Transplant Surgery
Hair transplant surgery involves moving hair follicles from a donor area, typically the back of the scalp, to a recipient area, usually the front or top of the scalp. The two primary techniques used are Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE):
- FUT: Involves removing a strip of skin from the back of the scalp and extracting individual follicles from this strip.
- FUE: Involves extracting individual follicles directly from the donor area using a small punch tool.
Both methods aim to create a natural-looking hairline and fuller hair volume, but they differ in terms of recovery time and potential scarring.
Pain Management During Hair Transplant Surgery
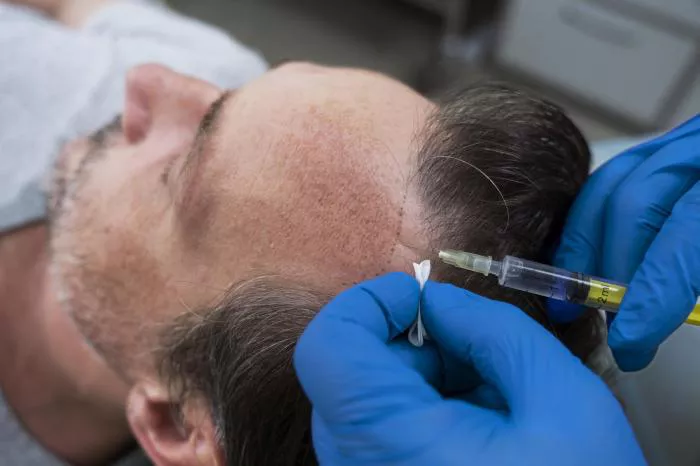
One of the most reassuring aspects of hair transplant surgery is the extensive use of anesthesia to ensure patient comfort. Here’s a breakdown of the pain management strategies used during the procedure:
Local Anesthesia
- Application: Local anesthesia is injected into the scalp to numb the area where the surgery will take place. This is done using a fine needle.
- Effectiveness: Local anesthesia is highly effective in blocking pain signals, allowing the surgeon to work without causing discomfort to the patient.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include a slight stinging sensation when the anesthesia is administered and mild swelling or bruising afterward. These side effects are usually temporary and manageable.
Sedation
- Types: Depending on the patient’s preference and the surgeon’s recommendation, sedation can be used in combination with local anesthesia to enhance comfort.
- Oral Sedation: Patients may be given a sedative pill to take before the procedure to help them relax.
- IV Sedation: Intravenous sedation is administered through a vein and provides a deeper level of relaxation. Patients are usually awake but feel very relaxed and may not remember parts of the procedure.
- Benefits: Sedation helps reduce anxiety and ensures a more comfortable experience. It can also make the procedure seem to pass more quickly.
Numbing Agents
- Topical Anesthetics: Before injecting local anesthesia, a topical numbing agent may be applied to the scalp to reduce the initial sting of the needle.
- Sprays and Creams: These can be used to numb the skin and make the injection of local anesthesia more comfortable.
Pain Levels During the Procedure
While the thought of having needles and surgical instruments on your scalp might seem daunting, the use of anesthesia ensures that the procedure itself is generally painless. Here’s what you can expect:
- Initial Injection: The initial injection of local anesthesia can cause a brief, mild stinging sensation. However, this discomfort is short-lived and is followed by numbness.
- During the Procedure: Once the area is numb, you should not feel pain during the extraction and implantation of hair follicles. Some patients report feeling pressure or a pulling sensation, but this is usually not painful.
- Sedation Effects: If you opt for sedation, you may feel very relaxed and may not be fully aware of the procedure. This can further reduce any discomfort.
Post-Operative Pain and Discomfort
While the surgery itself is generally painless, some degree of discomfort is normal in the days following the procedure. Here’s what to expect and how to manage it:
Immediate Post-Surgery (First 24-48 Hours)
- Swelling and Discomfort: Swelling, especially around the forehead and eyes, is common. Keeping your head elevated and using ice packs can help reduce swelling.
- Rest and Relaxation: Take it easy for the first few days. Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting to prevent bleeding and swelling.
- Pain Management: Your surgeon will likely prescribe pain relievers to manage any discomfort. Over-the-counter options like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can also be effective.
Week 1-4: Initial Healing
- Crusting and Shedding: Within the first week, you may notice crusting and shedding of the transplanted hair. This is a normal part of the healing process and does not indicate failure of the transplant.
- Avoiding Certain Activities: Stay away from alcohol, smoking, and excessive sun exposure, as these can interfere with the healing process.
- Medications: Take any prescribed medications, such as antibiotics and pain relievers, as directed. These can help manage discomfort and prevent infection.
- Monitoring for Discomfort: Pay attention to any discomfort or unusual sensations. If you experience pain or pressure, adjust your position accordingly.
Month 1-3: Continued Healing and Regrowth
- Reduced Swelling: By the first to third month, swelling should be significantly reduced. You may start to see some new hair growth, although it will be minimal at this stage.
- Avoiding Tight Headgear: Avoid wearing tight hats, helmets, or other headgear that can put pressure on the transplanted area.
- Maintaining Good Hygiene: Continue to follow your surgeon’s instructions for washing and caring for your scalp. Cleanliness is crucial to prevent infection and promote healing.
- Patience: Hair growth is a gradual process, and it can take several months to see significant results.
Managing Post-Operative Discomfort
While some discomfort is normal, there are several steps you can take to manage it effectively:
- Pain Relievers: Use prescribed pain relievers as directed. Over-the-counter options can also be helpful.
- Cold Compresses: Apply cold compresses to reduce swelling and soothe the scalp.
- Rest and Elevation: Keep your head elevated to reduce swelling and pressure on the transplanted area.
- Gentle Scalp Care: Wash your scalp gently and avoid using harsh chemicals or products that can irritate the skin.
- Avoiding Irritants: Stay away from alcohol, smoking, and excessive sun exposure, as these can interfere with the healing process.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon to monitor your progress and address any concerns.
Psychological and Emotional Impact
The psychological and emotional impact of hair transplant surgery can be significant. Here’s how to manage these aspects:
- Anxiety and Stress: It’s normal to feel anxious or stressed about the procedure and its outcomes. Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and gentle exercise to manage stress.
- Support System: Share your journey with friends and family who can provide emotional support and encouragement. Joining a support group or online community can also be beneficial.
- Positive Outlook: Maintain a positive outlook and trust the process. Hair growth is gradual, and the final results may take several months to become fully visible.
Factors Affecting Pain and Discomfort
Several factors can influence the level of pain and discomfort experienced during and after a hair transplant:
- Individual Pain Tolerance: Everyone has a different pain threshold. Some patients may experience more discomfort than others, but this is usually manageable with proper pain management.
- Technique Used: FUE typically has a shorter recovery time and less post-operative discomfort compared to FUT, as there is no linear scar from a strip excision.
- Number of Grafts: The more grafts transplanted, the longer the procedure and recovery time may be. Larger procedures can result in more post-operative discomfort.
- Post-Operative Care: Adhering to your surgeon’s post-operative care instructions is crucial for optimal healing. Poor care can lead to complications and increased discomfort.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and autoimmune disorders can affect the healing process. Inform your surgeon of any health issues beforehand.
Potential Complications and How to Manage Them
While hair transplants are generally safe, like any surgical procedure, they come with potential risks and complications. Being aware of these and knowing how to manage them can help ensure a smoother recovery:
- Infection: Signs of infection include redness, swelling, pus, and fever. Contact your surgeon immediately if you suspect an infection. They may prescribe antibiotics to treat it.
- Scarring: While FUE typically leaves minimal scarring, FUT can result in a linear scar. Proper care and follow-up treatments can minimize the visibility of scars.
- Itching and Irritation: Mild itching and irritation are common during the healing process. Use gentle, fragrance-free moisturizers and avoid scratching the scalp.
- Uneven Hair Growth: Sometimes, the transplanted hair may grow unevenly, resulting in patchy areas. Your surgeon can address this with touch-up procedures if necessary.
- Shock Loss: As mentioned earlier, shock loss is a temporary condition where some of the transplanted hair falls out. It usually regrows within a few months.
Tips for a Smooth and Comfortable Experience
To ensure the best possible outcome and a smooth, comfortable experience, follow these tips for your hair transplant journey:
- Choose a Qualified Surgeon: Select a board-certified surgeon with extensive experience in hair transplant procedures. A skilled surgeon can minimize discomfort and ensure optimal results.
- Pre-Operative Preparation: Follow your surgeon’s pre-operative instructions carefully. This may include stopping certain medications, avoiding alcohol and smoking, and preparing your scalp.
- Post-Operative Care: Adhere to your surgeon’s post-operative care instructions to promote healing and reduce discomfort. This includes proper scalp hygiene, avoiding certain activities, and taking prescribed medications.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and promote healthy hair growth.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Consume foods rich in vitamins and minerals, especially those that support hair health, such as biotin, vitamin E, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Avoid Stress: High stress levels can negatively impact the healing process. Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and gentle exercise.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon to monitor your progress and address any concerns.
Conclusion
Hair transplant surgery is a highly effective procedure for restoring hair and improving appearance, and advancements in pain management techniques have made it a relatively comfortable experience. By understanding the pain management strategies, what to expect during and after the procedure, and how to manage discomfort, you can approach your hair transplant journey with confidence. Remember, each person’s experience is unique, so listen to your body and consult your surgeon if you have any concerns. With the right care and preparation, you can achieve the full benefits of a hair transplant and enjoy a healthier, more vibrant appearance.
- What Age Can I Get a Hair Transplant
- Where Does the Hair Come From in a Hair Transplant?
- How Much Will a Hair Transplant Cost?