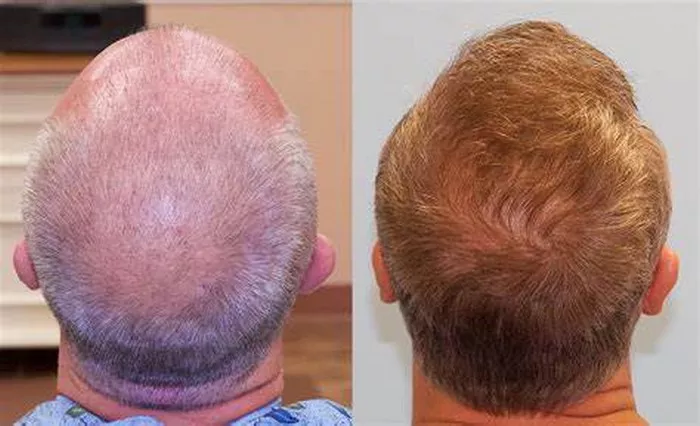
Hair transplants are a life-changing solution for individuals dealing with hair loss, offering a natural and long-lasting way to restore a fuller head of hair. One of the most common concerns patients have is whether the transplanted hair will fall out. This article will explore the phenomenon of hair fall after a transplant, the reasons behind it, what to expect, and how to manage it effectively.
Understanding Hair Transplant Surgery
Before diving into the specifics of hair fall after a transplant, it’s essential to understand the basics of the procedure. Hair transplant surgery involves moving hair follicles from a donor area, typically the back or sides of the scalp, to a recipient area where hair is thinning or absent. There are two primary techniques used in hair transplantation:
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): Also known as strip harvesting, this method involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area. The strip is then divided into individual follicular units, which are implanted into the recipient area.
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): This technique involves extracting individual hair follicles from the donor area and implanting them directly into the recipient area. FUE is minimally invasive and leaves minimal scarring, making it a popular choice.
Both methods aim to achieve a natural-looking hairline and fuller hair density, but the post-procedure experience can vary slightly between the two.
The Phenomenon of Hair Fall After Transplant
One of the most common and often concerning experiences after a hair transplant is the shedding of transplanted hair. This phenomenon, known as “shock loss” or “telogen effluvium,” is a normal part of the healing process and does not affect the final results of the transplant. Here’s a detailed look at when and why this happens.
Stage 1: Immediate Post-Operative Period (Day 1-7)
What to Expect:
- Swelling and Discomfort: Mild swelling and discomfort are common in the first few days after the procedure. The scalp may feel tender, and some patients may experience minor bruising around the eyes.
- Crusting and Scabbing: Small crusts or scabs may form over the transplanted areas. These are a normal part of the healing process and should not be picked or scratched.
- Itching: Some patients may experience itching as the scalp begins to heal. Resist the urge to scratch, as this can dislodge the transplanted hair follicles.
Care Instructions:
- Follow Post-Operative Guidelines: Adhere strictly to the surgeon’s post-operative care instructions, which may include:
- Shampooing: Use a gentle shampoo provided by the clinic to clean the scalp gently. Avoid rubbing or scrubbing the transplanted areas.
- Avoiding Direct Sunlight: Protect your scalp from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Taking Prescribed Medications: Take any prescribed medications, such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, to prevent infection and reduce swelling.
- Rest and Relaxation: Get plenty of rest and avoid strenuous activities. Sleep with your head elevated on pillows to reduce swelling.
Stage 2: Early Growth Phase (Week 2-4)
What to Expect:
- Continued Swelling: Swelling may persist for up to two weeks, but it should gradually decrease over time.
- Hair Shedding: It is normal for the transplanted hair to shed within the first few weeks after the procedure. This is called “shock loss” or “telogen effluvium.” The hair shafts may fall out, but the follicles remain in place and will regrow new hair.
- Healing of Crusts and Scabs: The crusts and scabs will naturally fall off, revealing the underlying skin. Do not attempt to remove them prematurely.
Care Instructions:
- Gentle Shampooing: Continue to shampoo gently, avoiding harsh movements or rubbing.
- Avoiding Physical Activity: Avoid strenuous physical activity, including heavy lifting and intense exercise, for at least two weeks.
- Protecting the Scalp: Continue to protect your scalp from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor your progress and address any concerns.
Stage 3: Mid-Growth Phase (Month 1-3)
What to Expect:
- Reduced Swelling: Swelling should be minimal by this stage, and any remaining discomfort should be manageable.
- New Hair Growth: By the end of the first month, you may notice fine, soft hair beginning to grow in the transplanted areas. This hair will continue to grow and thicken over the next few months.
- Natural Appearance: The transplanted hair will start to look more natural as it grows and blends with your existing hair.
Care Instructions:
- Regular Shampooing: Continue to shampoo regularly, using a gentle shampoo and avoiding harsh products.
- Styling: Avoid using hair styling products or tools on the transplanted areas until the hair is fully grown and stable.
- Sun Protection: Continue to protect your scalp from the sun, using hats or sunscreen when outdoors.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle to promote optimal hair growth and overall health.
Stage 4: Advanced Growth Phase (Month 4-6)
What to Expect:
- Thicker Hair Growth: By the fourth month, the transplanted hair should be thicker and more robust. The hair will continue to grow and blend with your existing hair, creating a natural-looking result.
- Final Results: By the sixth month, you should see significant improvement in hair density and appearance. However, the final results may not be fully visible until nine to twelve months after the procedure.
Care Instructions:
- Regular Maintenance: Continue to maintain good scalp hygiene and use gentle hair care products.
- Styling: You can begin to style your hair as desired, but avoid aggressive styling techniques that could damage the transplanted hair.
- Follow-Up Care: Attend any additional follow-up appointments to ensure the best possible results and address any ongoing concerns.
Stage 5: Long-Term Growth (Month 7-12)
What to Expect:
- Full Hair Growth: By the ninth to twelfth month, the transplanted hair should be fully grown and integrated into your scalp. The final results should be visible, with a natural-looking hairline and fuller hair density.
- Stability: The transplanted hair follicles are resistant to the hormones that cause hair loss, ensuring long-lasting results.
Care Instructions:
- Ongoing Maintenance: Continue to maintain good scalp hygiene and use gentle hair care products.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle to support overall hair health and prevent future hair loss.
- Follow-Up Care: If necessary, discuss any additional treatments or touch-ups with your surgeon to achieve the best possible results.
Why Does Transplanted Hair Fall Out?
Understanding the reasons behind the shedding of transplanted hair can help alleviate concerns and manage expectations. Here are the key factors:
- Shock Loss (Telogen Effluvium):
- Definition: Shock loss is a temporary condition where the transplanted hair enters the telogen (resting) phase of the hair growth cycle and falls out.
- Timing: This typically occurs within the first two to four weeks after the procedure.
- Mechanism: The trauma of the transplant causes the hair follicles to enter a resting phase. The hair shafts may fall out, but the follicles remain viable and will regrow new hair.
- Normal Healing Process:
- Regeneration: The shedding of transplanted hair is a normal part of the healing process. The hair follicles are still active and will regrow new hair.
- Duration: The new hair typically starts to grow back within three to six months after the procedure.
- Individual Variability:
- Genetics: Genetic factors can influence the extent and timing of shock loss. Some individuals may experience more significant shedding than others.
- Health: Overall health and any underlying medical conditions can also affect the healing process and hair growth.
- Post-Operative Care:
- Adherence: Following the surgeon’s post-operative care instructions is crucial for minimizing shock loss and promoting optimal hair growth.
- Medications: Taking prescribed medications, such as minoxidil or finasteride, can help support hair growth and prevent further hair loss.
Managing Hair Fall After a Transplant
While the shedding of transplanted hair is a normal and expected part of the recovery process, there are steps you can take to manage it effectively and promote healthy hair growth.
- Follow Post-Operative Instructions:
- Care Plan: Adhere to the surgeon’s post-operative care plan, which may include gentle shampooing, avoiding physical activity, and taking prescribed medications.
- Regular Check-Ups: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor your progress and address any concerns.
- Maintain Good Scalp Hygiene:
- Gentle Cleansing: Clean your scalp gently with a mild shampoo to prevent infection and promote healing.
- Avoid Scratching: Resist the urge to scratch or pick at the transplanted areas, as this can dislodge the hair follicles.
- Supportive Lifestyle Choices:
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support hair growth and overall health.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your body and scalp hydrated.
- Exercise: Engage in regular, moderate exercise to improve circulation and overall well-being, but avoid strenuous activities during the early recovery period.
- Stress Management: Manage stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga, to promote a healthy scalp environment.
- Use Hair Growth Products:
- Minoxidil: Minoxidil (Rogaine) can be used to stimulate hair growth and prevent further hair loss. Consult with your surgeon before using any hair growth products.
- Finasteride: Finasteride (Propecia) is a prescription medication that can help prevent further hair loss and promote hair growth. Discuss the potential benefits and side effects with your doctor.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals and Heat:
- Chemical Treatments: Avoid harsh chemical treatments, such as hair dyes and perms, on the transplanted areas until the hair is fully grown and stable.
- Heat Styling: Avoid using heat styling tools, such as blow dryers, straighteners, and curling irons, on the transplanted areas until the hair is fully grown and stable.
- Be Patient:
- Timeline Awareness: Understand that the final results of a hair transplant can take several months to become fully visible. Patience is key to achieving the best possible outcome.
Long-Term Stability of Transplanted Hair
One of the most significant advantages of hair transplants is the long-term stability of the transplanted hair. Unlike the hair in the recipient area, which may be prone to genetic hair loss, the transplanted hair follicles are taken from areas of the scalp that are resistant to the hormones that cause hair loss. This means that the transplanted hair is likely to remain permanent and continue to grow for many years.
However, it’s important to note that while the transplanted hair itself is generally stable, the surrounding hair may continue to thin or fall out over time. To maintain the best possible results, it’s essential to follow a comprehensive hair care routine and consult with your surgeon if you notice any changes in your hair density or quality.
Factors That Can Affect Transplanted Hair
While the transplanted hair is generally resistant to hair loss, certain factors can influence its growth and stability. Here are some key considerations:
- Genetic Predisposition:
- Androgenetic Alopecia: If you have a genetic predisposition to hair loss, the surrounding hair may continue to thin over time. Regular use of hair growth products and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate this risk.
- Medical Conditions:
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like alopecia areata can affect the growth of transplanted hair. If you have an autoimmune disorder, discuss your options with your surgeon and follow their recommendations for managing the condition.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Stress: High levels of stress can negatively impact hair growth. Practice stress management techniques and maintain a balanced lifestyle to support healthy hair.
- Diet and Nutrition: A poor diet lacking in essential nutrients can affect hair growth. Ensure you are consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Environmental Factors:
- Pollution and Sun Exposure: Exposure to pollution and excessive sun can damage the hair and scalp. Protect your hair with hats and use sunscreen when outdoors.
- Hair Care Practices:
- Aggressive Styling: Using harsh hair styling techniques, such as tight hairstyles, frequent use of heat styling tools, and chemical treatments, can damage the transplanted hair. Be gentle with your hair and avoid these practices.
Conclusion
Hair transplants are a highly effective solution for restoring a fuller head of hair, but the shedding of transplanted hair is a common and normal part of the recovery process. By understanding the typical timeline, reasons behind hair fall, and following the surgeon’s post-operative care instructions, you can manage this experience effectively and achieve the best possible results. Whether you choose FUT or FUE, the key is to prioritize quality, comfort, and natural results. With the right preparation, care, and follow-up, your hair transplant journey can be a transformative and rewarding experience.
- When Does Transplanted Hair Start to Grow?
- When Can I Touch My Transplanted Hair?
- How Many Hair Transplant Grafts Do I Need?