Hair loss is a common concern that affects millions of people worldwide. For those seeking a permanent solution, hair transplantation offers a promising option. However, many potential candidates have questions about the procedure, particularly regarding where the hair used in transplants is sourced from. Understanding the donor areas and the techniques involved in hair transplantation is crucial for anyone considering this procedure. This article delves into the intricacies of hair transplants, focusing on the donor sites, the methods used to harvest hair, and what candidates can expect throughout the process.
Understanding Hair Transplants
What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves relocating hair follicles from a donor site to areas of the scalp experiencing thinning or baldness. This technique is primarily used to treat androgenetic alopecia (male and female pattern baldness) but can also be beneficial for other types of hair loss, such as alopecia areata or hair loss resulting from trauma.
How Hair Transplants Work
The basic principle of hair transplantation is simple: healthy hair follicles are taken from a donor area, usually where hair is abundant, and implanted into areas where hair is thinning or absent. The transplanted hair follicles continue to grow in their new location, providing a natural-looking solution to hair loss.
Donor Areas for Hair Transplants
Common Donor Sites
The success of a hair transplant largely depends on the quality and quantity of hair available in the donor area. The most common donor sites include:
-
Occipital Region (Back of the Head): The most frequent donor site is the occipital region, located at the back of the scalp. Hair in this area is typically resistant to the effects of DHT (dihydrotestosterone), a hormone responsible for hair loss in genetically susceptible individuals. This makes it an ideal source for transplanting hair.
-
Temporal Region (Sides of the Head): The hair on the sides of the head can also be used as a donor site. While this hair is generally less resistant to hair loss than that from the occipital region, it can still provide viable follicles for transplantation.
-
Body Hair: In some cases, hair from other areas of the body, such as the chest, beard, or legs, can be harvested for transplantation. This method is particularly useful for individuals who have limited donor hair on their scalp.
Factors Influencing Donor Site Selection
Several factors influence the choice of donor site for hair transplantation:
-
Hair Density: The density of hair in the donor area is crucial. Areas with a higher density of hair follicles are preferred to ensure a sufficient number of grafts can be harvested.
-
Hair Texture and Color: The texture and color of the hair in the donor area should ideally match the recipient area to achieve a natural look.
-
Scalp Elasticity: The elasticity of the scalp can affect the harvesting process. A more elastic scalp allows for easier extraction of hair follicles.
Hair Harvesting Techniques
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT, also known as the strip method, is one of the most common techniques used for hair transplantation. Here’s how it works:
-
Strip Removal: A strip of skin containing hair follicles is surgically removed from the donor area, typically the occipital region.
-
Dissection: The strip is then dissected into individual follicular units, each containing one to four hair follicles.
-
Implantation: The follicular units are then implanted into the recipient area.
Advantages of FUT
- Higher Yield: FUT allows for the harvesting of a larger number of grafts in a single session, making it suitable for patients with extensive hair loss.
- Cost-Effective: This method is often more cost-effective than FUE due to the efficiency of harvesting a large number of grafts at once.
Disadvantages of FUT
- Scarring: FUT leaves a linear scar at the donor site, which may be visible if the hair is cut very short.
- Longer Recovery Time: The recovery time for FUT may be longer compared to FUE due to the surgical nature of the strip removal.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
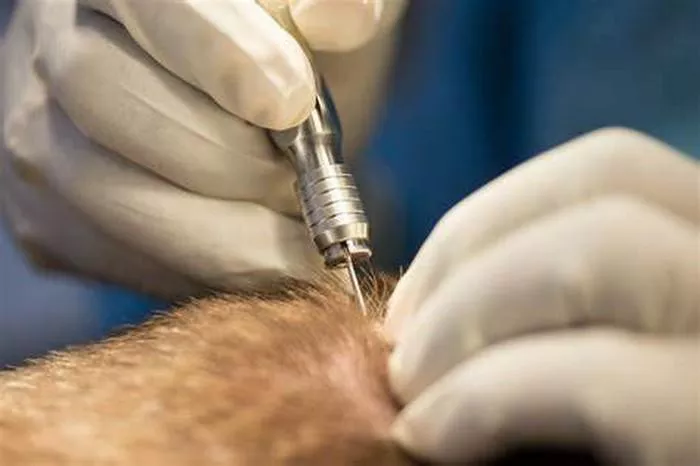
FUE is a less invasive technique that has gained popularity in recent years. Here’s how it works:
-
Individual Extraction: Using a specialized tool, individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area without the need for a strip of skin.
-
Implantation: The harvested follicles are then implanted into the recipient area.
Advantages of FUE
- Minimal Scarring: FUE leaves tiny dot-like scars instead of a linear scar, making it a more aesthetically pleasing option for many patients.
- Quicker Recovery: Patients typically experience a shorter recovery time with FUE compared to FUT.
Disadvantages of FUE
- Lower Yield: FUE may yield fewer grafts in a single session compared to FUT, which can be a consideration for patients with extensive hair loss.
- Cost: FUE is often more expensive due to the time and precision required for individual follicle extraction.
Robotic Hair Transplantation
Robotic hair transplantation is an advanced technique that utilizes robotic systems to assist in the FUE process. This technology enhances precision and efficiency in harvesting hair follicles.
Advantages of Robotic Hair Transplantation
- Precision: The robotic system can accurately identify and extract hair follicles, minimizing damage to surrounding tissue.
- Consistency: Robotic systems provide consistent results, reducing the variability associated with manual extraction.
Disadvantages of Robotic Hair Transplantation
- Cost: Robotic hair transplantation can be more expensive than traditional methods due to the technology involved.
- Availability: Not all clinics offer robotic hair transplantation, limiting access for some patients.
Preparing for a Hair Transplant
Initial Consultation
The first step in the hair transplant process is a thorough consultation with a qualified hair transplant surgeon. During this consultation, the surgeon will:
-
Evaluate Hair Loss: Assess the extent and pattern of hair loss to determine the most suitable approach.
-
Discuss Goals: Understand the patient’s expectations and desired outcomes.
-
Examine Donor Areas: Evaluate the donor areas for hair density and quality.
Pre-Operative Instructions
If the patient is deemed a suitable candidate, the surgeon will provide pre-operative instructions, which may include:
-
Avoiding Blood Thinners: Patients may be advised to avoid medications or supplements that can increase bleeding.
-
Preparing for the Day of Surgery: Arranging for transportation to and from the clinic is often necessary, as patients may feel groggy after the procedure.
The Hair Transplant Procedure
Day of the Procedure
On the day of the hair transplant, patients can expect the following:
-
Arrival at the Clinic: Patients should arrive at the clinic on time, ready for the procedure.
-
Preparation: The surgical team will prepare the patient by taking photographs and marking the areas for graft placement.
Anesthesia
Local anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient’s comfort during the procedure. This anesthesia numbs the scalp, allowing the surgeon to perform the transplant with minimal discomfort.
Harvesting Hair Follicles
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
- Strip Removal: The surgeon removes a strip of scalp from the donor area, usually the back of the head.
- Dissection: The strip is divided into individual follicular units under a microscope.
- Preparation for Transplantation: The follicular units are prepared for implantation.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
- Individual Extraction: Using a specialized tool, the surgeon extracts individual hair follicles from the donor area.
- Collection: The extracted follicles are collected in a solution to keep them viable for transplantation.
Creating Recipient Sites
After harvesting the follicles, the surgeon prepares the recipient area:
- Incisions: Tiny incisions are made in the thinning or bald areas of the scalp to create recipient sites for the transplanted follicles.
- Designing Hairline: The surgeon carefully designs the hairline to ensure a natural appearance, considering the patient’s facial features and preferences.
Implanting Hair Follicles
Once the recipient sites are prepared, the surgeon begins implanting the harvested follicles:
- Placement: Each follicular unit is meticulously placed into the recipient sites, ensuring proper angle and direction to mimic natural hair growth.
- Density Considerations: The surgeon considers the desired density and coverage, strategically placing grafts to achieve the best aesthetic outcome.
Duration of the Procedure
The length of the hair transplant procedure varies based on the technique used and the number of grafts being transplanted. Generally, the procedure can take anywhere from 4 to 8 hours.
Post-Operative Care
Immediate Post-Operative Period
After the procedure, patients will be monitored for a short period to ensure they are stable and comfortable. They will receive post-operative care instructions, which may include:
- Keeping the Scalp Clean: Gentle washing of the scalp is essential to prevent infection.
- Avoiding Touching the Scalp: Patients should refrain from touching or scratching the transplant area to allow for proper healing.
- Managing Discomfort: Over-the-counter pain relief may be recommended to manage any discomfort.
Recovery Timeline
First Few Days
In the first few days post-transplant, patients may experience:
- Swelling: Mild swelling on the forehead and around the eyes is common.
- Scabbing: Small scabs may form at the transplant sites, which should not be disturbed.
Weeks 1-2
During the first two weeks, patients should:
- Follow Hygiene Instructions: Clean the scalp as directed by the surgeon to prevent infection.
- Limit Physical Activity: Avoid strenuous activities that could increase blood flow to the scalp.
Months 1-3
After the initial healing phase, patients can expect:
- Shedding of Transplanted Hair: It is normal for the transplanted hair to shed during the first month as the follicles enter a resting phase.
- New Hair Growth: By the end of the second month, patients may start to see new hair growth, although it may be fine and sparse initially.
Months 4-12
By the end of the first year, patients can expect:
- Significant Hair Growth: Most patients see considerable improvement in hair density and coverage.
- Final Aesthetic Results: The full results of the hair transplant are typically visible within 9 to 12 months.
Risks and Considerations
Potential Risks
While hair transplantation is generally safe, there are potential risks and complications, including:
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection at the donor or recipient sites.
- Scarring: FUT may result in a linear scar, while FUE typically leaves tiny dot-like scars.
- Unnatural Appearance: If not performed correctly, the results may appear unnatural, leading to dissatisfaction.
- Shock Loss: Some patients may experience temporary shedding of existing hair around the transplant site.
Emotional Considerations
The decision to undergo a hair transplant can be emotionally charged. Patients should take the time to consider their motivations, expectations, and the potential impact on their self-image.
Financial Considerations
Hair transplant costs can vary widely based on factors such as the technique used, the extent of hair loss, and the surgeon’s expertise. It’s important to consider the financial implications and whether insurance will cover any part of the procedure.
Alternatives to Hair Transplantation
Non-Surgical Options
For individuals who may not be suitable candidates for hair transplantation, several non-surgical options are available:
-
Medications: FDA-approved medications like minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia) can help slow hair loss and promote regrowth.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: This treatment involves injecting a concentration of platelets from the patient’s blood into the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
-
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): This non-invasive treatment uses laser light to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes can also support hair health:
-
Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly those known to promote hair growth (like biotin, zinc, and iron), can be beneficial.
-
Stress Management: Reducing stress through mindfulness, exercise, and relaxation techniques can help mitigate hair loss.
-
Avoiding Harsh Treatments: Limiting the use of heat styling tools and harsh chemical treatments can help maintain hair health.
Conclusion
Understanding where hair transplants take hair from is essential for anyone considering this procedure. The choice of donor area, whether from the occipital region, temporal region, or even body hair, plays a critical role in the success of the transplant. Additionally, the techniques used for harvesting and implanting hair follicles can significantly impact the results and recovery. By being informed about the process, potential candidates can make better decisions and set realistic expectations for their hair restoration journey. Ultimately, hair transplantation can offer a life-changing solution for those struggling with hair loss, restoring not just hair but also confidence and self-esteem.
- Can I Shave My Head After a Hair Transplant
- Are Hair Transplant Results Permanent?
- How Much Does Hair Replacement Surgery Cost? A Detailed Guide