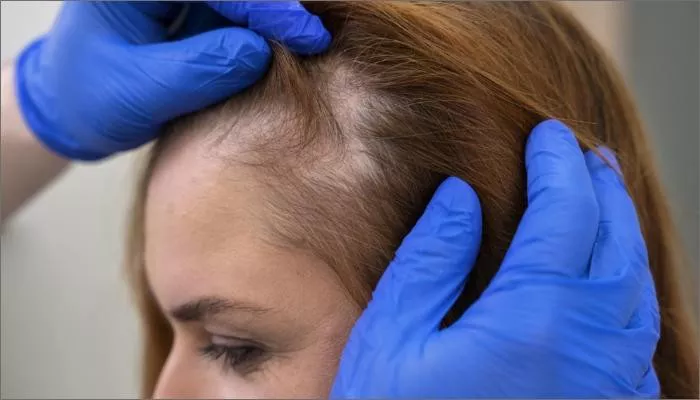
Hair loss is a common concern that affects millions of people worldwide, and it can happen for many reasons. One of the most common causes is hereditary hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia. This type of hair loss can occur in both men and women, though it is more prevalent in men. While there is no surefire way to completely stop hereditary hair loss, there are several ways to slow down its progression and manage the symptoms effectively. In this article, we will explore the causes, treatments, and steps you can take to protect your hair health and hairline.
What is Hereditary Hair Loss?
Hereditary hair loss is a genetic condition that causes hair to gradually thin and eventually fall out. The condition is typically passed down from one or both parents and can begin as early as in a person’s twenties or thirties. Men are more likely to experience a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, while women usually notice thinning all over the scalp, especially on the top.
This type of hair loss is mainly linked to hormones and genetics. It is often referred to as male-pattern baldness in men and female-pattern baldness in women.
What Causes Hereditary Hair Loss?
Hereditary hair loss occurs when there is an imbalance in the natural hair growth cycle. Normally, hair goes through three stages:
Anagen (Growth Phase): This is the phase where the hair is actively growing.
Catagen (Transitional Phase): The hair stops growing and detaches from the hair follicle.
Telogen (Resting Phase): The hair falls out, and a new hair begins to grow in its place.
In hereditary hair loss, the hair follicles shrink over time, making hair growth weaker and thinner. Over the years, these follicles may stop producing new hair entirely. Hormones, particularly a form of testosterone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT), play a significant role in this process. DHT binds to hair follicles and shrinks them, which leads to hair thinning and eventual hair loss.
Can You Prevent Hereditary Hair Loss?
At this time, it is difficult to completely prevent hereditary hair loss. Since the condition is genetic, it is a process that happens naturally and is hard to stop once it begins. However, there are treatments that can help slow it down and in some cases, reverse the process. Early intervention is key when trying to manage hereditary hair loss.
Hair Care Practices to Protect Your Hairline
Although you may not be able to stop hereditary hair loss entirely, maintaining good hair health is essential. Here are some hair care practices that can help protect your hairline:
Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild shampoo that is designed for your hair type. Harsh shampoos can strip the hair of its natural oils, making it more prone to breakage.
Conditioning: Apply conditioner after shampooing to help keep your hair moisturized and prevent dryness. This can keep your hair healthy and minimize further damage.
Avoid Heat Styling: Excessive heat can weaken hair strands and contribute to breakage. Try to limit the use of heat tools like blow dryers, straighteners, and curling irons.
Avoid Tight Hairstyles: Tight hairstyles, such as ponytails and braids, can cause traction alopecia, a type of hair loss caused by tension on the hair. Opt for looser styles to prevent unnecessary stress on your hair follicles.
Nutritional Support for Hair Health
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy hair. Hair growth relies on proper nutrition, so make sure you are getting the right vitamins and minerals:
Biotin: Biotin is known to support healthy hair growth. You can find it in foods like eggs, nuts, and whole grains.
Iron: Iron deficiencies can lead to hair loss. Include iron-rich foods such as spinach, red meat, and legumes in your diet.
Vitamin D: Vitamin D is important for hair follicle health. It can be found in fatty fish, fortified milk, and eggs.
Zinc: Zinc promotes hair repair and growth. You can find it in seeds, nuts, and whole grains.
Medications for Hereditary Hair Loss
There are several FDA-approved treatments for hereditary hair loss that can slow down hair thinning and, in some cases, promote new hair growth.
Minoxidil
Minoxidil, available over-the-counter, is one of the most popular treatments for hereditary hair loss. It is applied directly to the scalp and is believed to work by improving blood flow to the hair follicles, which can help stimulate hair growth. Minoxidil is effective for both men and women and can help maintain hair density, especially when used consistently. However, it is important to note that its effects may not be permanent, and once you stop using it, hair loss may resume.
Finasteride
Finasteride is a prescription medication that works by blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT. By lowering DHT levels, finasteride can prevent further hair loss and in some cases, promote hair regrowth. This medication is most effective in men but is not recommended for women, especially those who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Low-level laser therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses red light to stimulate hair follicles and improve hair growth. This treatment has shown promising results in both men and women and is available in various forms, including laser combs, helmets, and caps. While LLLT is not a cure for hereditary hair loss, it can help slow down the progression and increase hair density.
Hair Transplant Surgery
For individuals with advanced hair loss, hair transplant surgery may be an option. In this procedure, hair follicles from areas of thick hair (usually the back or sides of the head) are transplanted to areas with thinning or no hair. Hair transplant surgery can provide a more permanent solution for hereditary hair loss, although it comes with risks and a long recovery time.
There are two main types of hair transplant techniques:
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): Individual hair follicles are extracted and transplanted to the thinning areas.
FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): A strip of scalp with healthy hair follicles is removed and divided into small grafts for transplantation.
Hereditary Hair Loss in Women
While men are more likely to experience a receding hairline, women often experience diffuse thinning, particularly at the crown and top of the head. The causes of hair loss in women can be more complex, involving hormonal changes, age, and stress, in addition to genetics. Treatments such as minoxidil are effective for women, but they may also be prescribed other therapies, such as oral contraceptives to balance hormone levels or spironolactone, which can block DHT.
Thinning vs. Baldness
It is important to distinguish between thinning and baldness. Thinning refers to the gradual reduction of hair volume, while baldness is characterized by complete hair loss in certain areas of the scalp. Early signs of hereditary hair loss often include a widening part or a thinning crown, which can be addressed with treatment before it progresses to baldness.
Can Lifestyle Changes Help?
Although lifestyle changes cannot cure hereditary hair loss, they can support hair health and potentially slow down the progression. Here are a few habits to adopt:
Stress Management: High stress levels can lead to hair loss. Practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises to keep stress in check.
Get Enough Sleep: Sleep is essential for overall health, including hair health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support your body’s natural hair growth cycle.
Exercise Regularly: Physical activity improves circulation, which helps nourish the hair follicles and supports hair growth.
Conclusion
While hereditary hair loss cannot be completely stopped, advances in treatments are continually being made. From medications like minoxidil and finasteride to non-surgical solutions like laser therapy, there are multiple options available for managing hair loss and maintaining a healthy hairline. By adopting proper hair care practices, taking care of your overall health, and seeking medical advice early, you can slow the progression of hereditary hair loss and protect the hair you have. If you are concerned about hair loss, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider or dermatologist to explore the best treatment options tailored to your needs.
Related topics:
- What Can I Use to Make My Hair Grow Faster?
- How Can I Get My Thinning Hair to Grow Back?
- Why Is My Hair Coming Out in Clumps?