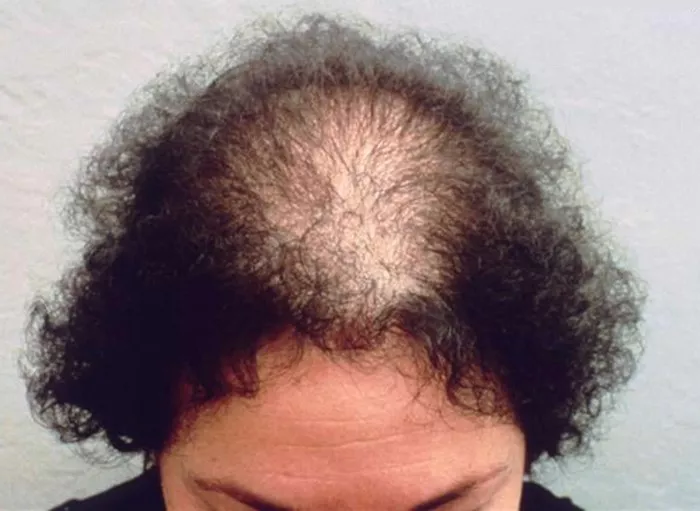
Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss, typically in patches on the scalp. The condition can also affect other areas of the body where hair grows, such as the eyebrows, beard, and body hair. While the exact cause of alopecia areata is unknown, researchers believe that it is a combination of genetic and environmental factors that trigger an immune response, leading to hair loss.
If you or someone you know is dealing with alopecia areata, it’s crucial to understand how to stop its progression and manage the condition effectively. In this article, we will explore various strategies and treatments that can help prevent alopecia areata from spreading and promote hair regrowth.
What is Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia areata is a non-scarring hair loss condition characterized by the sudden appearance of round or oval-shaped bald patches on the scalp, face, or body. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly targets the hair follicles, leading to inflammation and hair loss. The exact cause of alopecia areata is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
Types of Alopecia Areata
There are different types of alopecia areata, including:
Alopecia Areata (AA):
This is the most common form of alopecia areata, characterized by the appearance of round or oval-shaped bald patches on the scalp or other areas of the body.
Alopecia Totalis (AT):
Alopecia totalis involves the complete loss of hair on the scalp.
Alopecia Universalis (AU):
Alopecia universalis is the most severe form of alopecia areata, resulting in the complete loss of hair on the scalp, face, and body, including eyebrows and eyelashes.
Treatment Options to Halt the Spread of Alopecia Areata
While there is no definitive cure for alopecia areata, several treatment options can help stop its progression and promote hair regrowth. The effectiveness of these treatments varies from person to person, and a dermatologist specializing in hair disorders should guide the treatment plan. Let’s explore the different treatment options:
1. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are applied directly to the affected areas of the scalp or body to reduce inflammation and stimulate hair regrowth. Some common topical treatments for alopecia areata include:
Corticosteroids:
Corticosteroid creams or ointments can be applied to the affected areas to suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation, promoting hair regrowth.
Topical Immunotherapy:
This treatment involves applying chemicals such as diphencyprone (DPCP) or squaric acid dibutylester (SADBE) to the scalp, which provoke an allergic reaction. This allergic response stimulates the immune system, helping to reverse the autoimmune attack on hair follicles and encourage hair regrowth.
2. Injectables Treatments
For more extensive or severe cases of alopecia areata, injectable treatments directly into the affected areas may be recommended:
Corticosteroid Injections:
Corticosteroids can be injected into the affected areas to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response, promoting hair regrowth.
Other Medications:
Other medications, such as minoxidil or anthralin, may be injected to stimulate hair regrowth and control the spread of alopecia areata.
3. Oral Medications
In certain situations, oral medications may be prescribed to manage alopecia areata:
Corticosteroids:
Oral corticosteroids can be prescribed for severe cases to suppress the immune response systemically and reduce inflammation. However, long-term use of oral corticosteroids is generally avoided due to potential side effects.
Immunosuppressants:
Medications that suppress the immune system, such as methotrexate or cyclosporine, may be prescribed to halt the progression of alopecia areata. These medications require careful monitoring due to potential side effects.
4. Supportive Measures
In addition to medical treatments, adopting supportive measures can help manage alopecia areata and prevent its spread:
Stress Management:
Stress can potentially exacerbate autoimmune conditions, including alopecia areata. Effective stress management techniques such as exercise, meditation, or therapy can help reduce stress levels.
Healthy Lifestyle:
Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can support overall health and immune function, potentially improving the condition.
Protective Styling:
Opting for hairstyles that do not put excessive tension or stress on the remaining hair can help prevent further damage and reduce the risk of spreading.
5. Psychological Support
Alopecia areata can have a significant emotional impact, affecting self-esteem and confidence. Seeking psychological support or joining support groups can provide valuable emotional support, coping strategies, and a sense of community.
Precautions when treating alopecia areata
When treating alopecia areata, it is important to take certain precautions to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the treatment. Here are four key precautions to consider:
Consultation with a Dermatologist:
Before starting any treatment for alopecia areata, it is crucial to consult with a dermatologist who specializes in hair disorders. They can provide an accurate diagnosis, assess the extent of your condition, and recommend appropriate treatment options based on your specific needs.
Follow Treatment Instructions:
It is essential to carefully follow the treatment instructions provided by your dermatologist. This includes using topical treatments, medications, or undergoing procedures as prescribed. Adhering to the recommended dosage, frequency, and duration of treatment will maximize the potential benefits and minimize any potential risks.
Be Patient and Persistent:
Hair regrowth in alopecia areata can be a gradual process, and individual results may vary. It is important to have realistic expectations and be patient while giving the treatment time to work. It may take several months or longer to see noticeable improvements, so persistence and consistency with the treatment plan are key.
Monitor for Side Effects:
Some treatments for alopecia areata may have potential side effects. It is important to monitor your body’s response to the treatment and promptly report any adverse effects to your dermatologist. Regular check-ups and open communication with your dermatologist will allow for adjustments to the treatment plan, if necessary, to ensure your safety and well-being.
By taking these precautions, you can ensure that your treatment for alopecia areata is conducted in a safe and effective manner. Working closely with a dermatologist, following the prescribed treatment plan, and being patient and vigilant will increase the chances of successful management and potential hair regrowth.
Conclusion
While there is currently no known cure for alopecia areata, there are various treatment options and strategies available to help stop its progression and manage the condition effectively. Topical treatments, injectable medications, oral medications, and supportive measures can all contribute to halting the spread of alopecia areata and promoting hair regrowth. It is important to work closely with a dermatologist specializing in hair disorders to create a personalized treatment plan and ensure the most appropriate approach for individual needs. Additionally, seeking emotional support and practicing self-care can help individuals navigate the challenges associated with alopecia areata and enhance overall well-being. Remember, each person’s experience with alopecia areata is unique, and finding the right combination of treatments and supportive measures may require patience and ongoing adjustments.
Related topics:
- Does hair transplant hurt: A Simple Guide
- How much does a hair transplant cost: A Quick Guide
- The Efficacy of Hair Transplants: Does Hair Transplant Work?