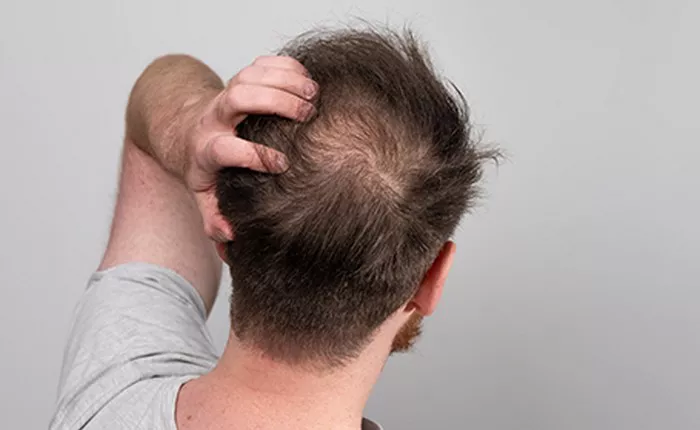
Alopecia is a condition that leads to hair loss, often beginning gradually. It affects many people around the world, both men and women. The first signs of alopecia can vary, and its progression depends on the type of alopecia. Understanding what alopecia looks like when it first starts is essential for early detection and treatment. In this article, we will explore the initial stages of alopecia, its causes, symptoms, and what you can do to manage it.
What Is Alopecia?
Alopecia is the medical term for hair loss. It can affect people of all ages and backgrounds. The most common form of alopecia is androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness. However, other forms of alopecia, such as alopecia areata, can also lead to hair loss. Alopecia can cause partial or complete hair loss, and in some cases, it can be permanent.
While hair loss can be distressing, it is important to remember that many people experience hair thinning or loss at some point in their lives. Early detection of alopecia can help you take steps to manage the condition and maintain healthy hair care habits.
What Does Alopecia Look Like When It First Starts?
1. Thinning Hair
The first noticeable sign of alopecia is often hair thinning. It can start slowly and may not be immediately obvious. People may notice their hair is not as thick as it used to be. This thinning can occur on the scalp or in other areas where hair typically grows.
For men, the hairline may start to recede from the forehead, forming an “M” shape. In women, the thinning is more diffuse and may affect the crown or part of the scalp. In both cases, the thinning hair may become more noticeable when combing or styling the hair.
2. Shedding of Hair
In the early stages of alopecia, people may notice increased hair shedding. It is normal to lose a small amount of hair each day, but with alopecia, the shedding becomes more significant. Hair may fall out during daily activities like brushing, washing, or even sleeping. For some people, this can be a frightening experience, as it may feel like their hair is falling out in large amounts.
3. Patchy Hair Loss
Alopecia areata is a form of alopecia that causes hair loss in small, round patches. These patches may appear suddenly and without warning. They are usually smooth and do not cause any pain or irritation. People with alopecia areata often notice that hair falls out in one or more spots on their scalp, or even in other areas like the eyebrows or eyelashes.
While patchy hair loss is most common with alopecia areata, other forms of alopecia can also cause similar symptoms. In some cases, the patches of hair loss may gradually expand over time.
4. Scalp Sensitivity
Some people with alopecia experience scalp sensitivity or tenderness. This may occur in the areas where hair is thinning or falling out. The scalp may feel sore to the touch or even itch. This can be distressing and may make it difficult to continue with normal hair care routines.
Scalp sensitivity is often associated with autoimmune forms of alopecia, such as alopecia areata, but it can also occur with other types of hair loss. It is important to avoid irritation and to be gentle when combing or washing the hair to prevent further damage to the scalp.
Causes of Alopecia
Alopecia can be caused by various factors, and its onset can vary from person to person. Some common causes of alopecia include:
1. Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in the development of alopecia. If your parents or grandparents experienced hair loss, you may be more likely to develop it as well. Androgenetic alopecia, which causes male and female pattern baldness, is primarily determined by genetic factors. This type of alopecia tends to progress slowly over time.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes can also contribute to hair loss. For women, changes during pregnancy, menopause, or birth control use can lead to thinning hair. Men may experience hair loss as they age due to changes in testosterone levels. These hormonal shifts can lead to temporary or permanent hair loss, depending on the severity and duration of the hormonal imbalance.
3. Autoimmune Disorders
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss. The exact cause of this condition is unclear, but it is thought to involve genetic and environmental factors. Alopecia areata typically causes round patches of hair loss on the scalp, although it can affect other parts of the body as well.
4. Stress and Trauma
Emotional or physical stress can also trigger hair loss. This is known as telogen effluvium, a type of hair loss where hair sheds excessively due to stress or trauma. Telogen effluvium can occur after a major life event, illness, surgery, or even a traumatic experience. The hair loss may be temporary and may improve once the stressor is resolved.
5. Nutritional Deficiencies
Poor nutrition can also lead to hair thinning and hair loss. Deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron, vitamin D, and biotin, can weaken the hair follicles and prevent healthy hair growth. Eating a balanced diet with the proper nutrients can help prevent hair loss and promote hair health.
How to Manage Alopecia When It First Starts
1. Visit a Dermatologist
If you notice any of the early signs of alopecia, it is important to consult a dermatologist. A dermatologist can diagnose the type of alopecia you are experiencing and recommend appropriate treatments. Early intervention can help slow the progression of hair loss and may even help restore some hair growth.
2. Consider Medical Treatments
There are several treatments available for alopecia, depending on the type and severity of the condition. Minoxidil is a common over-the-counter treatment that can help stimulate hair growth. It is often used for androgenetic alopecia and can be applied topically to the scalp.
In cases of alopecia areata, corticosteroid injections or oral medications may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and stimulate hair regrowth. Other treatments, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, may also be used to promote hair growth.
3. Hair Care Practices
Taking good care of your hair is important when dealing with alopecia. Use gentle shampoos and conditioners that are free from harsh chemicals. Avoid excessive heat styling and chemical treatments, which can further damage the hair and scalp. Opt for a wide-toothed comb or fingers to detangle the hair gently and reduce breakage.
4. Diet and Nutrition
Eating a nutritious diet is essential for hair health. Foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins can help strengthen the hair follicles and prevent further hair loss. Consider incorporating more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains into your meals. Additionally, supplements such as biotin or iron may be helpful if you have specific deficiencies.
Conclusion
Alopecia can be a challenging condition to deal with, but recognizing the early signs of hair loss is key to managing it effectively. The first stages of alopecia often involve thinning hair, shedding, patchy hair loss, and scalp sensitivity. Understanding these early symptoms can help you take proactive steps to address the condition. If you experience any of these signs, it is important to seek professional advice from a dermatologist to determine the best course of action for your hair care and hair loss concerns. Early intervention can make a significant difference in maintaining healthy hair and preventing further loss.
Related topics:
- 8 Best Treatments for Alopecia in 2025
- Excessive Hair Loss: Causes & Treatments
- What to Do for Hair Loss Due to Medication?