Hair loss is a common problem that affects millions of people around the world. Whether it’s due to genetics, aging, or other factors, hair loss can have a significant impact on one’s appearance and self-esteem. The good news is that modern medical advancements have provided solutions, and one of the most effective treatments for hair loss is the hair graft procedure. In this article, we will explore what a hair graft is, how the procedure works, the types of hair grafting techniques, the benefits, risks, and aftercare involved.
What is a Hair Graft?
A hair graft, also known as a hair transplant, is a surgical procedure used to treat hair loss. It involves the transfer of hair follicles from one area of the body (usually the back or sides of the scalp) to areas where hair is thinning or missing. The primary goal of this procedure is to restore a natural-looking hairline and improve the density of hair in the affected areas.
Hair grafting is commonly used to treat male pattern baldness, female pattern baldness, and other types of hair loss. The procedure can be done on both men and women, and it has become increasingly popular due to its effectiveness and long-lasting results.
Hair Graft Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
The hair graft procedure involves several steps, which are carried out under local anesthesia to ensure that the patient does not feel any pain. The process can take several hours, depending on the extent of the hair loss and the number of grafts required.
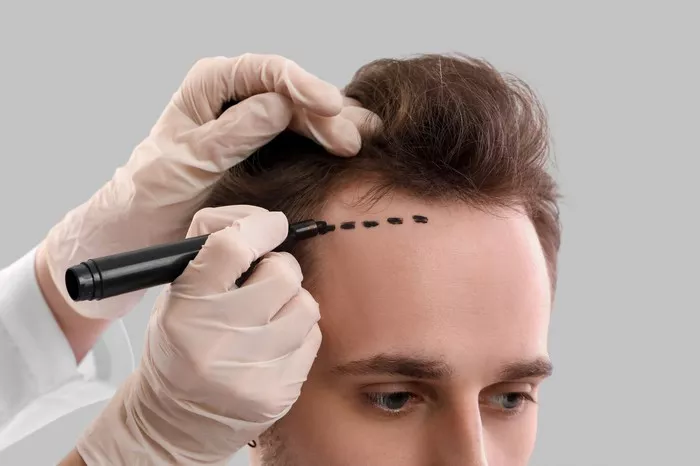
Step 1: Consultation and Planning
Before the procedure, the patient will have a consultation with the surgeon. During this meeting, the surgeon will assess the patient’s hair loss pattern, discuss expectations, and determine the best approach for the transplant. The surgeon will also explain the different types of hair grafting techniques and help the patient choose the one that is best suited to their needs.
Step 2: Harvesting the Hair Follicles
Once the patient is ready for the procedure, the first step is to harvest the hair follicles. The surgeon will remove a small strip of hair-bearing skin from the donor area, which is typically located at the back or sides of the head. This area is chosen because the hair follicles in this region are usually more resistant to hair loss.
In some cases, a technique called follicular unit extraction (FUE) may be used instead of strip harvesting. FUE involves removing individual hair follicles from the donor area using a small punch tool. This method is less invasive and leaves smaller scars compared to strip harvesting.
Step 3: Preparing the Hair Follicles
After the hair follicles are harvested, they are carefully prepared for transplantation. The surgeon will trim and separate the hair follicles, ensuring that only the healthiest ones are used for the graft. The follicles are then placed in a special solution that keeps them viable until they are ready to be implanted.
Step 4: Creating the Recipient Sites
Next, the surgeon will create tiny incisions in the recipient area, which is the area of the scalp where hair is thinning or balding. These incisions are made in a natural pattern to ensure that the transplanted hair will blend seamlessly with the existing hair. The surgeon must be skilled in creating these incisions to achieve the most natural-looking results.
Step 5: Implanting the Hair Follicles
Once the recipient sites are prepared, the surgeon will begin implanting the hair follicles. The hair follicles are carefully placed into the incisions one by one, ensuring that they are positioned at the correct angle and direction to mimic natural hair growth. This step requires great precision, as improper placement can lead to unnatural-looking results.
Step 6: Post-Procedure Care
After the hair follicles are implanted, the patient may be given instructions for post-procedure care. This may include taking prescribed medications to prevent infection and minimize swelling. The surgeon will also advise the patient on how to care for their scalp and hair in the days and weeks following the procedure.
Types of Hair Graft Techniques
There are two main types of hair graft techniques: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). Each technique has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on the patient’s individual needs.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT, also known as strip harvesting, is the traditional hair transplant method. It involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area and then dissecting it into individual follicular units. These units are then transplanted into the recipient area.
The main advantage of FUT is that it can harvest a larger number of hair follicles in a single session. This makes it a good option for patients who require a significant amount of hair restoration. However, FUT does leave a linear scar in the donor area, which may be noticeable if the patient has short hair.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a more modern and minimally invasive hair transplant technique. Instead of removing a strip of skin, individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area using a small punch tool. These follicles are then transplanted into the recipient area.
The main advantage of FUE is that it leaves minimal scarring and is less invasive than FUT. This makes it a good option for patients who want to avoid visible scars. However, FUE can be more time-consuming and may require more sessions to achieve the desired results.
Benefits of Hair Grafting
Hair grafting offers several benefits for individuals experiencing hair loss. Some of the key advantages include:
1. Natural-Looking Results
One of the main benefits of hair grafting is that it produces natural-looking results. The transplanted hair follicles grow in a way that closely resembles the natural growth pattern of the patient’s own hair. This ensures that the results are undetectable and blend seamlessly with the existing hair.
2. Permanent Solution
Unlike other hair loss treatments, such as medications or wigs, hair grafting provides a permanent solution. Once the hair follicles are transplanted and begin to grow, they continue to grow for the rest of the patient’s life. This makes hair grafting an excellent long-term solution for hair loss.
3. Low Maintenance
After the procedure, the patient can treat the transplanted hair just like their natural hair. This means there is no need for special products or treatments to maintain the results. With proper care, the transplanted hair will continue to grow and thrive.
4. Boosts Confidence and Self-Esteem
Hair loss can have a significant impact on a person’s confidence and self-esteem. By restoring a fuller head of hair, hair grafting can help individuals feel more confident and improve their self-image.
Risks and Considerations
Like any surgical procedure, hair grafting does come with some risks and considerations. Some of the potential risks include:
1. Infection
While rare, infection is a potential risk after a hair transplant. The surgeon will take precautions to minimize the risk of infection, but it is important for patients to follow aftercare instructions carefully to reduce the chance of complications.
2. Scarring
Although FUE leaves minimal scarring, FUT may leave a linear scar in the donor area. While this scar is usually hidden by hair, it may be noticeable if the patient has very short hair.
3. Swelling and Bruising
Swelling and bruising in the recipient and donor areas are common after the procedure. These symptoms typically subside within a few days, but it is important for patients to follow the surgeon’s instructions to minimize discomfort.
4. Unnatural Results
Inexperienced or unskilled surgeons may produce unnatural-looking results if the hair follicles are not placed correctly. It is crucial to choose a qualified and experienced surgeon to ensure the best possible outcome.
Aftercare and Recovery
After the hair graft procedure, proper aftercare is essential to ensure the best results. Some of the key post-procedure guidelines include:
- Avoid touching or scratching the scalp for several days after the procedure.
- Take prescribed medications to reduce swelling and prevent infection.
- Follow the surgeon’s instructions on how to wash and care for the scalp.
- Avoid sun exposure for a few weeks to protect the healing scalp.
- Be patient, as it may take several months for the transplanted hair to fully grow.
Conclusion
The hair graft procedure is an effective and long-lasting solution for hair loss. Whether you choose FUT or FUE, the results can significantly improve your appearance and self-esteem. While there are some risks associated with the procedure, these can be minimized by selecting an experienced surgeon and following proper aftercare guidelines. With the right care, hair grafting can provide you with a fuller head of hair and a more confident you.
Related topics:
- Hair Follicular Units: Everything You Need to Know
- Hair Transplant Extraction: Process, Benefits & What to Expect
- Hair Transplant to Fix Receding Hairline: A Complete Guide