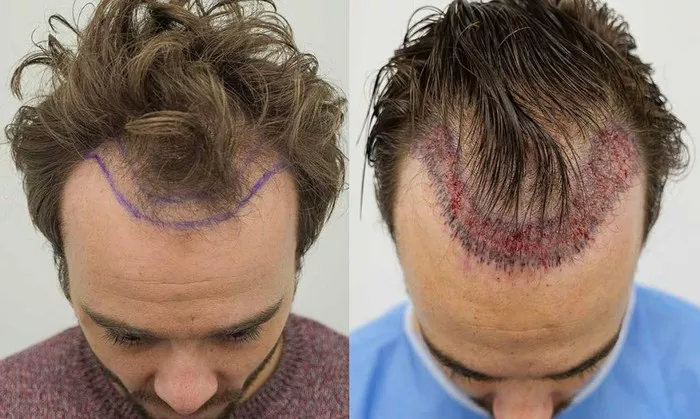
Hair loss can be a distressing experience for many people. It affects not only one’s appearance but also self-esteem and confidence. While there are various treatments available to address hair loss, one of the most effective and long-lasting solutions is hair transplantation. But how does a hair transplant actually work? Why is it so successful for many people?
In this article, we will explore the science behind hair transplants, why they work, and how they help individuals regain a natural, fuller head of hair. We’ll break down the process in simple terms to help you understand the key factors that contribute to the success of a hair transplant.
What Is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a medical procedure where hair follicles are moved from one area of the scalp, typically the back or sides, to areas where hair is thinning or missing. The goal is to restore hair to balding areas and create a fuller, more natural look.
There are two main types of hair transplant techniques:
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) – Individual hair follicles are extracted from the donor area and transplanted into the thinning or balding area.
FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) – A strip of scalp is removed from the donor area, and hair follicles are harvested from that strip before being transplanted to the thinning area.
Both methods are highly effective, but they differ in how the hair is harvested and the type of scarring they leave behind. Despite these differences, both techniques rely on the same underlying principles to deliver lasting, natural results.
The Science Behind Hair Transplants
To understand why hair transplants work, it’s essential to first understand the basics of hair growth and hair loss.
The Growth Cycle of Hair
Hair grows in cycles, and each follicle on your scalp follows this cycle. The cycle consists of three main phases:
Anagen Phase (Growth Phase): During this phase, hair actively grows. This phase can last for several years.
Catagen Phase (Transition Phase): This is a short, transitional phase when hair stops growing, and the follicle shrinks.
Telogen Phase (Resting Phase): The hair rests during this phase, and it eventually sheds. After shedding, the follicle enters the anagen phase again, and the cycle repeats.
Each hair follicle follows its own growth cycle, which is why we lose hair gradually, rather than all at once. In people with male pattern baldness or other types of hair loss, the follicles in the affected areas gradually shrink and stop producing hair. This is often caused by genetics and the effects of DHT (dihydrotestosterone), a hormone that shrinks hair follicles over time.
Why Hair Transplants Work
Hair transplant procedures work because they focus on using the patient’s own healthy hair follicles to restore hair in areas where the follicles have been damaged or are no longer producing hair. The key reasons hair transplants are effective are:
DHT-Resistant Follicles: In male and female pattern baldness, hair loss usually occurs at the front and top of the scalp. However, the hair follicles at the back and sides of the scalp are typically resistant to DHT and continue to grow healthy hair. These follicles are used as “donor hairs” in the transplant process.
Permanent Results: The follicles that are transplanted are taken from areas that are less likely to be affected by hair loss in the future. These donor follicles retain their natural resistance to DHT and continue to grow hair in their new location, providing permanent results.
Restoration of Natural Hair Growth: Because the transplanted follicles are from the patient’s own scalp, the new hair grows naturally and seamlessly blends in with the existing hair. This leads to a result that looks entirely natural, as the texture, color, and growth pattern of the transplanted hair match the original hair.
Safe and Minimally Invasive: Hair transplant procedures, especially FUE, are relatively minimally invasive. FUE, for example, does not require a large incision, and there is no need for stitches. The risk of complications is low, and most patients can return to their daily activities within a few days.
How Does the Transplant Process Work?
Step 1: Consultation and Planning
Before undergoing a hair transplant, you will need to have a consultation with a qualified hair transplant surgeon. During this consultation, the surgeon will assess your hair loss pattern, the health of your scalp, and your overall suitability for the procedure. The surgeon will also discuss your goals for the transplant and create a customized plan to achieve the best results.
Step 2: Harvesting Donor Hair
Once you’ve agreed to move forward, the surgeon will begin by harvesting healthy hair follicles from the donor area, typically the back or sides of your scalp. These areas are chosen because the hair follicles here are generally resistant to the hormones that cause hair loss.
For FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted one by one using a small punch tool. For FUT, a strip of skin containing hair follicles is removed, and the follicles are carefully separated under a microscope before being transplanted.
Step 3: Transplanting the Hair Follicles
After the follicles are harvested, the surgeon prepares the recipient area—where the hair is thinning or balding. Tiny incisions are made in the scalp, and the harvested follicles are carefully placed into these incisions. The surgeon will pay special attention to the angle and direction of hair growth to ensure that the transplanted hair looks as natural as possible.
Step 4: Recovery and Regrowth
Once the transplant is complete, the scalp will be bandaged, and you will be given post-operative instructions. The transplanted area may be red and slightly swollen initially, but this should subside within a few days.
During the first few weeks, the transplanted hair will shed, which is normal. This is called “shock loss” and happens because the follicles temporarily enter a resting phase after being moved. However, new hair will begin to grow in the transplanted area after a few months.
Step 5: Long-Term Results
Full results from a hair transplant are typically visible within 12 to 18 months. The transplanted hair will grow just like natural hair and should continue to do so for a lifetime. The procedure is effective in restoring a natural-looking hairline and thickening areas that were previously balding.
Factors That Contribute to the Success of Hair Transplants
While hair transplants are generally very successful, the outcome of the procedure depends on several factors. Some of these factors include:
1. Quality of Donor Hair
The success of a hair transplant depends largely on the quality of the donor hair. If the donor area has healthy, thick hair, the transplant will likely be more successful. If the donor hair is thinning or weak, the results may not be as satisfactory.
2. Skill of the Surgeon
The skill and experience of the surgeon play a crucial role in the outcome of a hair transplant. An experienced surgeon can ensure that the hair follicles are harvested and transplanted in a way that maximizes their growth potential and blends seamlessly with your existing hair.
3. Post-Operative Care
Proper aftercare is essential for the success of a hair transplant. Following your surgeon’s post-operative instructions carefully will help reduce the risk of infection, minimize swelling, and promote the growth of transplanted hair.
4. Health and Lifestyle Factors
Overall health and lifestyle can impact the success of a hair transplant. Patients who maintain a healthy diet, manage stress, and avoid smoking may have better results. Additionally, managing any underlying medical conditions such as thyroid issues or hormonal imbalances will support the growth of healthy hair.
Benefits of Hair Transplants
Hair transplants offer several benefits, which is why they are such a popular solution for hair loss. Some of the main advantages include:
Natural Results: Hair transplants use your own natural hair, so the results look completely natural and blend with your existing hair.
Permanent Solution: Unlike other hair loss treatments, hair transplants offer a permanent solution. The transplanted hair will continue to grow for the rest of your life.
Minimal Downtime: Most patients can return to work and normal activities within a few days to a week, depending on the extent of the procedure.
Boost in Confidence: Restoring a fuller head of hair can significantly improve self-esteem and overall confidence, positively affecting your social and professional life.
Limitations of Hair Transplants
While hair transplants are effective, they do have some limitations. For example:
Not Suitable for Everyone: Not everyone is a good candidate for a hair transplant. Factors such as the extent of hair loss, age, and general health can affect whether a transplant will be successful.
Multiple Sessions May Be Needed: In some cases, more than one hair transplant session may be required to achieve the desired result, especially for individuals with extensive hair loss.
Risk of Scarring: While the risk of scarring is minimal with FUE, FUT can leave a linear scar, which may be visible if the hair is cut very short.
Conclusion
A hair transplant works because it takes advantage of the natural, DHT-resistant hair follicles from the donor area and transplants them into areas affected by hair loss. This process restores a natural, full-looking hairline and promotes long-lasting, permanent results. With the right candidate, an experienced surgeon, and proper aftercare, hair transplants can offer a transformative solution for those struggling with hair loss.
If you’re considering a hair transplant, it’s important to consult with a qualified professional to discuss your specific needs and ensure the best possible outcome.
Related topics:
- Thicken Your Hairline with a Hair Transplant: A Complete Guide
- Hair Transplant for Lowering Hairline: A Detailed Guide
- Hair Transplant to Fix Receding Hairline: A Complete Guide