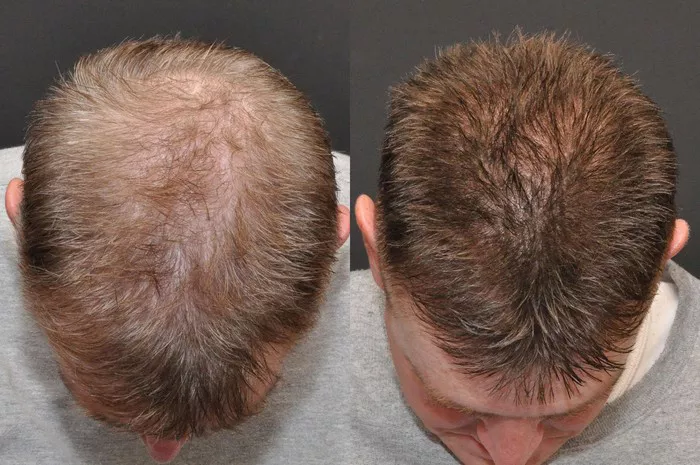
Hair transplantation is an effective solution for those suffering from hair loss. It can restore a person’s natural hairline and boost their self-confidence. However, like any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications that can arise. In this article, we will explore what can go wrong with a hair transplant, the possible side effects, and how to minimize the chances of experiencing them.
Understanding the Hair Transplant Process
Before diving into the potential issues, it’s important to understand how hair transplant surgery works. There are two main types of hair transplant techniques:
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): In this method, individual hair follicles are removed from the donor area (typically the back or sides of the scalp) and transplanted into the thinning or bald areas.
FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): In FUT, a strip of tissue containing hair follicles is removed from the donor area, and the follicles are then transplanted into the recipient sites.
Both methods involve careful planning, skilled surgical execution, and significant aftercare to ensure the best results. However, despite advances in technology and techniques, complications can still arise. Let’s take a closer look at what could go wrong during or after a hair transplant.
What are the risks and complications of hair transplantation?
While hair transplants are generally safe, there are a few risks and complications that patients should be aware of. These include:
1. Infection
Infection is one of the most common risks associated with hair transplants. Although the procedure is generally performed in a sterile environment, there is still a chance that bacteria could enter the scalp during the transplant process. Infections can lead to swelling, pain, and discomfort, and if left untreated, they may result in scarring or permanent hair loss.
To minimize the risk of infection, it is crucial to follow proper post-surgery care. This includes taking prescribed antibiotics, keeping the scalp clean, and avoiding touching the transplant area.
2. Poor Graft Survival
One of the key factors in the success of a hair transplant is the survival rate of the transplanted hair follicles. Sometimes, the grafts do not take or secure properly within the scalp. This can happen due to various factors, such as poor surgical technique, improper handling of the grafts, or lack of adequate blood supply to the newly transplanted follicles.
When grafts fail to survive, it leads to poor hair growth, which may result in patchy areas or thinning in the transplanted region. In some cases, additional hair transplant surgeries may be necessary to fix the problem.
3. Scarring
Scarring is a potential side effect of any surgical procedure, and hair transplants are no exception. While the goal is to minimize visible scarring, some patients may develop noticeable scars at the donor or recipient sites.
In FUT, the scar is typically linear, running along the donor area, whereas in FUE, small circular scars are scattered across the scalp. Scarring can become more noticeable if the patient has a tendency to form keloid scars (raised, thick scars) or if the hair transplant is not performed with precision.
There are also risks of scarring if post-surgery care is not followed correctly, such as excessive scratching or rubbing of the transplant area.
4. Swelling and Inflammation
Swelling is a normal part of the healing process after a hair transplant. However, excessive or prolonged swelling can cause discomfort and may indicate an underlying issue. Inflammation can occur around the transplanted area or the forehead, especially in the first few days after surgery.
Swelling usually subsides within a week or two, but in some cases, it may be prolonged or severe, requiring medical attention. To minimize swelling, patients should follow post-op care instructions, such as keeping the head elevated and applying cold compresses.
5. Unnatural Results
One of the most concerning outcomes for patients is the possibility of unnatural-looking hair growth. This can happen if the surgeon does not have enough experience or expertise in creating natural hairlines, leading to a transplant that looks artificial. A poorly executed hair transplant can result in a “pluggy” or “scalped” appearance, where the hair grows in clumps or with visible gaps.
To avoid unnatural results, it is important to choose a skilled and experienced surgeon who specializes in hair transplantation. They will be able to craft a hairline that complements your natural features and provides the most aesthetically pleasing outcome.
6. Shock Loss
Shock loss refers to the temporary shedding of both transplanted and existing hair after a hair transplant. This can occur due to the trauma of the surgery, causing hair follicles to go into a resting phase before new hair grows in. It is a normal and temporary phenomenon that typically resolves within a few months.
Shock loss can be concerning for patients, especially if they notice significant thinning of existing hair. However, it is important to understand that this phase is temporary, and new hair will begin to grow back within a few months.
7. Hair Follicle Damage
Sometimes, hair follicles can be damaged during the transplant process, leading to poor or no hair growth in the recipient area. Damage can occur if the follicles are not harvested properly or if they are handled too aggressively during implantation.
In some cases, hair follicles may be over-harvested from the donor area, leading to thinning or even permanent hair loss in that area. This can create an unnatural look, and the patient may need further procedures to restore density.
8. Excessive Bleeding
Bleeding is a normal part of any surgical procedure, but excessive bleeding after a hair transplant can be problematic. Some patients may experience prolonged or heavy bleeding during or after the surgery, which can lead to complications such as hematoma (a collection of blood under the skin).
Excessive bleeding can be caused by a variety of factors, including the patient’s pre-existing medical conditions, the use of blood-thinning medications, or improper aftercare. To minimize bleeding, patients are advised to avoid taking aspirin or anti-inflammatory medications before the procedure and follow post-operative care instructions carefully.
9. Numbness or Tingling
Some patients may experience numbness or tingling sensations in the scalp after a hair transplant. This is usually due to nerve irritation or trauma during the surgery. In most cases, this sensation is temporary and subsides within a few weeks.
However, in rare instances, nerve damage can occur, leading to persistent numbness or discomfort. If this happens, it is important to consult with the surgeon to address the issue.
10. Allergic Reactions to Medications
After a hair transplant, patients may be prescribed medications such as pain relievers, antibiotics, or anti-inflammatory drugs to aid in recovery. While these medications are generally safe, some individuals may experience allergic reactions, including skin rashes, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
If you have a history of allergies to certain medications, be sure to inform your surgeon beforehand. They will be able to adjust your medication regimen to avoid adverse reactions.
How to Minimize the Risks of Complications
While complications can arise, there are steps that patients can take to minimize the risk of problems after a hair transplant:
1. Choose an Experienced Surgeon
The success of your hair transplant largely depends on the skills and experience of your surgeon. Make sure to choose a board-certified surgeon with a proven track record of successful procedures. A skilled surgeon will be able to create natural-looking results and minimize the risk of complications.
2. Follow Aftercare Instructions Carefully
Proper aftercare is essential for ensuring the success of your hair transplant. Follow your surgeon’s instructions on how to care for your scalp in the days and weeks following the procedure. This includes avoiding strenuous activities, keeping the scalp clean, and using any prescribed medications as directed.
3. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol
Smoking and alcohol can interfere with the healing process, potentially leading to complications like infection or poor graft survival. It is recommended that patients refrain from smoking and drinking for at least a few weeks before and after the surgery.
4. Manage Your Expectations
While hair transplants are highly effective, they may not always produce instant results. It can take several months for the transplanted hair to start growing, and full results may take up to a year. Patience is key, and understanding the timeline can help prevent disappointment.
Conclusion
Although hair transplants are generally safe, there are several potential risks and complications that patients should be aware of. These include infection, graft failure, scarring, shock loss, and unnatural results. To minimize the chances of these issues, it is essential to choose an experienced surgeon, follow aftercare instructions diligently, and manage your expectations.
By understanding what can go wrong with a hair transplant and taking proactive steps to avoid complications, you can increase the likelihood of achieving successful, natural-looking results.
Related topics:
- How to Grow Back Your Edges Naturally?
- When Does Transplanted Hair Start Shedding? A Comprehensive Guide
- What Age Should You Get a Hair Transplant?