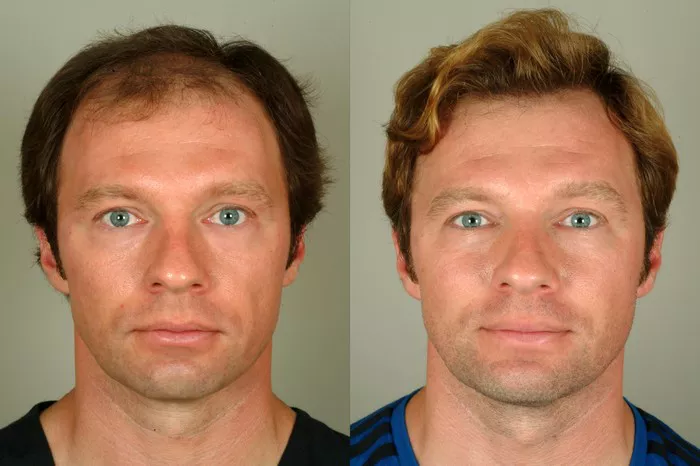
Hair transplant surgery has become a popular solution for individuals looking to restore their hair and regain their confidence. But if you’ve ever wondered, how do they do hair transplant surgery?, you’re not alone. The procedure involves a series of detailed steps, precise techniques, and careful planning to achieve the best possible outcome.
In this article, we will break down the entire process of hair transplant surgery, explaining each step involved from the consultation to the final results. We’ll explore the techniques used, the technology behind the surgery, and what you can expect before, during, and after the procedure.
What is Hair Transplant Surgery?
Hair transplant surgery is a medical procedure designed to move healthy hair follicles from one part of the body, typically the back or sides of the scalp (known as the donor area), to a thinning or bald area (the recipient area). It’s most commonly used for people experiencing male or female pattern baldness, but it can also be used to restore hair for people who have lost hair due to trauma or other conditions.
The transplanted hair follicles are resistant to the hormone DHT (dihydrotestosterone), which is responsible for pattern baldness, and as a result, the transplanted hair continues to grow naturally.
There are two main methods used in hair transplant surgery:
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
Both techniques involve moving hair follicles, but they do so in different ways. Let’s explore each technique in detail.
Step 1: Initial Consultation
The first step in any hair transplant journey is the initial consultation with a skilled surgeon. During this consultation, the surgeon will assess your hair loss pattern, evaluate your donor area, and discuss your goals for the procedure. You will also go over your medical history to ensure that you’re a good candidate for surgery.
What Happens During the Consultation?
Hair Loss Assessment: The surgeon will assess the degree of hair loss you have and discuss potential outcomes based on your hair pattern.
Donor Area Evaluation: The donor area, typically the back and sides of the head, is examined to ensure there is enough healthy hair to transplant.
Surgeon’s Recommendations: Based on your hair type, goals, and donor area condition, the surgeon will recommend the most appropriate method (FUE or FUT).
Realistic Expectations: It’s crucial that the surgeon manages your expectations, explaining the likely results, risks, and recovery process.
At this stage, the surgeon may also provide you with pre-operative instructions, which typically include discontinuing certain medications, avoiding alcohol and smoking, and taking any prescribed medications.
Step 2: Preparing for Hair Transplant Surgery
The next step is the preparation phase before the surgery itself. This is where you’ll make sure everything is ready for the procedure.
What Happens in the Preparation?
Shaving the Donor Area: The donor area, where the healthy hair follicles will be harvested from, is shaved to make the process easier for the surgeon.
Local Anesthesia: A local anesthetic is administered to numb the areas where the hair will be harvested and where the follicles will be transplanted. This ensures that you remain comfortable and pain-free throughout the procedure.
Marking the Recipient Area: The surgeon will mark the recipient area (the area of hair loss) to determine where to place the new follicles. This step is critical for achieving a natural look.
During the preparation phase, the surgical team will ensure everything is sterilized, and you’ll be made as comfortable as possible.
Step 3: The Hair Transplant Procedure
Now, let’s take a closer look at how the actual hair transplant surgery is performed. There are two main techniques that can be used during this stage: FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) and FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction).
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
In FUT, the surgeon removes a strip of skin from the donor area, typically at the back of the head, where hair is thickest. The strip is then divided into individual follicular units under a microscope, which contain one to four hair follicles each. These follicular units are then transplanted to the recipient area.
Harvesting the Strip: The surgeon removes a strip of tissue, which is usually about 1-2 centimeters wide. The area is then sutured, and a linear scar may be left behind, though this can be hidden under longer hair.
Dissecting the Follicular Units: The strip of tissue is carefully dissected into tiny follicular units, each containing 1-4 hair follicles.
Placing the Grafts: The surgeon then creates tiny incisions in the recipient area and places the individual follicular units into these incisions. The goal is to create a natural hairline and density.
FUT is ideal for people who need a large number of grafts, as the method allows for the harvesting of more follicles in a single session. However, the linear scar left behind may be visible if the hair is worn very short.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a more advanced and less invasive technique compared to FUT. In FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area using a tiny punch tool, without the need for removing a strip of tissue.
Harvesting the Follicles: The surgeon uses a small, circular punch tool to remove individual hair follicles from the donor area. This process leaves tiny, dot-like scars rather than a long, linear scar.
Placing the Grafts: Similar to FUT, the surgeon creates tiny incisions in the recipient area and places the harvested follicles into those incisions.
FUE is ideal for people who prefer shorter hairstyles because it leaves minimal scarring. It also has a shorter recovery time, but it may not be suitable for patients needing a large number of grafts.
The Entire Surgery Process
The procedure typically takes 4-8 hours depending on the number of grafts being transplanted.
During the surgery, the patient may take short breaks for hydration or restroom visits, but the majority of the time will be spent under local anesthesia.
Step 4: Post-Operative Care
After the hair transplant surgery, proper care is essential for the survival and growth of the transplanted follicles. You will receive detailed aftercare instructions to follow during the healing process.
Immediate Post-Surgery Care
Rest and Recovery: After the procedure, you may feel slightly groggy from the anesthesia, and it’s essential to rest for a few hours before heading home.
Washing the Scalp: You will be instructed on how to gently wash your scalp to prevent damaging the newly transplanted follicles. Most surgeons recommend waiting 1-2 days before washing.
Avoiding Sun Exposure: Direct sun exposure should be avoided for several weeks to prevent irritation and to help the healing process.
Long-Term Care
Hair Growth Timeline: The transplanted hair will shed within the first 2-3 weeks, but new hair will start to grow back in 3-4 months. Full results are typically visible after 12-18 months.
Medications: Some patients may be prescribed medications such as minoxidil or finasteride to help promote hair growth and prevent further hair loss.
Follow-Up Visits: You will have follow-up appointments with your surgeon to ensure the transplanted hair is growing properly and to address any concerns.
Step 5: Expected Results and Timeline
Hair transplant results don’t appear overnight. It typically takes time for the transplanted hair to grow fully. Here is what you can expect:
Weeks 1-2: The transplanted hair will begin to shed, which is completely normal.
3-4 Months: New hair growth starts to emerge. This growth may be thin at first.
6-12 Months: Hair thickens, and the results become more noticeable.
12-18 Months: Full results are visible. The transplanted hair blends naturally with existing hair.
The results of a hair transplant can be life-changing, but patience is required. Over time, you will notice a fuller, natural-looking hairline and thicker hair.
Risks and Potential Complications
Like any surgical procedure, hair transplants come with some risks. Potential complications include:
Infection: Though rare, infection can occur after surgery. Following the surgeon’s aftercare instructions reduces this risk.
Scarring: While FUE leaves minimal scarring, FUT may leave a linear scar at the donor site.
Poor Graft Survival: In some cases, the transplanted follicles may not take root, leading to less satisfactory results.
Shock Loss: Some of the existing hair may shed after surgery, but this typically grows back within a few months.
Conclusion
Hair transplant surgery is a highly effective and life-changing procedure for people experiencing hair loss. The process involves detailed planning, precision, and skill, whether you undergo FUT or FUE. By understanding how the surgery is performed, managing your expectations, and following proper post-operative care, you can achieve successful and long-lasting results.
If you’re considering a hair transplant, be sure to consult with an experienced and reputable surgeon who can guide you through the process, ensure your safety, and help you achieve the best possible outcome.
Related topics:
- How to Find a Good Hair Transplant Surgeon?
- What Hair Surgery Can Do for You?
- At What Age Can You Get a Hair Transplant?