Hair loss is a common concern for many people, but thanks to advancements in modern hair restoration techniques, there are now effective solutions available. One of the most popular methods is Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), a procedure that has gained widespread recognition for its natural results and minimally invasive nature.
If you’re considering a hair transplant or just curious about the process, you might be wondering: What exactly is FUE? How does it work? Is it the right choice for you? This article will answer all of those questions and more. We’ll break down the FUE procedure, how it differs from other hair transplant methods, its benefits, and what you can expect if you decide to undergo the treatment.
What Is Follicular Unit Extraction?
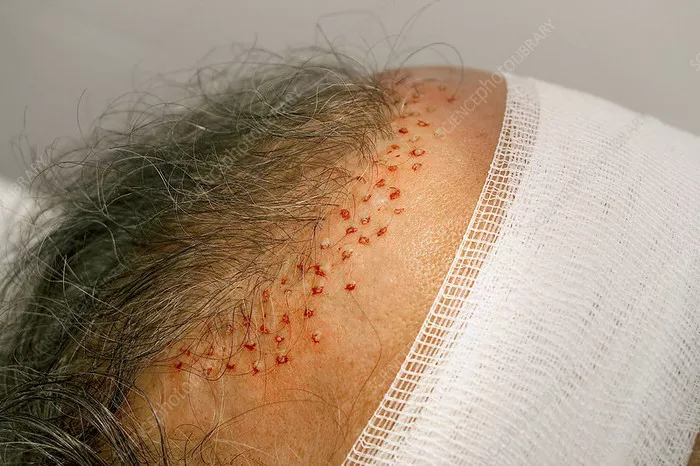
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a method of harvesting hair follicles from the donor area (usually the back or sides of the scalp) and transplanting them to the areas where hair is thinning or balding. Unlike older methods, FUE is a minimally invasive procedure that does not require large incisions or sutures, making it a popular choice for many people looking to restore their hairline.
In FUE, individual follicular units, which are groups of 1–4 hair follicles, are extracted one by one using a small, circular punch tool. These units are then carefully transplanted into the thinning or balding areas of the scalp. The result is a natural-looking hairline with minimal scarring and a quicker recovery time compared to other methods like strip harvesting (FUT).
How Does the FUE Procedure Work?
The process of Follicular Unit Extraction involves several steps. Here’s a breakdown of how it typically works:
1. Consultation and Planning
Before undergoing the FUE procedure, you’ll need to have a consultation with a hair transplant specialist. During this consultation, the doctor will assess your scalp, hair density, and hair loss pattern to determine whether you’re a good candidate for FUE. The specialist will also discuss your goals and expectations to ensure that the procedure can meet them.
If you’re a suitable candidate for FUE, the doctor will plan out the donor and recipient areas. The donor area is usually the back or sides of the scalp, where hair follicles are genetically resistant to hair loss. These areas are marked to ensure a well-balanced hairline after the transplant.
2. Preparation and Anesthesia
On the day of the procedure, the first step is to prepare the scalp for the procedure. Your scalp will be cleaned thoroughly, and local anesthesia will be applied to numb the areas where the hair follicles will be extracted and transplanted. The anesthesia ensures that you won’t feel any pain during the procedure, although you might feel some pressure.
3. Extraction of Follicular Units
Once you’re numb, the hair transplant specialist will begin extracting follicular units from the donor area. This is done using a small, specialized punch tool (often 0.8–1.0 mm in diameter). The tool is used to create tiny circular incisions around each follicular unit, and then the follicles are gently extracted.
Each follicular unit contains 1 to 4 hairs, which are ideal for transplanting to the balding area. The extraction process is done one follicle at a time, which can take several hours depending on the number of follicles needed for the transplant.
4. Preparation of the Recipient Area
While the follicles are being extracted, the recipient area is prepared for implantation. The hair transplant surgeon will create tiny incisions in the thinning or balding areas where the follicles will be placed. The incisions are made at specific angles and directions to ensure that the new hair grows in a natural pattern that blends seamlessly with your existing hair.
5. Implantation of Hair Follicles
After the recipient area has been prepared, the hair follicles are carefully implanted one by one into the tiny incisions. The surgeon uses precision instruments to place each follicular unit in a way that mimics the natural growth pattern of your hair. The goal is to create a natural-looking hairline and coverage in the thinning areas.
6. Post-Procedure Care
Once the follicles are implanted, the procedure is complete. The surgeon will provide post-procedure instructions, which may include avoiding certain activities, washing your hair carefully, and taking prescribed medications to reduce swelling and prevent infection. The transplanted follicles will begin to shed after a few weeks, but new hair will start to grow in the transplanted area within 3 to 4 months.
What Are the Benefits of FUE?
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) offers several advantages over traditional hair transplant methods, such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). Some of the key benefits include:
1. Minimally Invasive
FUE is a minimally invasive procedure that doesn’t require large incisions or stitches. This means that the risk of complications, such as infection or scarring, is significantly lower than with traditional hair transplant techniques.
2. Natural Results
Because FUE uses individual follicular units, the hair transplant results are more natural-looking. The surgeon can precisely place the follicles at the correct angle and direction to match the natural growth pattern of your existing hair.
3. No Linear Scarring
One of the biggest advantages of FUE is that it leaves no linear scar, unlike FUT, which involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area. With FUE, only tiny, round scars are left where each follicle was extracted, which are almost invisible, even with short haircuts.
4. Quicker Recovery Time
The recovery time for FUE is faster compared to FUT. Since the procedure is less invasive, patients typically experience less pain and swelling and can return to their normal activities in a shorter amount of time. Most people can resume work within 2–3 days after the procedure.
5. Minimal Discomfort
Because FUE only requires local anesthesia, most patients experience minimal discomfort during the procedure. The recovery process is also relatively smooth, with many people reporting little to no pain after the treatment.
6. Ideal for Short Haircuts
Since FUE leaves tiny, dot-like scars that are virtually undetectable, patients can opt for shorter hairstyles without worrying about visible scarring.
How Is FUE Different from Other Hair Transplant Methods?
There are other methods of hair transplantation, such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), and it’s important to understand the key differences between them:
1. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT, also known as the “strip method,” involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area, usually the back of the scalp. The strip is then dissected under a microscope to separate the individual follicular units, which are then transplanted into the recipient area.
Advantages of FUT: FUT may allow for the harvesting of a larger number of follicles in a single session, making it ideal for patients who require a significant amount of hair restoration.
Disadvantages of FUT: The biggest drawback of FUT is the linear scar it leaves in the donor area. Additionally, the recovery time is longer, and there may be more pain and swelling after the procedure.
2. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE, on the other hand, involves extracting individual follicular units directly from the scalp without the need for a strip of tissue. This method offers more precision and minimal scarring.
Advantages of FUE: No linear scar, quicker recovery, and more natural-looking results.
Disadvantages of FUE: The procedure may take longer to complete, especially if a large number of follicles need to be transplanted. It is also typically more expensive than FUT.
Is FUE Right for You?
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is an excellent option for many people, but it may not be suitable for everyone. Here are some factors to consider:
Hair Loss Pattern: FUE is ideal for people with a stable donor area who want natural-looking results. It works best for those with male or female pattern baldness, as well as individuals who have lost hair due to injury or scarring.
Donor Area: The success of FUE depends on the quality and quantity of the hair in your donor area. People with sufficient healthy hair in the donor area are generally good candidates for FUE.
Age and Health: FUE is a safe procedure for healthy individuals of all ages, but it’s essential to be in good health to undergo any surgical procedure.
Budget: FUE tends to be more expensive than FUT, so it’s important to consider the cost. However, many people find the results and minimal scarring worth the investment.
What to Expect After FUE Hair Transplant?
After the FUE procedure, you may experience some redness, swelling, and mild discomfort in both the donor and recipient areas. These side effects are normal and should subside within a few days. The newly transplanted hair will shed within the first few weeks, but don’t be discouraged—this is a natural part of the process.
New hair growth typically begins around 3 to 4 months after the transplant, and full results can take up to 12–18 months to become visible. Regular follow-up visits with your hair transplant surgeon will help monitor progress and ensure optimal results.
Conclusion
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is one of the most advanced and effective methods of hair restoration available today. Its minimally invasive nature, natural-looking results, and faster recovery time make it a popular choice for people looking to restore their hairline. By understanding how FUE works, its benefits, and how it compares to other methods like FUT, you can make an informed decision about whether this procedure is right for you.
If you’re considering an FUE hair transplant, be sure to consult with a qualified specialist to discuss your goals, expectations, and suitability for the procedure. With the right care and attention, FUE can help you achieve the thick, healthy hair you desire.
Related topics:
- Where Is Hair Transplanted From? A Detailed Guide
- What Can Go Wrong with Hair Transplant? Potential Risks Explained
- What Doctor does Hair Transplant?