In the realm of hair restoration, Platelet – Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy has emerged as a popular option, offering hope to those struggling with hair loss. But what exactly does PRP do? This article will delve into the science behind PRP, its mechanism of action in promoting hair growth, and its applications in the context of hair restoration.
Understanding Platelet – Rich Plasma
What is PRP?
PRP is a concentrated form of a patient’s own platelets in plasma, the liquid component of blood. Platelets are small, colorless cell fragments that play a crucial role in the body’s natural healing process. When an injury occurs, platelets are activated and release a variety of growth factors, which are proteins that stimulate cell growth, proliferation, and tissue repair.
Preparation of PRP
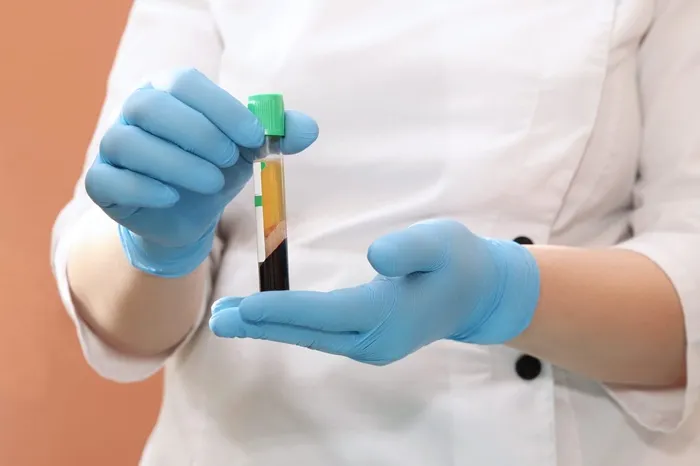
The process of obtaining PRP starts with drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood, typically from the arm. The blood is then placed in a centrifuge, a machine that spins the blood at high speeds. This centrifugation process separates the blood into its different componentsthese,red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. The platelets and a small amount of plasma are carefully collected, resulting in PRP. The concentration of platelets in PRP can be several times higher than in normal blood, usually 5 – 10 times, enhancing its therapeutic potential.
How PRP Promotes Hair Growth
Stimulating Hair Follicle Growth
Activation of Follicular Cells
PRP contains multiple growth factors that can directly stimulate the cells within the hair follicles. For example, Platelet – Derived Growth Factor (PDGF) stimulates the growth and division of dermal papilla cells, which are located at the base of the hair follicles. Dermal papilla cells play a crucial role in regulating hair growth, and by enhancing their activity, PDGF promotes the growth and development of the hair follicles.
Prolonging the Anagen Phase
The anagen phase is the active growth phase of the hair follicles. PRP helps to prolong this phase, allowing the hair follicles to produce hair for a longer period. Transforming Growth Factor – beta (TGF – β) is one of the growth factors in PRP that can regulate the hair growth cycle, promoting the transition of hair follicles from the resting phase (telogen) to the anagen phase. This leads to increased hair growth and a higher density of hair.
Increasing Hair Follicle Size
PRP can also contribute to an increase in the size of the hair follicles. Larger hair follicles are capable of producing thicker and stronger hair shafts. Insulin – like Growth Factor – 1 (IGF – 1) in PRP stimulates the growth and differentiation of follicular cells, leading to an increase in the size and volume of the hair follicles.
Improving Scalp Microenvironment
Enhancing Blood Circulation
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in PRP plays a crucial role in angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels. By promoting angiogenesis in the scalp, VEGF improves blood circulation to the hair follicles. A well – vascularized scalp ensures that the hair follicles receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients, which are essential for their normal functioning and growth.
Reducing Inflammation
PRP has anti – inflammatory properties. It can help reduce inflammation in the scalp, which is often associated with hair loss. Chronic inflammation can damage the hair follicles and disrupt the hair growth cycle. By reducing inflammation, PRP creates a more favorable environment for hair follicles to grow and thrive.
Clinical Applications of PRP in Hair Restoration
Treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as male – pattern or female – pattern baldness, is the most common form of hair loss. PRP therapy has shown promising results in treating androgenetic alopecia. Multiple clinical studies have demonstrated that PRP can increase hair density and thickness in patients with androgenetic alopecia. The growth factors in PRP help counteract the effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that causes hair follicles to shrink in androgenetic alopecia.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to attack the hair follicles, resulting in patchy hair loss. PRP therapy can be used to treat alopecia areata by reducing inflammation in the scalp and promoting the regeneration of damaged hair follicles. Some patients with alopecia areata have reported significant hair regrowth after undergoing PRP treatment.
Post – Surgical Hair Restoration Support
PRP can also be used in combination with hair transplant surgery. Applying PRP to the donor area before follicle extraction can improve the quality and viability of the follicles. Injecting PRP into the recipient area after transplantation can enhance the growth and integration of the transplanted follicles, increasing the success rate of the hair transplant.
Potential Risks and Limitations of PRP Therapy
Injection – Site Reactions
One of the most common side effects of PRP therapy is injection – site reactions. These can include pain, swelling, bruising, and redness at the injection site. These reactions are usually mild and resolve within a few days. However, in some cases, they may be more severe and require medical attention.
Infection
There is a small risk of infection associated with PRP therapy. The injection of PRP into the scalp creates small puncture wounds, which can potentially become infected. To minimize the risk of infection, it is essential to ensure that the treatment is performed in a sterile environment by a qualified healthcare provider.
Variability in Results
The effectiveness of PRP therapy can vary from person to person. Factors such as the patient’s overall health, the cause and severity of hair loss, and the technique used to prepare and administer PRP can all influence the results. In some cases, patients may not experience significant hair regrowth despite undergoing multiple PRP sessions.
Conclusion
Platelet – Rich Plasma (PRP) has shown significant potential in promoting hair growth and treating various forms of hair loss. Its unique composition of growth factors allows it to stimulate hair follicle growth, improve the scalp microenvironment, and enhance the success of hair transplant surgery. While PRP therapy is generally considered safe and effective, it is not without its risks and limitations. If you are considering PRP therapy for hair loss, it is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare provider who can assess your individual situation, discuss the potential benefits and risks, and determine whether PRP is the right treatment option for you.
Related topics:
- How Does Medication Cause Hair Loss?
- How Much Is Platelet Rich Plasma Hair Loss Treatment?
- What’s the Ultimate Diet Guide for Preventing Hair Fall?